Course
Nemotron 3 is NVIDIA’s response to the emerging constraints of multi-agent AI systems. What I mean is, as AI systems move toward multi-agent workflows, inference costs grow, coordination becomes hard, and long-running tasks strain context limits.
With Nemotron 3, each model is built on the same architectural foundation but targets a different balance of reasoning depth, throughput, and efficiency.
In this article, we’ll look at how the Nemotron 3 family is structured, what’s changed under the hood, and where it fits within agent systems commonly used.
What Is Nemotron 3?
The core idea behind Nemotron 3 is specialization. Some agents need to be lightweight and fast, handling routine tasks such as routing or summarization. Others are responsible for deeper analysis or long-horizon planning. By offering multiple models within the same generation, Nemotron 3 supports that division of labor while remaining transparent and self-hostable.
Nemotron 3 nano
Nemotron 3 Nano is the most efficiency-focused model in the family. It is a 30B-parameter model that activates up to 3B parameters per token using a hybrid mixture-of-experts architecture. This selective activation allows Nano to achieve high throughput and low inference costs while maintaining competitive accuracy for its size.
Nano is intended for tasks such as summarization, retrieval, classification, and general assistant workflows. In multi-agent systems, it works well as a high-volume worker handling frequent or intermediate steps without becoming a cost bottleneck.
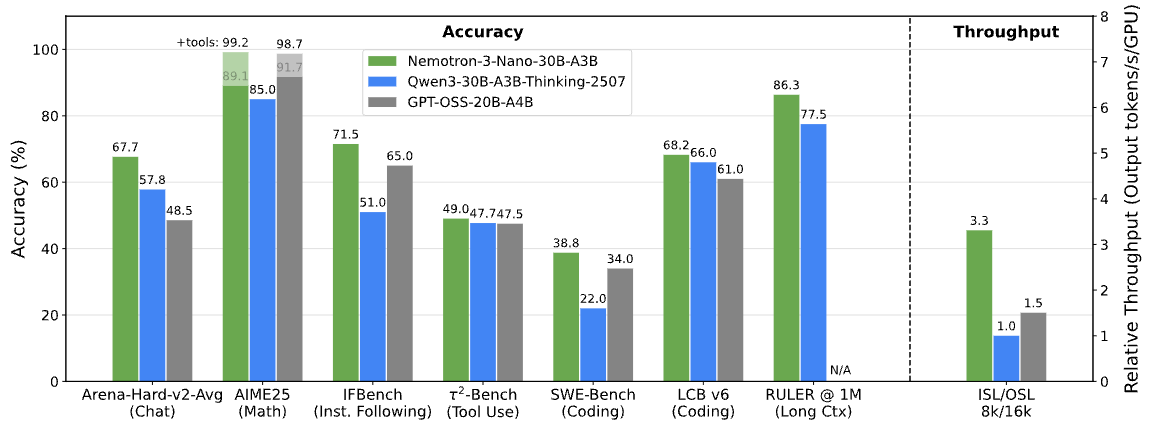
Nemotron 3 Benchmarks. Image by NVIDIA Research
Nemotron 3 super
Nemotron 3 Super targets scenarios that require stronger reasoning while still operating under latency constraints. It has roughly 100B parameters, with up to 10B active per token, and is optimized for coordinated multi-agent workloads.
Super sits between Nano and Ultra. It offers higher reasoning capability than Nano without the full compute requirements of the largest model, making it a good fit for agents that need to combine multiple inputs or reason across steps.
Nemotron 3 ultra
Nemotron 3 Ultra is the most capable model in the lineup. With approximately 500B parameters and up to 50B active per token, it serves as a high-end reasoning engine for complex agentic workflows.
Ultra is designed for tasks involving deep analysis, long-horizon planning, or strategic decision-making. While it has higher compute requirements, it’s meant to operate alongside smaller Nemotron models, with only the most demanding tasks routed to it.
What’s New in Nemotron 3’s Architecture
Now that the model lineup is clear, the next question is how NVIDIA balances scale and efficiency across such different tiers.
Rather than relying on a single architectural breakthrough, Nemotron 3 combines several complementary design choices to make large, multi-agent systems practical to run.
Hybrid latent mixture-of-experts design
At the core of Nemotron 3 is a hybrid latent mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture. Instead of activating all parameters for every token, the model routes each token through a small subset of specialized expert networks.
This reduces inference cost while preserving the capacity of a much larger model. In agent-based systems where many agents may generate intermediate outputs simultaneously, selective activation helps keep compute requirements manageable as scale increases.
Use of 4-bit precision in training
Nemotron 3 Super and Ultra are trained using NVIDIA’s 4-bit NVFP4 precision format on the Blackwell architecture. Lower-precision training reduces memory usage and accelerates training, enabling work with larger MoE models on existing infrastructure.
Importantly, this is done without a meaningful drop in accuracy relative to higher-precision formats, which helps explain how Nemotron 3 can scale while remaining practical to deploy.
Expanded context window for long sequences
Nemotron 3 Nano supports context windows of up to one million tokens. This allows the model to retain information across long documents, extended logs, or multi-step task histories.
For agent workflows such as routing tasks between planning, retrieval, and execution agents longer context reduces the need for aggressive chunking or external memory systems.
Key Features of Nemotron 3
These architectural decisions aren’t abstract. They show up directly in how Nemotron 3 behaves in real systems.
Reduced reasoning token generation
NVIDIA reports that Nemotron 3 Nano generates up to 60% fewer reasoning tokens than Nemotron 2 Nano. In multi-agent systems, where intermediate reasoning steps can dominate total token usage, this reduction directly impacts cost and scalability.
Shorter reasoning traces help keep inference efficient without sacrificing task accuracy.
Higher throughput for multi-step workflows
The combination of MoE routing and selective parameter activation allows Nemotron 3 to maintain high throughput as workflows grow more complex. This makes it easier to support longer task chains or more concurrent agents without proportional increases in latency.
1m context window for long-horizon reasoning
With support for up to one million tokens in Nano, Nemotron 3 enables long-horizon reasoning over extended inputs. Agents can reference earlier steps or large documents without repeatedly summarizing or reloading state, improving consistency over time.
Taken together, these features explain why Nemotron 3 emphasizes efficiency and coordination over raw single-model performance.
Nemotron 3 Vs. Nemotron 2: What’s Improved
At this point, the design goals of Nemotron 3 should be clear. Comparing it with Nemotron 2 helps validate whether those goals translated into measurable improvements.
Nemotron 3 refines mixture-of-experts routing, increases throughput, reduces reasoning token generation, and significantly expands context length. NVIDIA reports up to 4× higher token throughput for Nemotron 3 Nano compared to Nemotron 2 Nano, along with a large reduction in reasoning tokens.
Another difference is scope. Nemotron 3 expands beyond models alone, shipping with reinforcement learning datasets, agent safety data, and open tooling such as NeMo Gym and NeMo RL. Nemotron 2 focused primarily on model releases, while Nemotron 3 is positioned as a more complete stack for agent development.
Nemotron 3 Vs. Competitors
With the architecture and benchmarks in context, it becomes clearer where Nemotron 3 fits in the current model landscape. NVIDIA is not positioning Nemotron 3 as a drop-in replacement for frontier proprietary models. Instead, it targets a different challenge: making agent-based AI systems efficient, predictable, and scalable in real deployments.
Compared to other large open models, Nemotron 3 places less emphasis on maximizing single-model benchmark scores and more on system-level concerns such as throughput, reasoning-token efficiency, long context handling, and coordination across agents. This framing is similar to how Mistral positions its own lineup, but with a stronger focus on multi-agent workloads.
Where Nemotron 3 excels (compared to other models)
The table below summarizes the key dimensions where Nemotron 3 stands out, relative to other popular open and proprietary models.
|
Dimension |
Nemotron 3 |
Mistral Large 3 |
DeepSeek-Class Models |
Frontier Proprietary Models |
|
Primary Design Goal |
Multi-agent efficiency at scale |
Single-model capability |
Reasoning depth per prompt |
Frontier reasoning & agents |
|
Architecture Focus |
Hybrid latent MoE |
Sparse MoE |
Dense / MoE |
Dense, proprietary |
|
Throughput (Tokens/sec) |
Very high (Nano leads peers) |
High but compute-heavy |
Moderate |
Moderate to high |
|
Reasoning Token Usage |
Reduced (up to ~60% fewer in Nano) |
Moderate |
Higher |
Higher |
|
Context Window |
Up to 1M tokens (Nano) |
Up to ~256K |
Long, but smaller |
Long (varies by model) |
|
Multi-Agent Suitability |
Excellent |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Strong but costly |
|
Self-Hosting & Control |
Full (open weights) |
Full (open weights) |
Full (open weights) |
Limited / none |
|
Best Use Case |
Agent coordination, routing, summarization |
Deep reasoning, coding |
Math & reasoning tasks |
Complex planning, SWE |
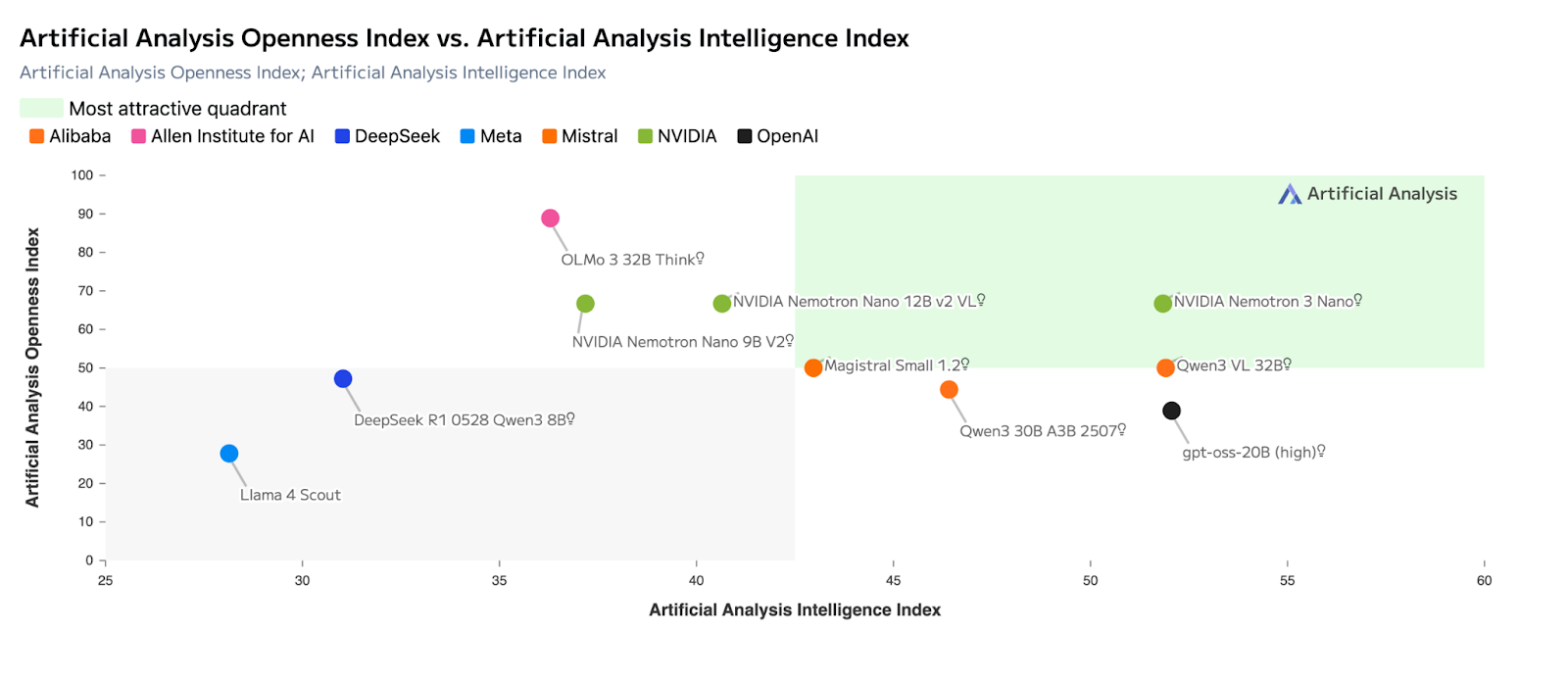
Nemotron 3 vs. Mistral Large 3
Mistral Large 3 and Nemotron 3 both rely on mixture-of-experts architectures, but they optimize for different outcomes.
Mistral Large 3 is designed to maximize single-model capability, performing strongly on reasoning, coding, and general-purpose benchmarks such as LMArena and SWE-style evaluations. It is often the better choice when one model is expected to handle an entire task end-to-end.
Nemotron 3, by contrast, is optimized for system-level efficiency. Its hybrid latent MoE design activates fewer parameters per token and prioritizes throughput over peak reasoning depth. This makes it better suited for coordination-heavy roles—routing, summarization, and intermediate reasoning where many agents operate simultaneously.
How Can I Access Nemotron 3?
Once the design goals are clear, the next question is practical: how can you actually run Nemotron 3 today, and which options make sense given your setup? NVIDIA offers several access paths, ranging from fully hosted APIs to self-managed deployments.
Api access via hosted inference providers
The fastest way to get started is through hosted inference providers. Nemotron 3 Nano is available today on platforms such as Baseten, DeepInfra, Fireworks, FriendliAI, OpenRouter, and Together AI. These services expose standard API interfaces, allowing you to test the model’s behavior, throughput, and long-context handling without provisioning hardware.
This option is well-suited for prototyping agent workflows, benchmarking performance, or integrating Nemotron 3 into existing applications with minimal setup.
Open weights and self-hosting
The Nemotron 3 models are also released with open weights on Hugging Face, enabling full control over deployment. This route is intended for teams that want to self-host the models, fine-tune them on domain-specific data, or integrate them into custom agent pipelines.
With open weights, you can:
- run the models on your own infrastructure,
- modify or fine-tune them as needed,
- and manage latency, privacy, and cost end-to-end.
This approach aligns with NVIDIA’s emphasis on transparency and ownership for long-lived, production-grade agent systems.
Nvidia nim and deployment frameworks
For teams that want a more managed self-hosting experience, Nemotron 3 Nano is also available as an NVIDIA NIM microservice. NIM packages the model for secure, scalable deployment on NVIDIA-accelerated infrastructure, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
As the ecosystem matures, Nemotron models are also expected to integrate with common deployment frameworks and runtimes used for local and edge inference. These options make it easier to experiment with Nemotron 3 in controlled environments without building a deployment stack from scratch.
Model availability timeline
At the time of release:
- Nemotron 3 Nano is available now via hosted APIs, open weights, and NVIDIA NIM.
- Nemotron 3 Super and Ultra are expected to become available in the first half of 2026.
In practice, this means developers can start experimenting with Nano immediately, while the larger models are positioned for later-stage deployments that require stronger reasoning capacity.
How Good Is Nemotron 3?
Nemotron 3 is strong within its intended scope. Its main contribution isn’t pushing the limits of single-model reasoning, but making agent-based systems more practical to deploy and scale.
The architectural choices translate into real operational benefits, especially for workflows that rely on many cooperating agents. That said, if your primary requirement is deep, single-model reasoning or complex tool-driven planning, frontier proprietary models still tend to be more consistent.
Viewed through the right lens, Nemotron 3 complements those models rather than replacing them.
Nemotron 3 Use Cases
Nemotron 3 fits best in scenarios where efficiency, transparency, and scalability matter.
- Multi-agent systems: routing, coordination, and intermediate reasoning
- Long-document processing: summarization, extraction, and analysis over large inputs
- Enterprise assistants: internal tools requiring predictable performance and self-hosting
- Workflow automation: classification, retrieval, and decision support at scale
- Privacy-sensitive deployments: on-premises or sovereign AI environments
Because the models are open and designed to work together, teams can assign different roles to different model sizes rather than relying on a single, monolithic system.
Final Thoughts
NVIDIA’s focus on efficiency, openness, and system-level design reflects how many real-world AI applications are now being built.
Now, to build effectively with models like Nemotron 3, it helps to understand both LLM fundamentals and system integration.
Our Large Language Models (LLMs) Concepts course provides conceptual grounding, while our Building APIs in Python skill track covers the practical side of integrating models into applications.
Viewed as part of a larger system, Nemotron 3 feels less like a model release and more like a foundation for how agent-based AI is being deployed today.
Tech writer specializing in AI, ML, and data science, making complex ideas clear and accessible.