Track
You’ve probably heard about NotebookLM thanks to its ability to generate realistic podcasts from documents.
However, NotebookLM is much more than that. It can quickly summarize complex documents, answer specific questions about them, and even transform them into briefings, study guides, or podcasts.
Another advantage is that we no longer have to juggle between different windows or apps to ask questions, generate summaries, or take notes—NotebookLM brings AI near the content.
I’ve had great fun using NotebookLM so far, and in this tutorial, I want to show you how it can make research and learning more dynamic, hands-on, and enjoyable. And, of course, we’ll create a few podcasts along the way.
What Is NotebookLM?
NotebookLM is an experimental AI-first notebook developed by Google. It uses the documents you upload to train a specialized AI. The AI in that notebook then becomes an expert on your documents, giving you an invaluable resource, specific to your needs.
AI-first notetaking
Many note-taking tools have been integrating AI features into their products lately. But NotebookLM is unique in that it is completely built around AI. When you use NotebookLM, it’s almost as if the AI is a partner, reading the documents with you.
NotebookLM can highlight key ideas in dense papers, offer concise summaries, and help you learn the material faster. And it can help you understand how different documents on the same topic relate to each other.
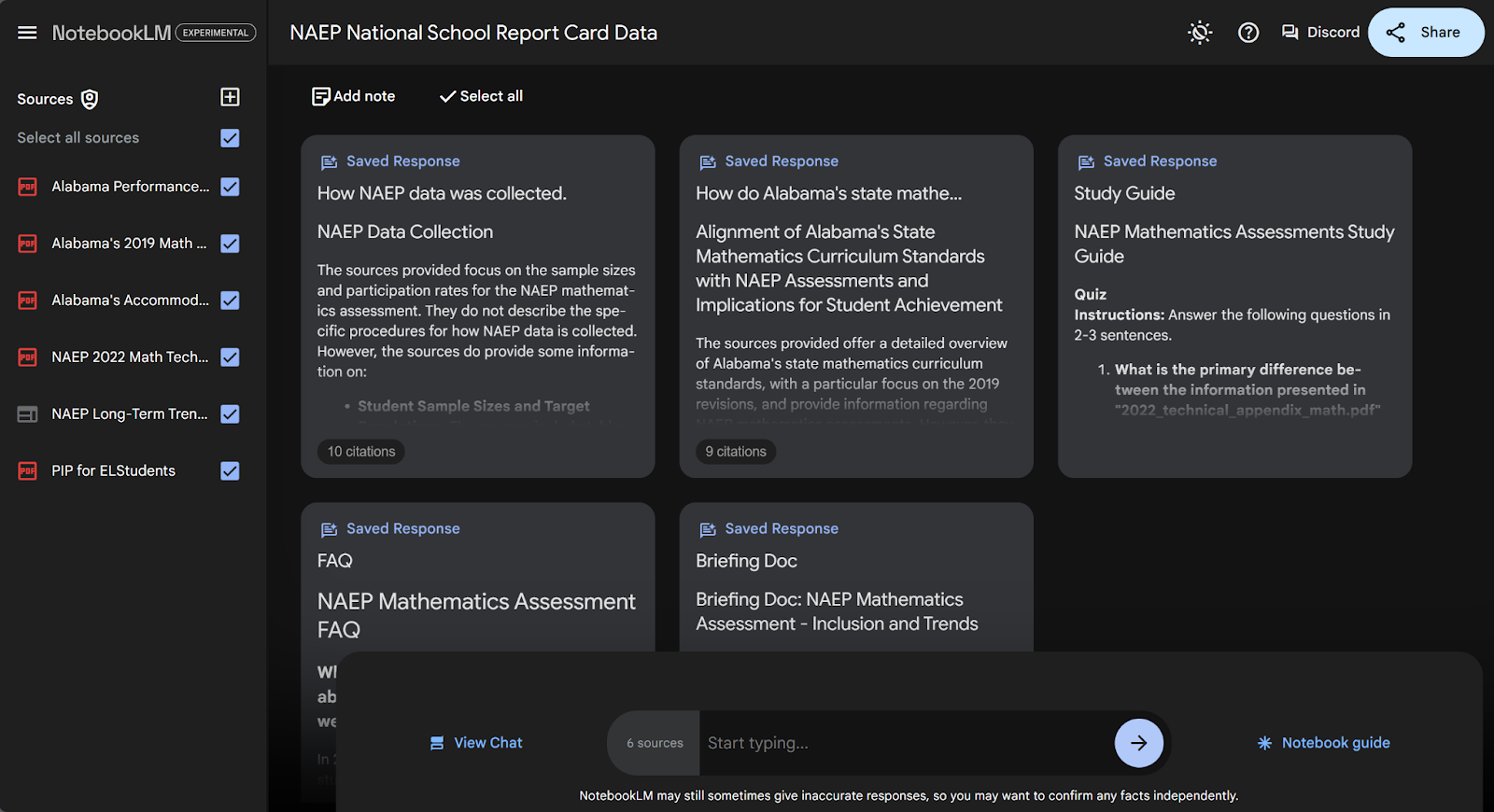
Below, you can see an example of how NotebookLM can be used. On the left are several documents about math education at the national and state level (specifically for Alabama) that I uploaded. On the right, NotebookLM generated a series of notes consolidating the information from those documents.
Grounding in your sources
Who among us hasn’t copied text into ChatGPT and asked it to summarize it for us? While this is is a great use case for ChatGPT, it’s not perfect. The model drifts from your uploaded document and brings in other ideas it’s learned about. And this effect gets exacerbated the farther your conversation gets from the copied text.
NotebookLM, however, remains focused on your specific uploaded materials. When you upload documents—whether they are PDFs, Google Docs, or other text files—NotebookLM learns the information contained within them and adjusts its responses based on those sources.
The AI works within the context of your own content, making its summaries and insights more relevant and accurate. You can trust that you know which sources NotebookLM is pulling from.
You can see this clearly when you upload a unique work of fiction. Writers can use this product to query their own writings to ensure clarity, flow, and consistency. As an example, I uploaded a fictional story that I asked ChatGPT to generate. Because NotebookLM is only drawing from my uploaded materials, its answers stay grounded within the fictional story.
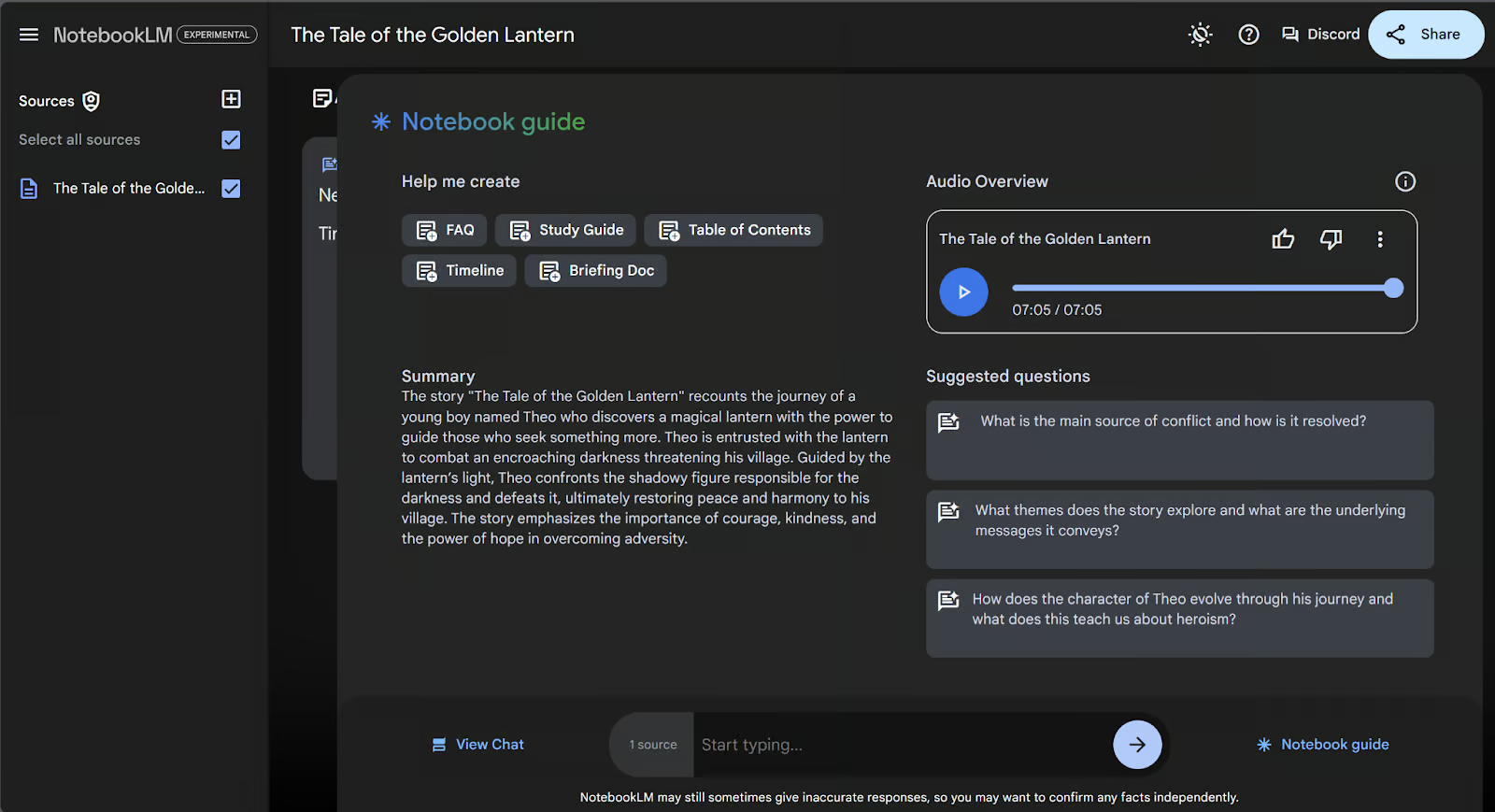
Below, you can see that NotebookLM has generated a summary, podcast, and suggested questions based on this fictional story.
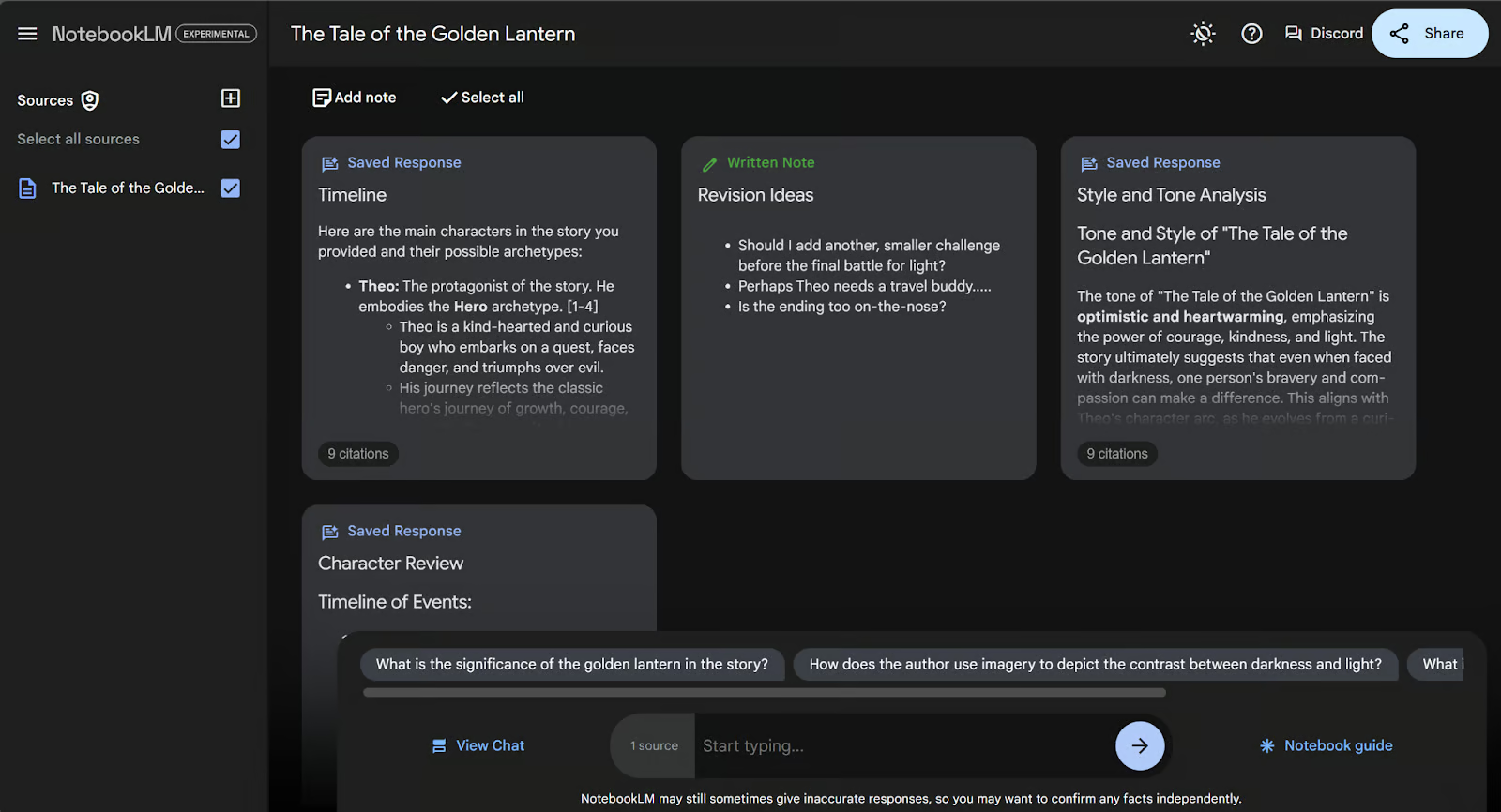
Both generated and written notes show up on the notes page. Generated notes stay on topic no matter how many there are.
The podcast feature
One of NotebookLM’s flashier features is the ability to create a curated podcast based on your documents. Instead of slogging through a dense research paper, you can listen to two AI voices have a conversation, summarizing it.
This can be a game-changer for busy professionals or students who want to digest information while multitasking. When testing this product, I was able to get in a 7-minute workout while listening to a custom podcast describing the Federal Reserve’s Beige Book for September 2024. I encourage you to try out this feature for yourself if you haven’t already.
While this is already a cool feature, it’s not hard to imagine the potential future applications. What if you could get personalized news podcasts, custom book summaries, or even an audio breakdown of your meeting notes? This could be a glimpse into the future of content consumption, where we’re listening to custom content created just for us.
Getting Started With NotebookLM
To get started with NotebookLM, navigate to the NotebookLM website and log in using your Google account.
Once you’re signed in, you’ll see an easy guide to get started with your first notebook. Press “Create”.
You’ll be prompted to upload a document to start the notebook.
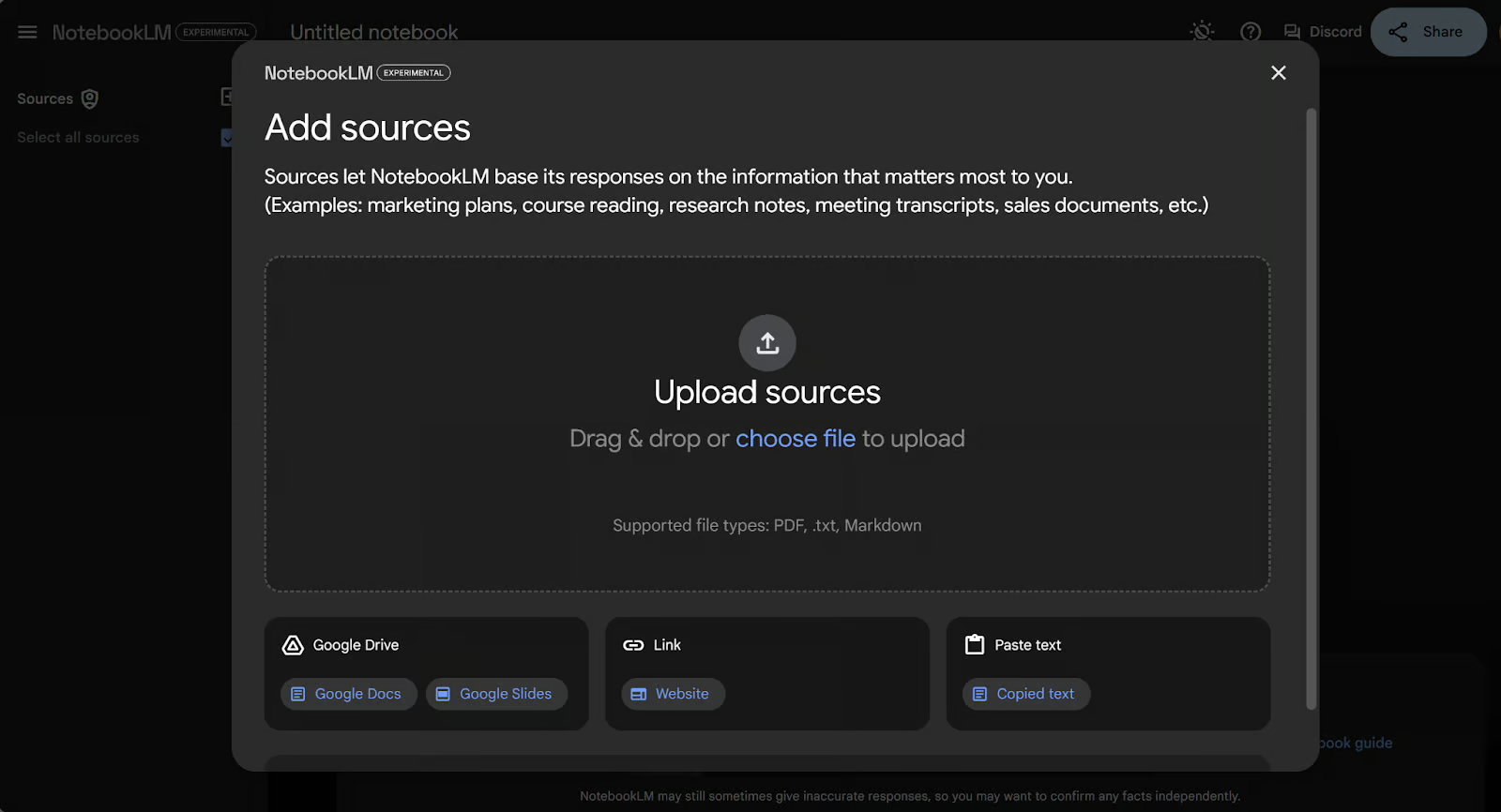
There are 5 different options for how to upload documents:
- You can upload files from your computer in PDF, .txt, or Markdown formats.
- You can link directly to a website using its URL.
- You can copy and paste text directly into the notebook.
- You can link to a Google Doc.
- You can link to a Google Slideshow.
Simply choose the option that contains the information you’re interested in and link to your document.
There are a few limitations you need to keep in mind:
- As of now, you can only upload a maximum of 50 files, with up to 500,000 words each.
- Its main use is for text documents, so it won't work with Excel file just yet.
- Larger documents may take more time to process. If you’re working with dozens of files, you may want to prioritize key sources for faster insights.
Once your documents are uploaded, NotebookLM is ready to work its magic.
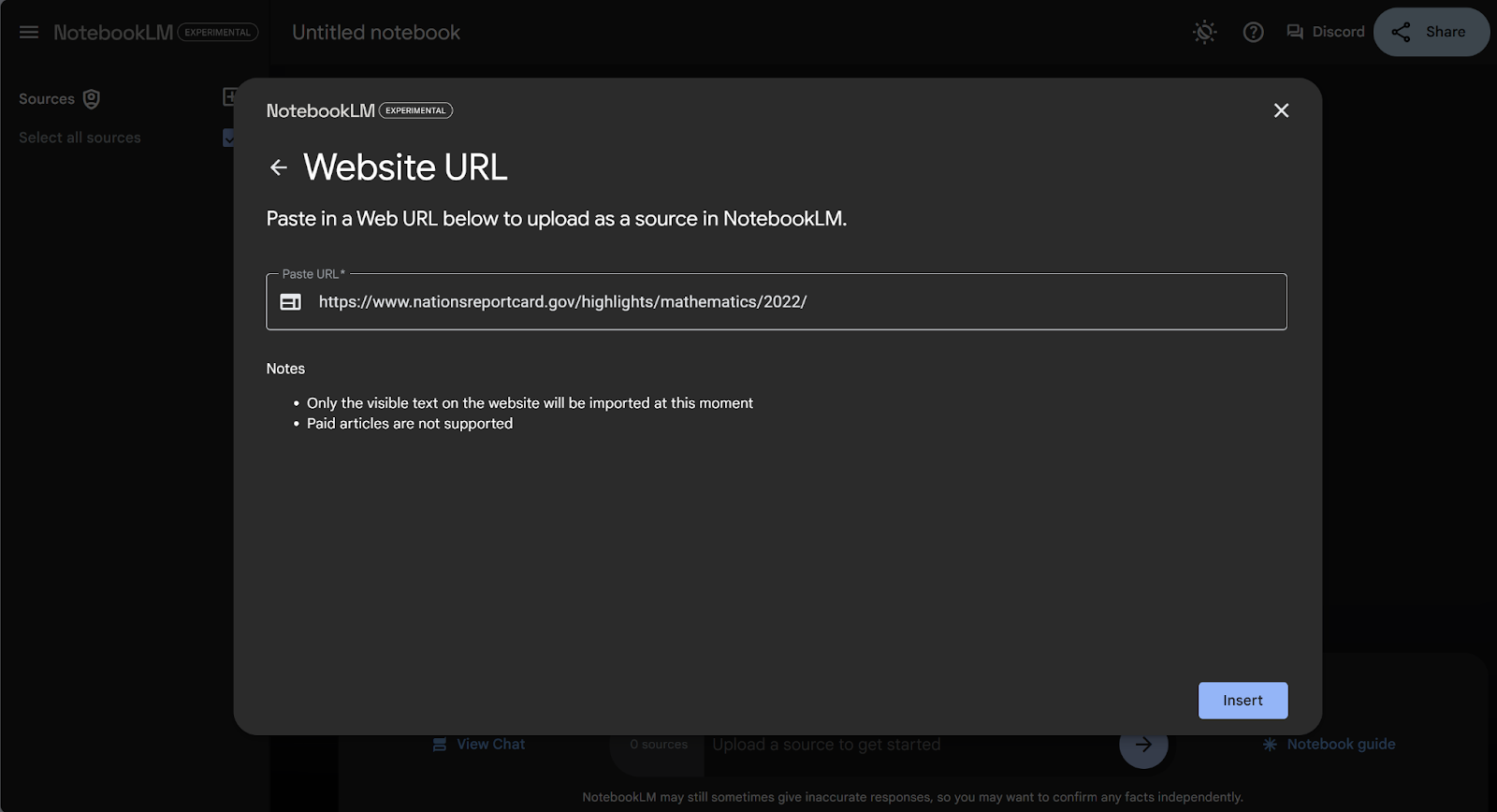
Note: In the rest of the tutorial, I’ll be using The National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) 2022 Mathematics Report Card as the source for all my examples. If you’d like to follow along, choose “Link” as your document source, copy the URL above into the box, then press “Insert”.
Key Features of NotebookLM
Let’s explore NotebookLM’s features through our example document.
The notebook guide
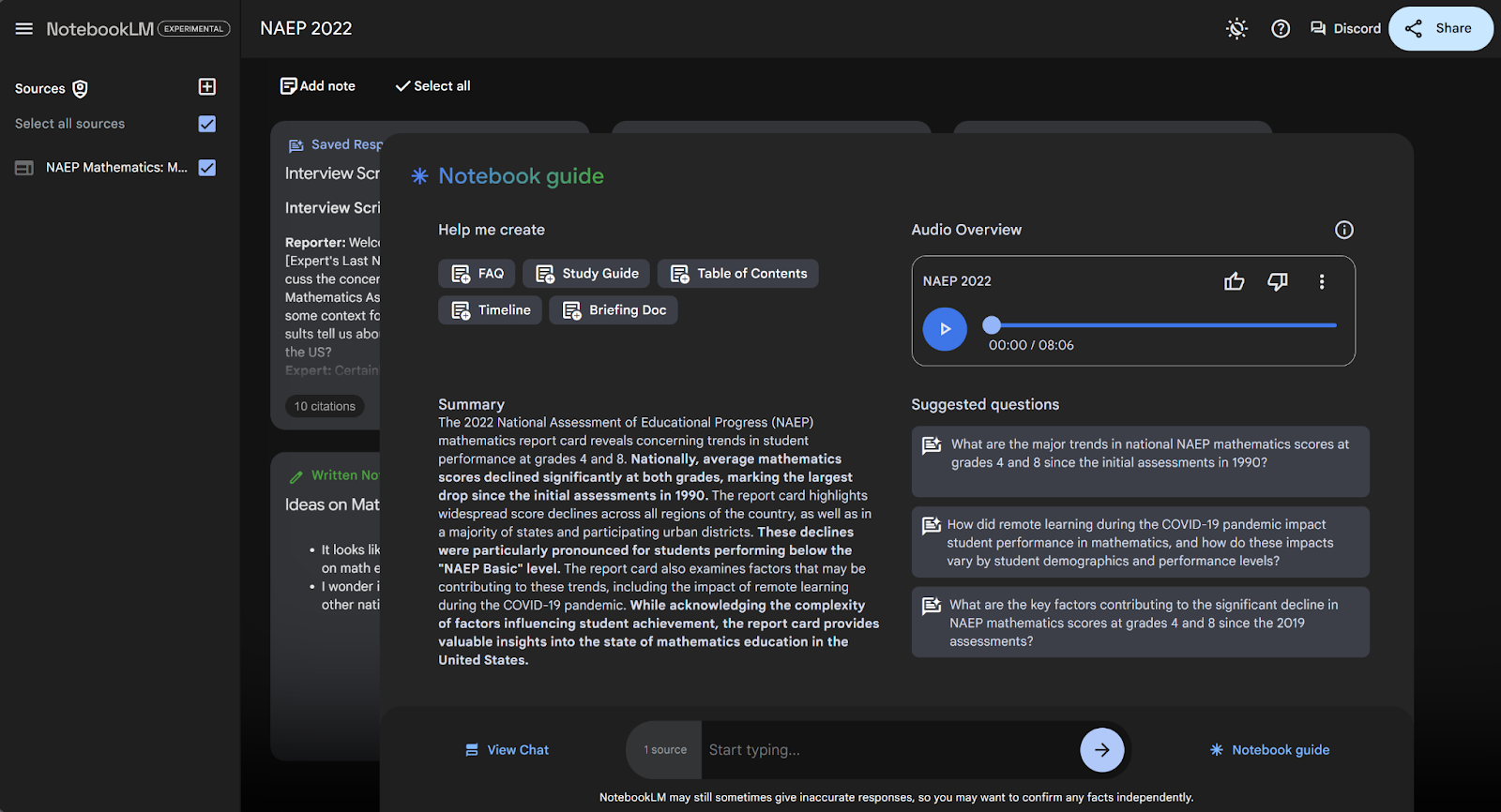
When you upload a document into NotebookLM, the first thing you’ll see is a dashboard called the “Notebook Guide”.
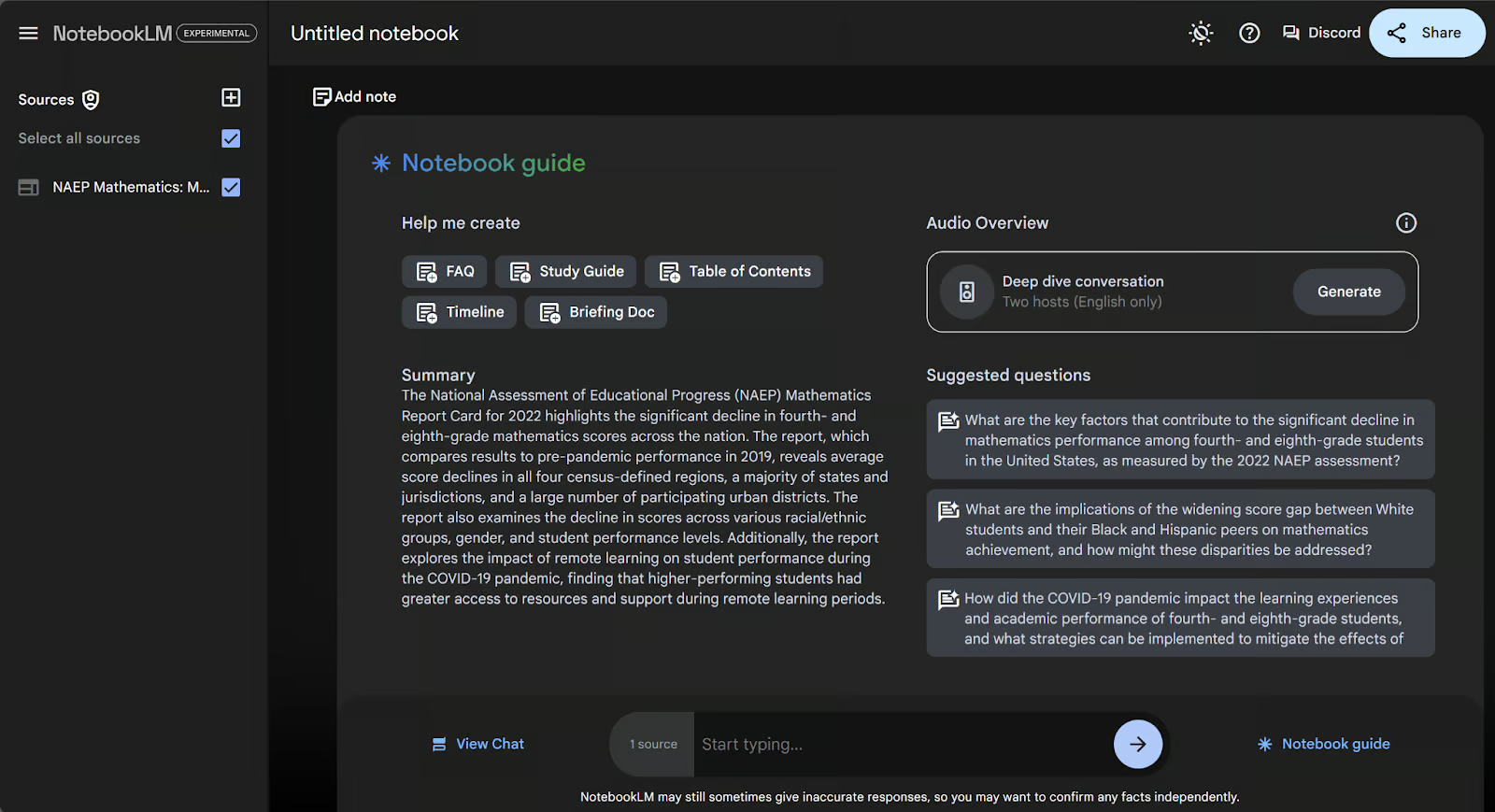
This dashboard contains:
- An automatically generated summary of your uploaded documents
- Suggested questions you may want to ask that are tailored to your documents
- Buttons to create a few standard summary documents, like briefing docs or tables of contents
- A prompt to generate a personalized podcast.
Asking questions
One of the best parts of NotebookLM is that it allows you to ask natural language questions about your uploaded documents. There are three ways you can ask questions:
- You can click one of the “Suggested questions” on the right of the Notebook guide (see screenshot above).
- You can start typing your own question in the bar on the bottom of the page.
- You can click “View Chat” on the lower left side of the page to go to the chat page and type your question in the bar.
Whichever way you choose, it will take you to the chat page to answer your question. For example, I’m going to type, “What are the five biggest takeaways from this document?” into the bar on the bottom.
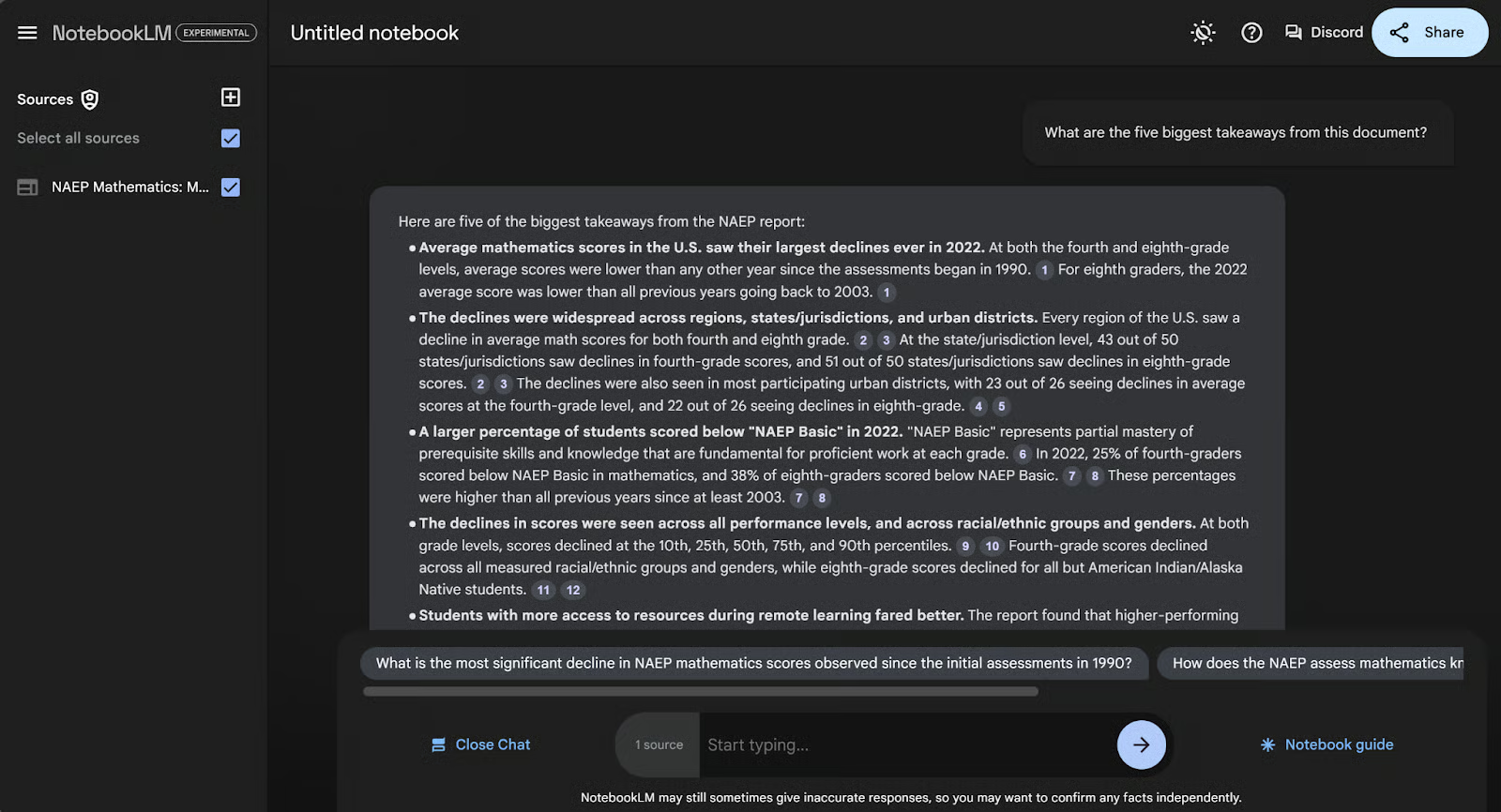
Here I asked about the five biggest takeaways from the document and the AI provided me with a bulleted list.
In addition to simply answering the question, NotebookLM provides specific citations showing you where it got its answer from. These are shown as little numbers in grey ovals next to the information. When you hover or click on the number, the specific location in the document appears. Let’s click on the number 3, as an example.
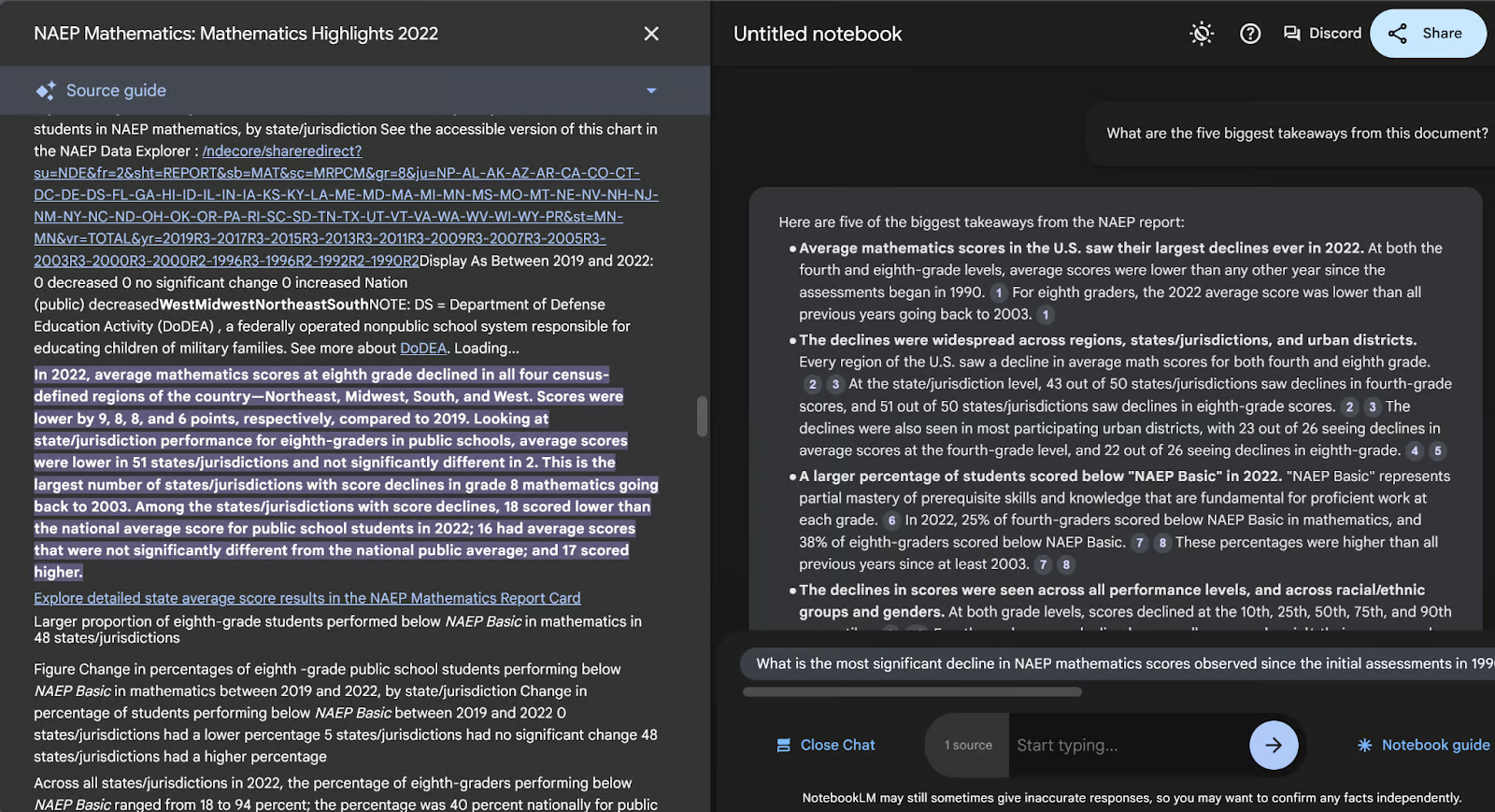
When I click the reference number 3 in the answer, the “Source guide” opens on the left side showing me the specific reference for that statement in the answer. The specific location is highlighted. Very useful!
Generating ideas
In addition to asking questions, you can ask the AI to generate ideas for you in this chat page. As an example, let’s ask the AI to brainstorm ideas to improve math education in the US.
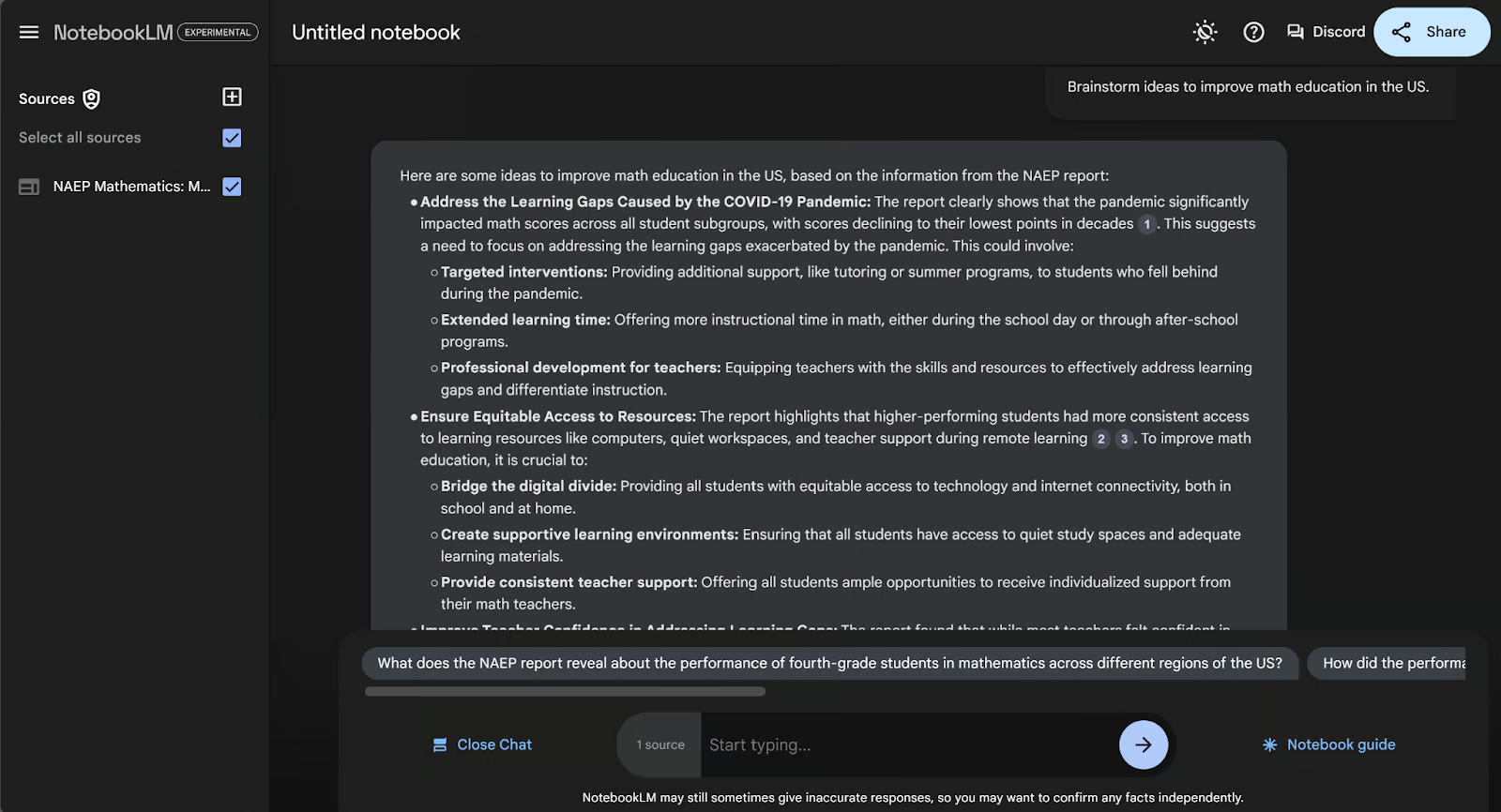
Here we’ve asked the AI to help us find solutions to the problems presented in the document.
Or how about something more esoteric? Maybe we need to create an awareness campaign and want a short way to explain this document. Let’s ask NotebookLM to write a haiku about the problem and the solutions.
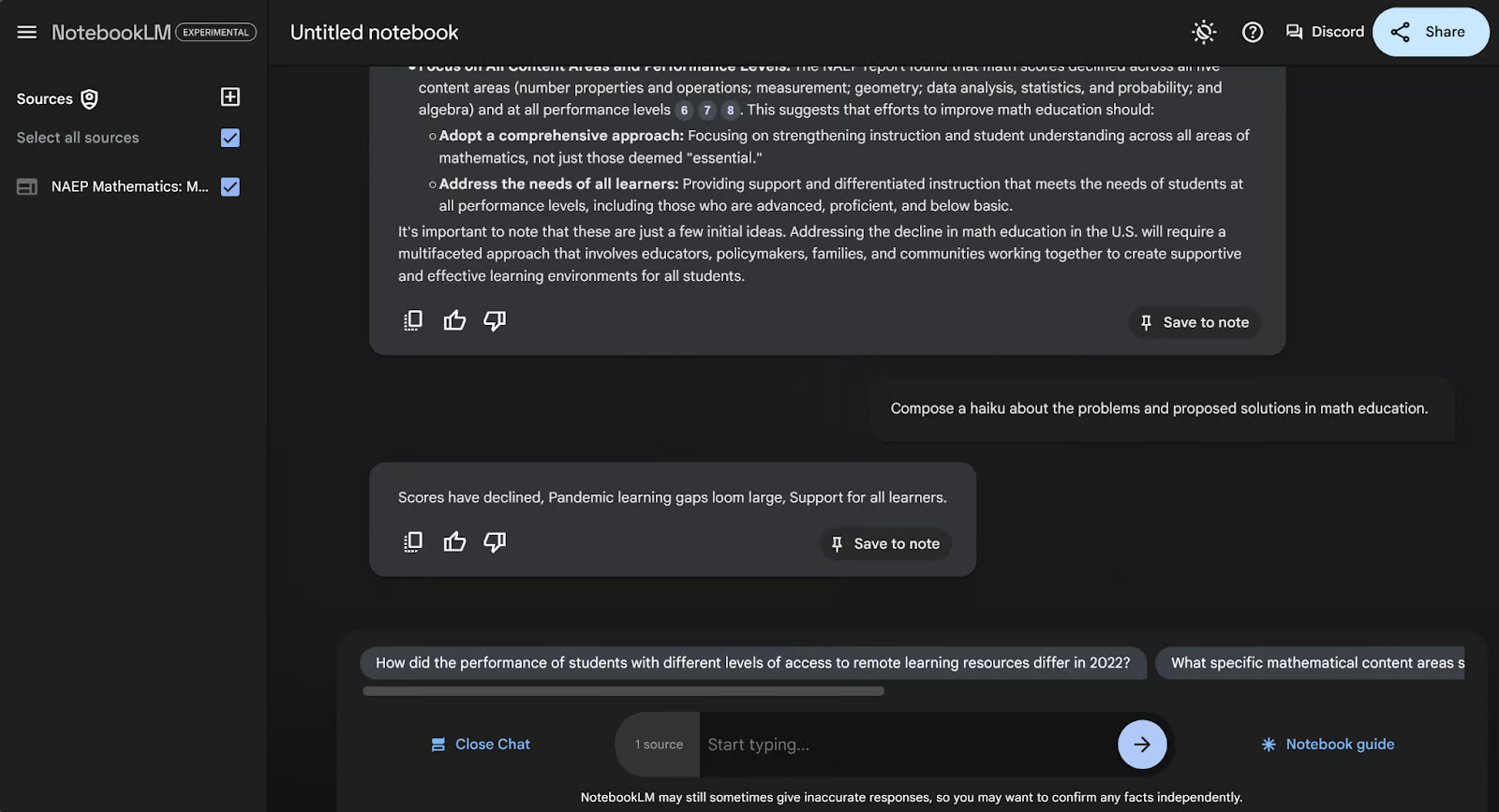
Note that the chat page is ephemeral. When you close or refresh the browser, your chat will disappear. If you want to keep any part of the conversation, be sure to save the outputs as notes by clicking “Save to note” at the bottom right of each AI reply in the chat.
The notes page
When neither the notebook guide, nor the chat are open, the default screen is the notes page.
The default notes page contains no notes.
Let’s start populating this page with notes. There are two types of notes: written and AI generated.
Written notes are notes you type in yourself. To create a new note, click “Add note” at the top of the notes page. This will generate a new, blank note for you.
To edit this note, click on it. It will expand into the center of the screen. You can change the title (which defaults as “New Note”) and add text to the note.
The note is automatically updated as you type. Once you’re finished writing your note, you can click anywhere off the note for it to shrink back. Your written note is added to the notes page and labeled with a green “Written Note” label. This differentiates it from AI written notes.
Now let’s create an AI note. Let’s go back into the chat by clicking “View Chat”, and ask it to give us a step-by-step plan to improve math education in the next year.
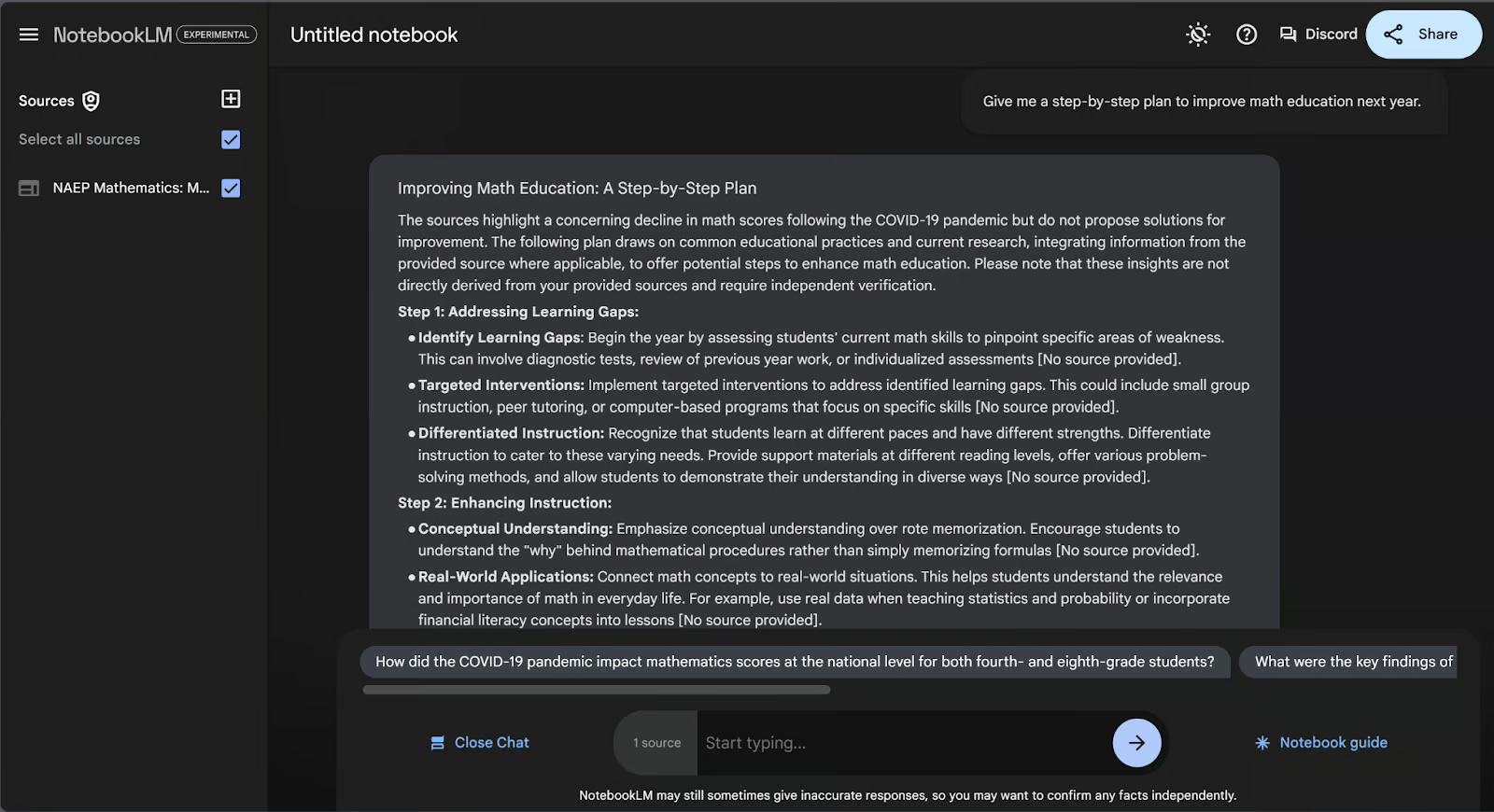
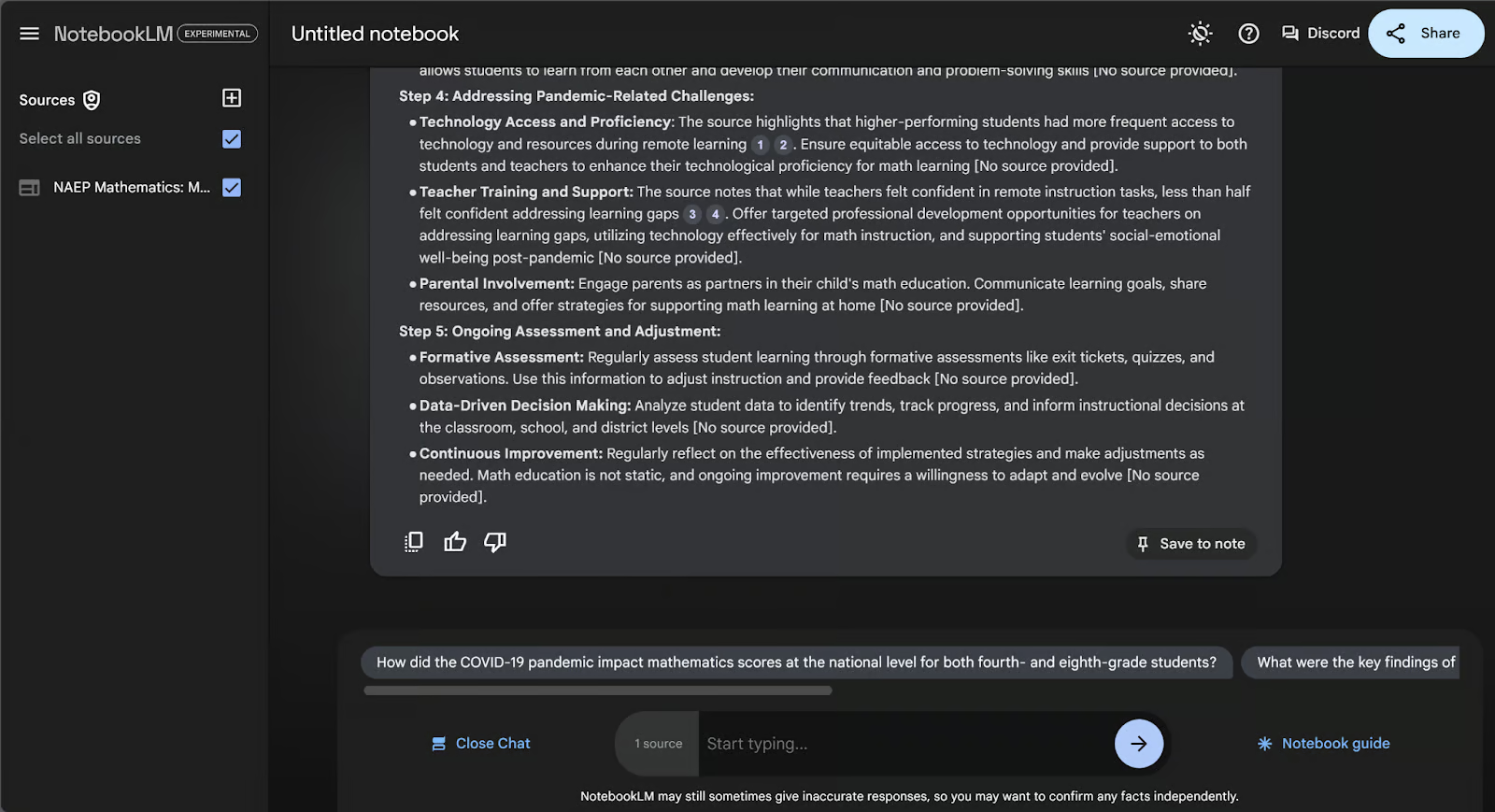
If we scroll down to the end of the answer, we will find the “Save to note” button in the bottom right corner. That will turn the AI’s answer into a saved note.
Now we’ll see our written note from earlier and our AI generated note, both on the notes page. The AI generated note is labeled in blue as “Saved Response”.
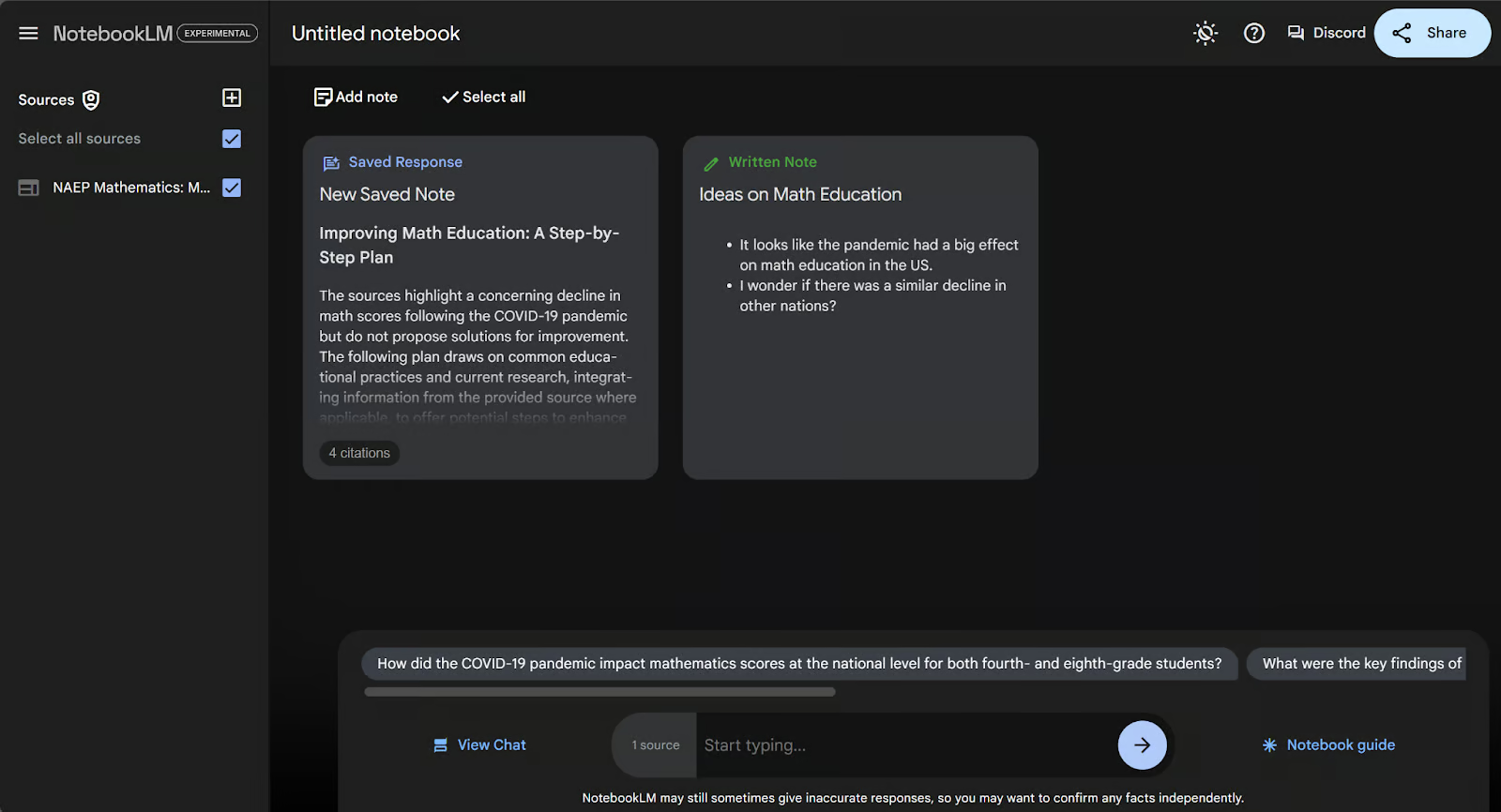
The automatic title is “New Saved Note”, which we can change by clicking into the note. However, we cannot edit any other part of this note.
You can see how we can quickly and easily consolidate all our thoughts into one organized area in this section. And it’s easy to keep the best of the chat results organized here too. Any unsaved chat disappears when you leave the notebook.
Podcast generation with NotebookLM
One of the most innovative features of NotebookLM is its ability to create customized podcasts with two AI voices discussing your documents. This feature is more than just text-to-speech software—the podcast is not a verbal transcription. Instead, it’s a conversation between two hosts discussing the key points of the documents. The format is really like listening to a podcast. The voices are remarkably human and emotive.
Let’s try generating a podcast about our NAEP document. First, navigate to the Notebook guide by pressing the button in the lower right corner.
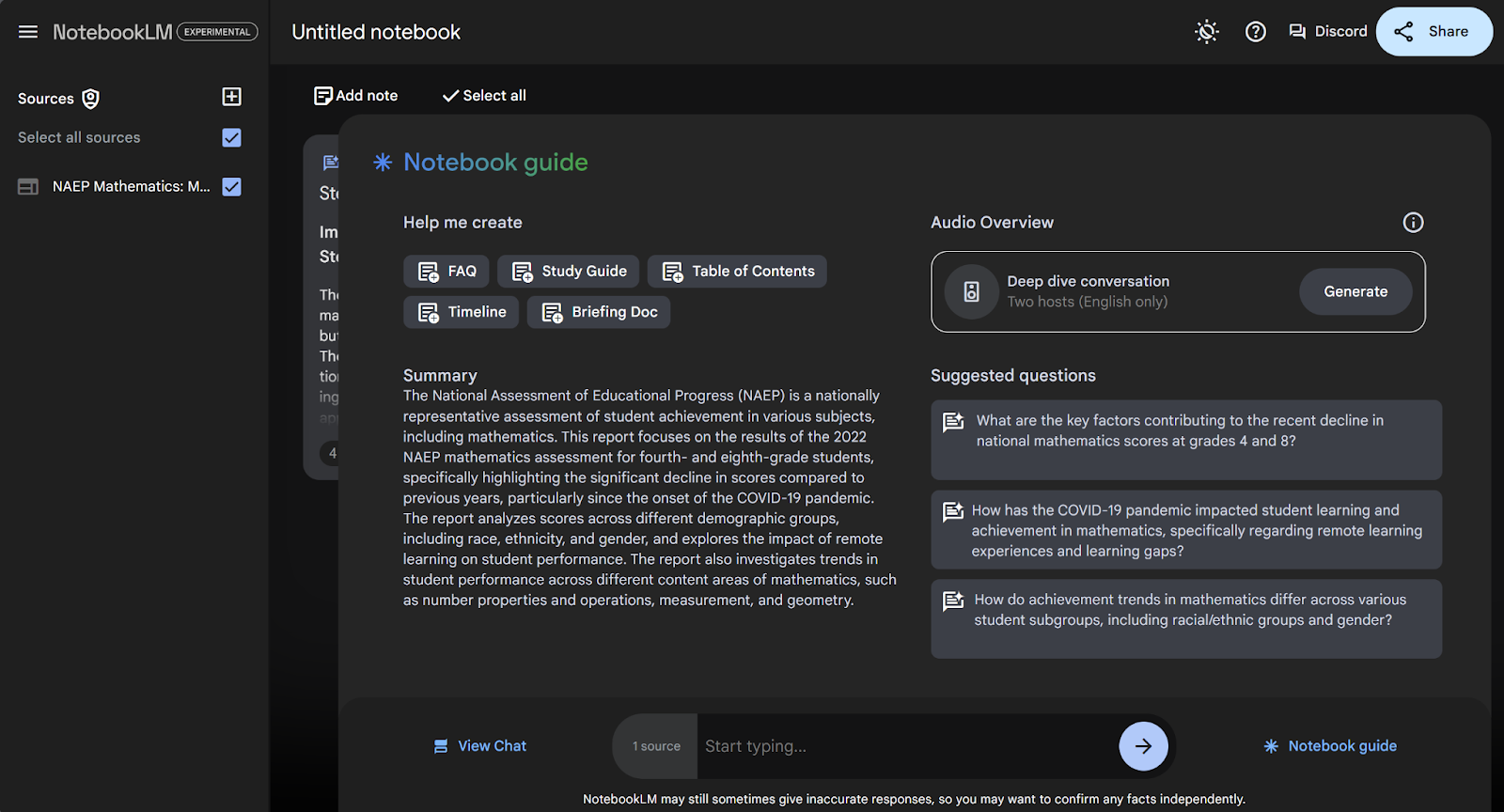
As of now, there is only one type of podcast you can create: the deep dive conversation. Simply press “Generate” under Audio Overview and wait several minutes for the podcast to be created.
The podcast length is indeterminate, though I’ve always gotten somewhere between a 6- and a 15-minute podcast. I’ve heard of people getting as long as 30 minutes of content. The podcast does not cover every little thing in the documents. Instead, the AI decides what the most important parts to cover are, and discusses those.
There are currently still some oddities with this feature. For example, in any given podcast the voices may give examples of their personal lives, say things like, “tune in next time”, or sometimes pause for commercial breaks that don’t exist. These oddities are sure to be improved upon as the development of this product continues.
You’ll have a few options once you generate your podcast. If you click on the three dots in the upper right corner of the podcast rectangle, you’ll see options for changing the playback speed, downloading the file, or deleting the podcast. If you delete it, you can regenerate a new one.
Structured formats
NotebookLM isn’t just about generating insights. It can also help you organize your notes into structured formats. Some new formatting tools in the notebook guide make it easy to create FAQs, study guides, or timelines directly within your notebook.
There are two ways you can do this. The first is by selecting one of the five preset buttons at the top of the notebook guide (FAQ, Study Guide, Table of Contents, Timeline, and Briefing Doc).
Let’s try this out in our example by clicking the FAQ button.
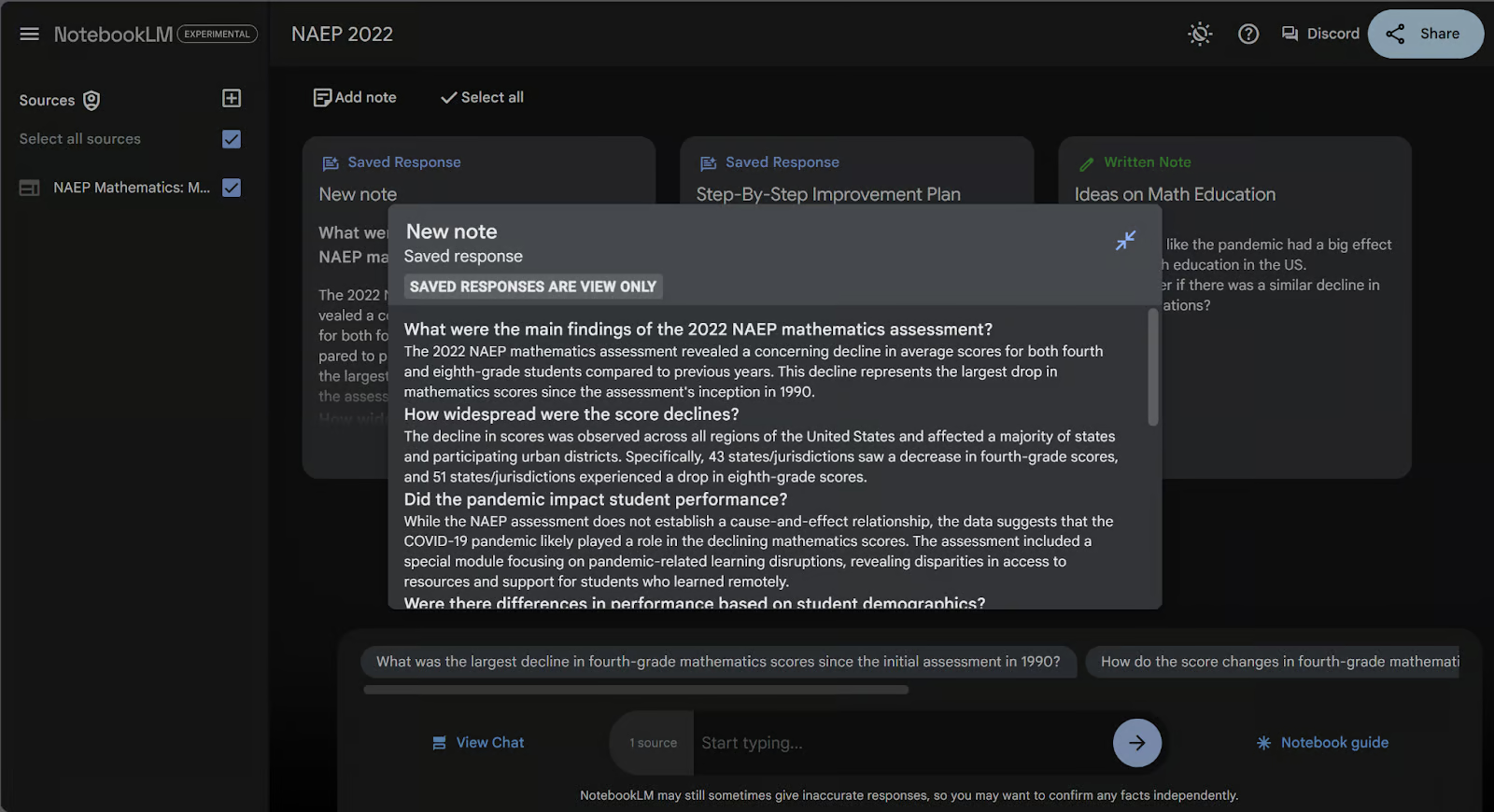
As you can see, this created a new note on our note page with the blue “Saved Response” label. Inside this note is a curated FAQ for our government document. As with other AI-generated notes, we cannot edit the content of this note, but we can edit the title. I will rename this “FAQ.”
But what if we want a formatted note that isn’t one of the five buttons listed in the notebook guide? We can always ask for specific formats in the chat bar at the bottom. Let’s ask for an interview script between a reporter and an expert in math education.
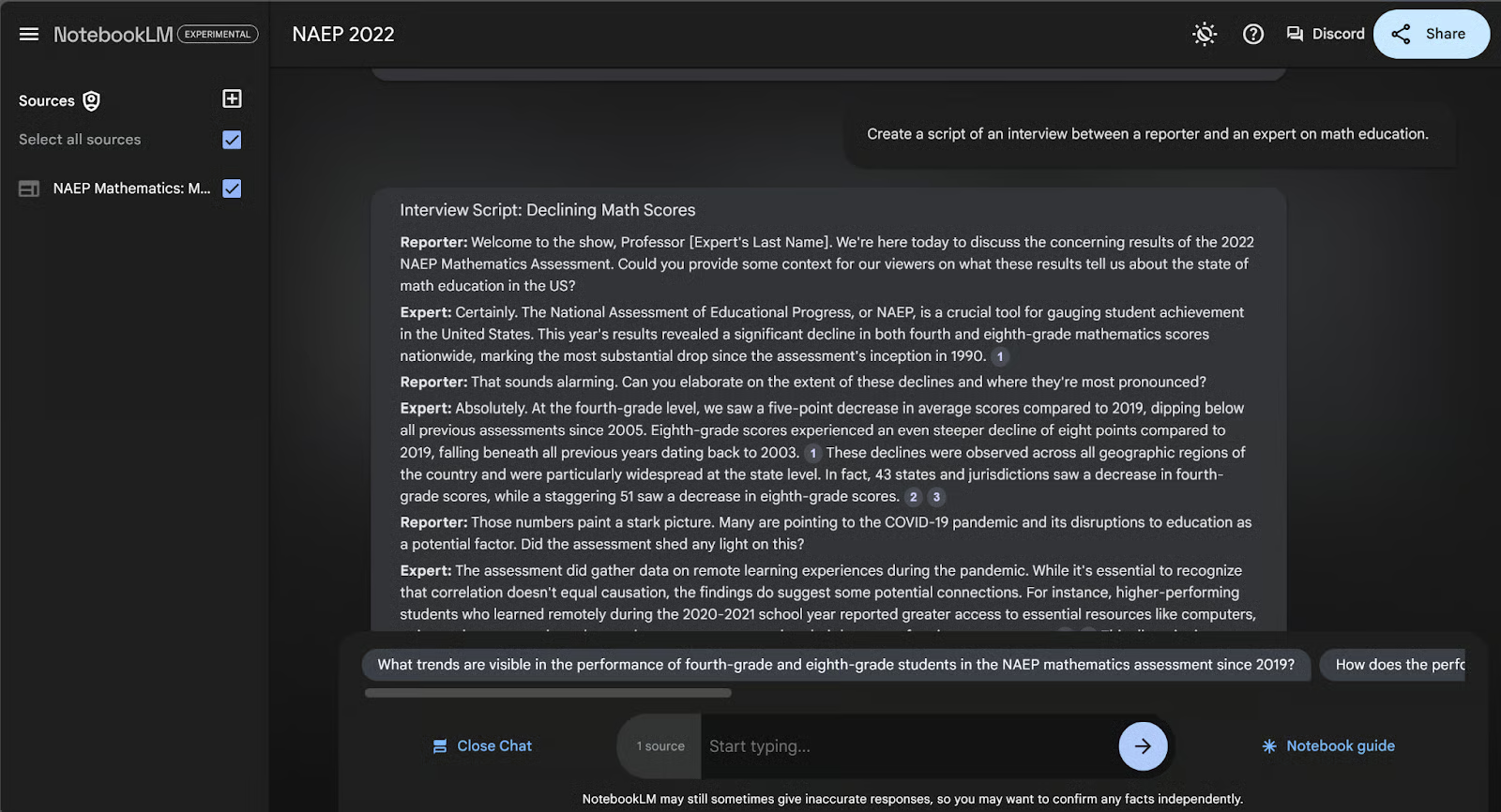
When typing this request into the chat bar, it takes us to the chat page. We can scroll to the bottom of this answer block and click “Save to note” to create the formatted note. Here’s what it looks like after I renamed the new note.
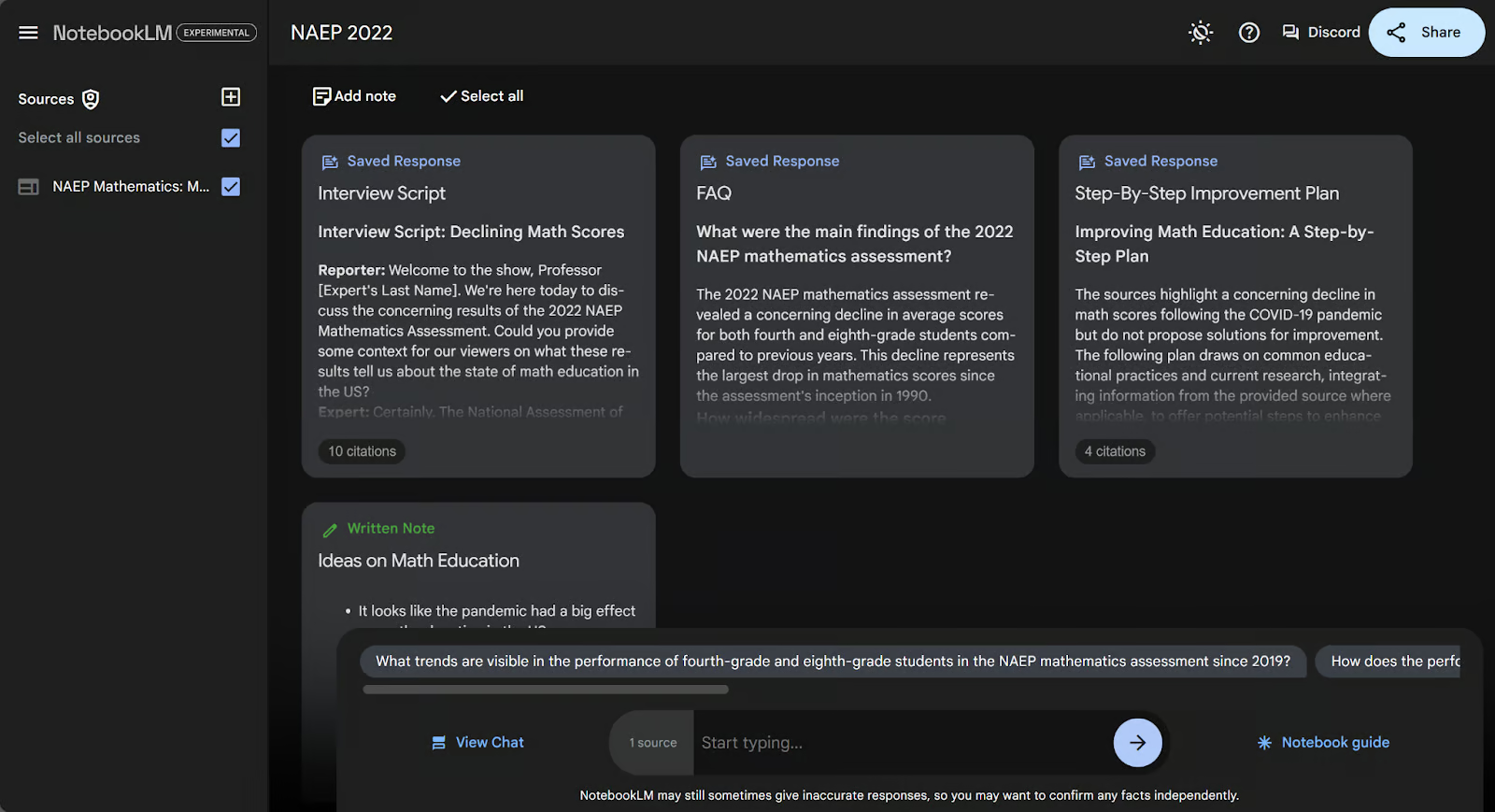
This process saves notes the same way as answers.
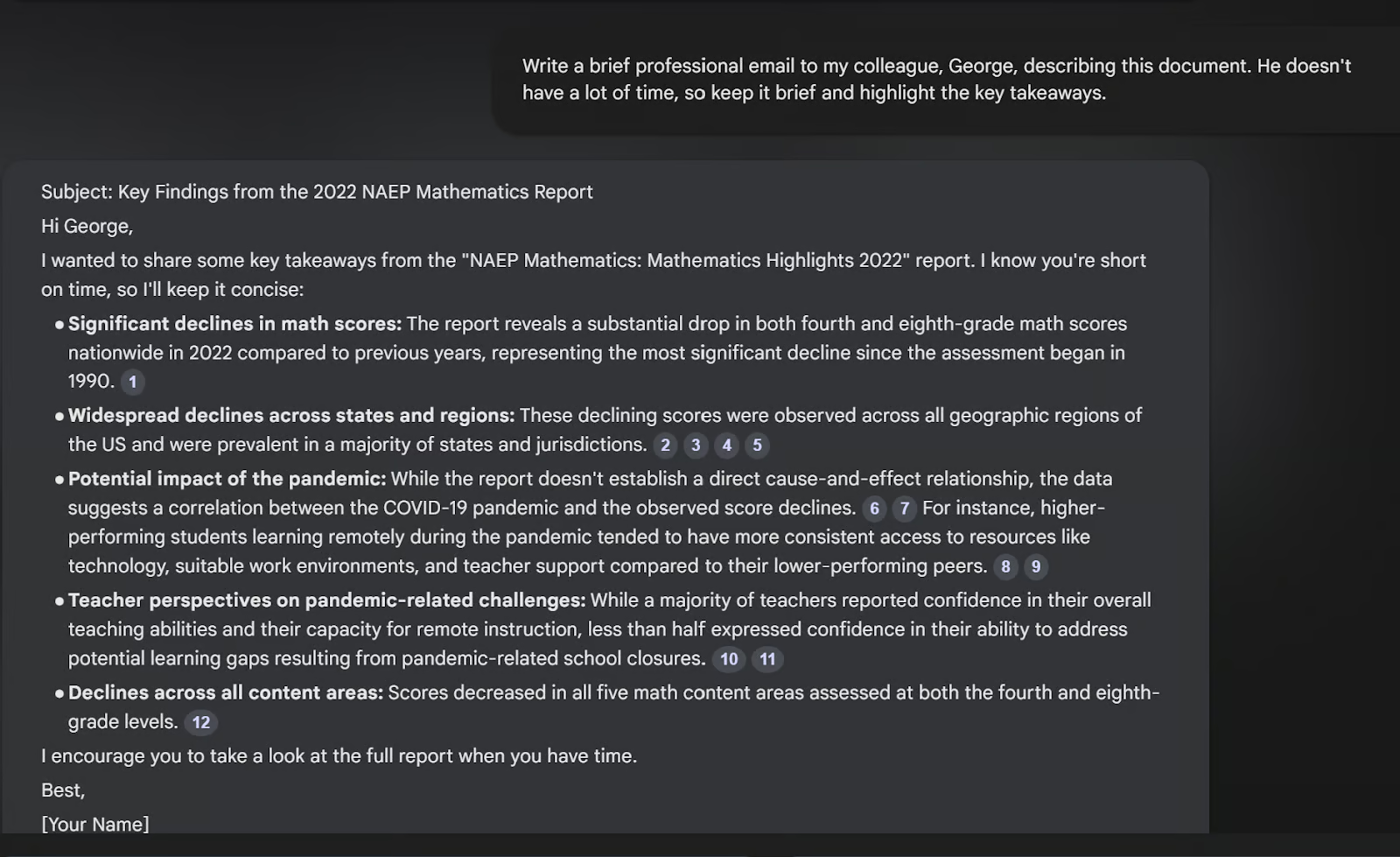
I encourage you to try asking for different formats. One I particularly like is asking for an email to a colleague.
NotebookLM Troubleshooting
NotebookLM is still an experimental product, so you may run into problems while using it or struggle with a new feature update. Fortunately, there are two, easily-accessible places to find answers. Both are found in the upper right corner:
- The question mark in a circle opens a support page.
- The Discord button brings you to a custom Discord forum for NotebookLM users.
The support page is full of information on how to use NotebookLM. This is especially helpful for when new features are updated.
The Discord forum is another good resource. Both Googlers and NotebookLM users are active on the platform, making it a great place to provide feedback, request features, seek inspiration, or ask for help.
Best Practices
NotebookLM has the power to make research easier and more intuitive. But to take full advantage of this, it’s important to follow certain best practices.
Choose relevant sources
As with any research project, it’s vital that you choose the right information sources. The accuracy and usefulness of NotebookLM's insights are directly tied to the quality of the documents you upload. It’s important to select relevant and specific sources that align closely with your research project and contain reliable information.
By choosing focused and reliable materials, you’ll get more precise insights and avoid irrelevant or misleading information. Remember, NotebookLM will treat your fictional sources the same as your true sources.
Ask clear and specific questions
Prompt engineering isn’t just for ChatGPT. Being clear about what you want will help you get the most out of any LLM. When querying NotebookLM, make sure your questions are clear and specific. Asking vague questions can result in broad or less-than-helpful responses. Crafting more targeted questions will allow the AI to provide focused answers that align with your needs.
For example, look at the prompt I gave when I asked for an email to my colleague. I specified that it needed to be brief and include the key points from the document. Optimizing my prompt in this way resulted in a better email.
Experiment with different prompts
Don’t hesitate to experiment with different ways of interacting with NotebookLM. Whether you're asking for summaries, brainstorming ideas, or generating new content, varying your prompts can unlock creative insights you may not have anticipated.
For instance, instead of just asking for an overview, try prompting NotebookLM to compare two different policies or identify emerging trends. The tool’s flexibility means there’s always room for discovery.
Here are some prompt ideas for you to try:
- Explain this document in the form of a short story.
- Compare and contrast Document 1 with Document 2.
- Give me a pro/cons list for the solutions proposed in this document.
- Format a proposal for X based on the information in these documents.
Review and verify information
While NotebookLM can save you time by summarizing and organizing content, it’s crucial to remember that AI-generated information isn’t always perfect. Always review and verify the material for accuracy, especially when dealing with complex data or sensitive topics. The AI is a powerful assistant, but your human judgment is essential to ensure the insights you get are reliable and useful.
Conclusion
NotebookLM is reshaping how we interact with content, offering a blend of AI-powered insights, easy document summaries, and even podcast-style audio overviews.
Whether you're breaking down dense government reports or brainstorming your next big project, this tool is designed to speed up and simplify your workflow.
I encourage you to check out NotebookLM for yourself! Experiment with different features, and see how NotebookLM can enhance your work.
To learn more about AI, check out DataCamp’s AI Fundamentals course and AI Ethics course.
For more on recent AI developments, check out the following blogs:
FAQs
What is NotebookLM?
NotebookLM is an AI-powered research tool from Google that helps users consume complex documents more effectively. It offers AI-driven summaries, question answering, idea generation, and podcast creation, all based on uploaded documents.
How does NotebookLM work?
NotebookLM lets you upload your own documents, which it analyzes and uses to answer questions, generate summaries, create presentations, and produce podcasts, all tailored to your specific documents.
What is the podcast feature of NotebookLM, and how does it work?
The podcast feature transforms your documents into engaging audio discussions. Two AI voices summarize the key points and offer thoughtful insight.
What kinds of documents can I upload to NotebookLM?
NotebookLM is primarily designed for text-based files like PDFs, .txt files, Google Docs, Google Slides, and web articles. Currently, it doesn't support spreadsheets or highly visual content.
How is NotebookLM different from other AI tools like ChatGPT?
While tools like ChatGPT offer general knowledge and text generation, NotebookLM focuses specifically on the documents you upload. It becomes an expert on your content, ensuring all its responses and insights are grounded in your source material.

I am a PhD with 13 years of experience working with data in a biological research environment. I create software in several programming languages including Python, MATLAB, and R. I am passionate about sharing my love of learning with the world.