Track
China’s Manus AI, developed by the startup Monica, is making waves as one of the first fully autonomous AI agents—an AI that doesn’t just respond to instructions but independently plans and executes tasks.
Since its launch on March 6, 2025, Manus has sparked both hype and skepticism. While some call it China’s second “DeepSeek moment,” others question whether it truly lives up to its claims, pointing to early reports of glitches, looping errors, and performance inconsistencies.
In this article, I’ll break down what Manus AI is, how it works, what it can actually do, and whether it represents a leap forward or just another overhyped AI experiment.
We keep our readers updated on the latest in AI by sending out The Median, our free Friday newsletter that breaks down the week’s key stories. Subscribe and stay sharp in just a few minutes a week:
What Is Manus AI?
Manus AI is an autonomous AI agent that can perform multi-step tasks with minimal human input. Instead of waiting for continuous user prompts and responding reactively, Manus can plan, execute, and refine tasks on its own.
The idea behind Manus is to move beyond basic chatbot-style AI and create a system that can function as a true digital assistant capable of making informed decisions.
For instance, it can start with a single prompt and produce a dashboard without additional prompts, like in this example:
Notice that Manus deployed the dashboard to a permanent public URL, which you can access here.
Whether it’s analyzing financial transactions, screening job applicants, or searching for rental properties, Manus is designed to process large amounts of information, compare options, and provide structured, optimized solutions. You can see more examples here, but be aware that the Manus AI team made the selection, and the examples might be cherry-picked.
In the meantime, we've got access to Manus and tried our own examples—check them them in this separate blog on Manus AI.
How Does Manus AI Work?
Manus AI operates as an autonomous AI agent by being able to perform:
- Information retrieval and fact-checking using online sources.
- Data processing and visualization, including structured analysis and interactive dashboards.
- Code execution and automation, allowing it to write, test, and deploy scripts.
- Web automation, enabling interactions with web applications, filling forms, and scraping data.
Let’s explain in more detail how Manus AI works.
Multi-agent system and task execution
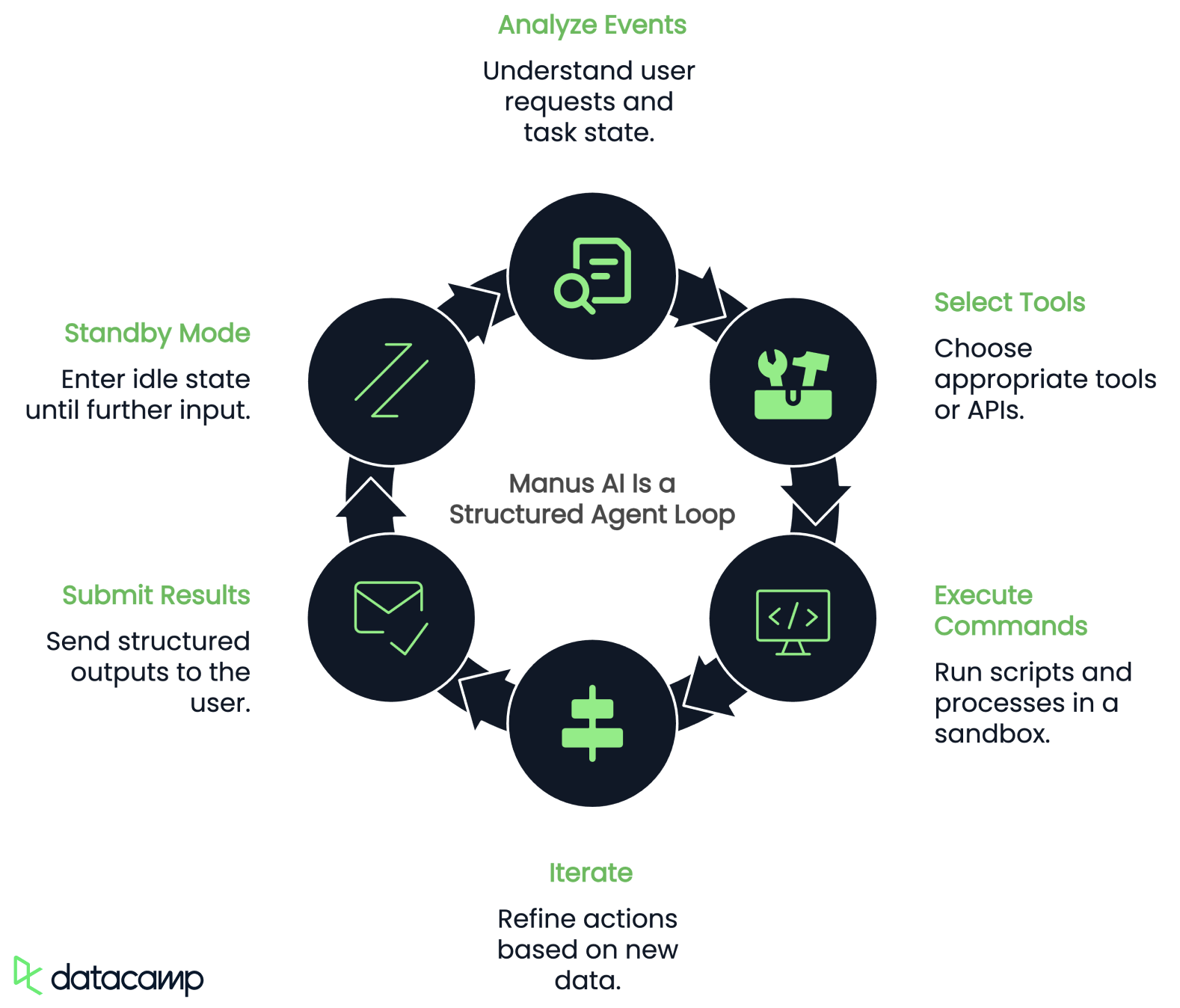
Based on initial discoveries by Jian Liao, Manus AI functions through a structured agent loop, iteratively processing tasks in a step-by-step manner. Each session follows this process:
- Analyze events: Understands user requests and the current state of the task.
- Select tools: Chooses the appropriate tool or API call for the next step.
- Execute commands: Runs shell scripts, web automation, or data processing in a Linux sandbox.
- Iterate: Refines its actions based on new data, repeating the cycle until the task is completed.
- Submit results: Sends structured outputs to the user in the form of messages, reports, or deployed applications.
- Standby mode: Enters an idle state until further user input is required.
Core architectural features
Manus AI's core architectural features enable it to interact with a computer like a human would, but within a controlled environment. These features include:
- Linux sandbox environment: Manus operates within a controlled execution space, where it can install software, run scripts, and manipulate files.
- Shell and command-line execution: The AI can execute shell commands, manage processes, and automate system tasks.
- Integrated web browser control: Manus can navigate websites, extract data, interact with web elements, and even execute JavaScript within a browser console.
- File system management: It can read, write, and organize files, making it useful for handling document-based workflows.
- Deployment capabilities: Manus can deploy applications, including setting up websites and hosting services on public URLs.
Security and limitations
Each Manus AI session operates in isolation, preventing users from accessing each other's execution environments. Additionally, tools and commands are sandboxed, mitigating the risk of unauthorized system access. Manus AI is also restricted from creating user accounts or bypassing security measures without explicit permissions.
Despite its autonomy, Manus AI still has limitations on the amount of data it can process at once due to its limited context window.
Manus AI Benchmarks
While we don’t have extensive benchmark data yet, Manus AI was evaluated using the GAIA benchmark, a test designed to measure how well AI agents handle real-world problem-solving tasks. To ensure reproducible results, Manus was evaluated using the same configuration as its production version.
The results suggest that Manus performs significantly better than previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) models, including OpenAI’s Deep Research system:
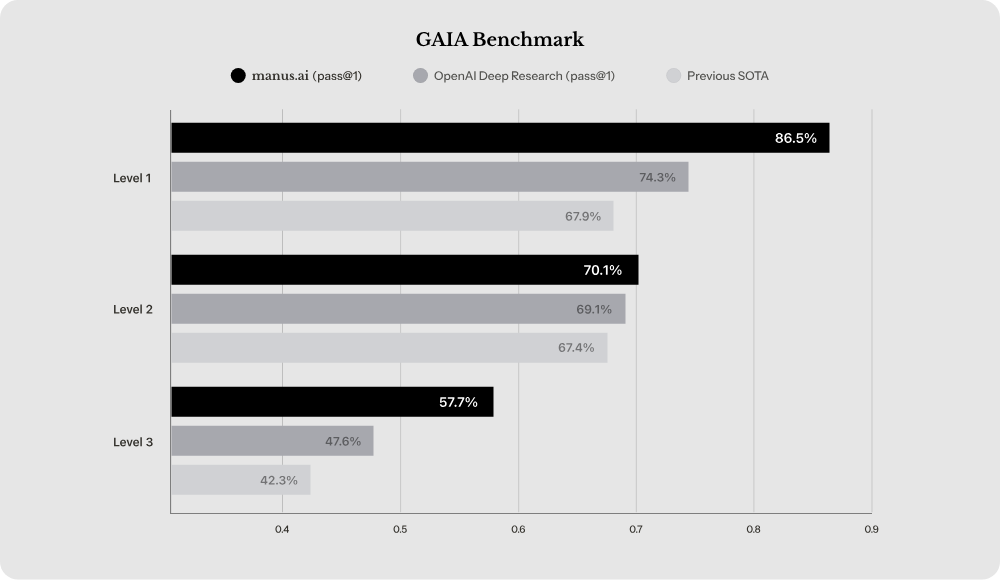
Source: Manus AI
The benchmark evaluates AI agents across three difficulty levels:
- Level 1 (basic tasks): Manus AI scored 86.5%, significantly higher than OpenAI Deep Research at 74.3%, and well above the previous SOTA at 67.9%.
- Level 2 (intermediate tasks): Manus maintained a strong performance at 70.1%, narrowly surpassing OpenAI Deep Research (69.1%) and improving on the previous SOTA (67.4%).
- Level 3 (complex tasks): Manus also leads this category, scoring 57.7%, compared to 47.6% for OpenAI and 42.3% for the previous best model.
The fact that Manus AI leads across all difficulty levels suggests that it may be one of the most capable autonomous AI agents currently available. However, the decreasing scores at higher difficulty levels indicate that even the best AI models still struggle with the most complex, multi-step reasoning tasks.
While these benchmarks are impressive, real-world performance often differs from controlled testing. Manus AI’s actual usability will depend on how well it handles unpredictable tasks and whether its autonomy leads to practical improvements in user workflows.
How to Access Manus AI?
Access to Manus AI is currently limited to an invitation-only beta phase. If you’re interested in gaining access, follow these steps: 
- Visit the official website: Navigate to the Manus AI website.
- Join the waitlist: Click on the “Get Started” button at the top right and then click “Apply for access.”
- Await invitation: After joining the waitlist, you’ll need to wait for an invitation code to be sent to your registered email. Due to high demand, this process may take some time.
- Activate your account: Once you receive your invitation code, follow the instructions provided in the email to activate your Manus AI account.
Be cautious of unofficial sources offering invitation codes, as they may not be legitimate. Always use official channels to get access to Manus AI. 
Is Manus AI a “DeepSeek Moment?”
Manus AI could be a “DeepSeek moment” for AI, and let me explain why. DeepSeek-R1 didn’t change the landscape because we all suddenly switched to it. In fact, many of us tried it in the first few days and couldn’t even use it because their servers couldn’t handle the load—and they still struggle with this today. But DeepSeek was a turning point because it proved three things:
- We can build strong reasoning models at a fraction of the cost we thought necessary.
- Advanced AI chips might not be as crucial as we assumed.
- Open-source AI is no longer playing catch-up—it’s on par with, or even surpassing, closed proprietary models.
I see Manus AI as a potential DeepSeek moment for agentic AI instead of reasoning. It challenges the assumption that powerful AI agents require massive infrastructure, closed ecosystems, and high costs.
Based on the initial discoveries by Jian Liao, Manus operates on a mix of Claude Sonnet, Qwen finetunes, and modular AI agents, showing that you can build a highly capable autonomous system without training a massive proprietary model from scratch.
This release also comes at a very interesting time—just as rumors are swirling that OpenAI plans to launch three advanced AI agents with subscription fees ranging from $2,000 to $20,000. If Manus AI delivers on its promise of low-cost, open access to autonomous AI, it could force companies like OpenAI to rethink whether AI automation needs to be locked behind expensive paywalls.
That said, there are still valid concerns, and we’ll explore them in the next section.
Manus AI Early Issues
Manus has already been criticized for looping errors, over-reliance on existing models, and security risks. And while it’s exciting in theory, whether it actually works at scale is still an open question. If it follows DeepSeek’s path, it could be revolutionary in concept but frustrating in execution—a powerful system that few can reliably use.
For instance, early testers have pointed out several issues:
- Glitches and inconsistencies: Some users have reported that Manus loops or gets stuck in repetitive cycles, struggling with complex decision-making when tasks aren’t well-defined.
- Over-reliance on existing models: Investigations into its architecture suggest that Manus heavily integrates Claude Sonnet and Qwen finetunes, rather than using a unique, proprietary model. This has raised concerns about whether it is truly pioneering new AI methods or just orchestrating existing technologies in a clever way.
- Security and privacy risks: Manus’s ability to execute commands, retrieve files, and interact with external systems has led some to question its security controls. If not properly sandboxed, an autonomous AI with access to sensitive data could introduce unintended vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Manus AI is a bold move toward autonomous AI agents, but it remains uncertain whether it truly delivers on the promise of agentic AI that can reliably complete complex, real-world tasks.
The comparison to DeepSeek-R1 is justified, but not because everyone will suddenly switch to Manus. Instead, like DeepSeek, Manus challenges the economics of AI, showing that autonomous agents don’t necessarily require massive infrastructure or proprietary models to function.
That said, the technology still has gaps. Reports of looping errors, execution failures, and over-reliance on existing models suggest that Manus is not quite the revolutionary AI system it claims to be—at least not yet. If it can overcome these issues, it could be a game-changer in AI automation. If not, it risks becoming just another overhyped AI experiment, more valuable for what it represents than what it actually delivers.
Introduction to AI Agents
FAQs
Does Manus AI support languages other than English?
Yes, Manus AI supports multiple languages, allowing users to interact and receive outputs in their preferred language.
Can Manus AI handle real-time data processing tasks?
Yes, Manus AI is capable of processing real-time data, making it suitable for tasks that require up-to-date information, such as live data analysis and monitoring.
What platforms and operating systems is Manus AI compatible with?
Manus AI is a cloud-based service accessible through web browsers on various devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones, regardless of the operating system.
Does Manus AI support multimodal inputs?
Yes, Manus AI is designed with multimodal capabilities, allowing it to process and generate various types of data, including text, images, and code. This enables Manus to handle complex tasks that require understanding and producing different forms of information.
Can Manus AI generate content across different modalities?
Yes, Manus AI can create content in various formats, such as generating textual reports, creating visual data representations, and writing executable code, depending on the task requirements.
I’m an editor and writer covering AI blogs, tutorials, and news, ensuring everything fits a strong content strategy and SEO best practices. I’ve written data science courses on Python, statistics, probability, and data visualization. I’ve also published an award-winning novel and spend my free time on screenwriting and film directing.


