Track
Large language models (LLMs) often fall short when it comes to knowledge-intensive tasks that require up-to-date and precise information. This is where retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) steps in, combining the generative capabilities of LLMs with external knowledge bases to enhance accuracy and relevance.
Despite its effectiveness, traditional RAG systems face challenges in managing long and complex documents, leading to increased latency and sometimes less accurate results. To address these issues, the concept of speculative RAG has emerged as a promising solution. Let’s find out more about it.
What Is Speculative RAG?
Speculative retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is an innovative framework designed to improve the efficiency and accuracy of RAG systems by dividing the generation process into two distinct steps:
- Drafting: The first step involves a smaller, specialized language model known as the RAG Drafter. This model generates multiple answer drafts from different subsets of retrieved documents. Each subset is carefully selected to represent diverse perspectives, minimizing redundancy and enhancing the quality of drafts.
- Verification: The drafts generated by the RAG Drafter are then passed to a larger, generalist LM, known as the RAG Verifier. This model evaluates the drafts, focusing on selecting the most accurate and reliable one based on the rationale provided. The verification process uses the language modeling capabilities of the generalist LM to ensure that the final output is both accurate and contextually relevant.
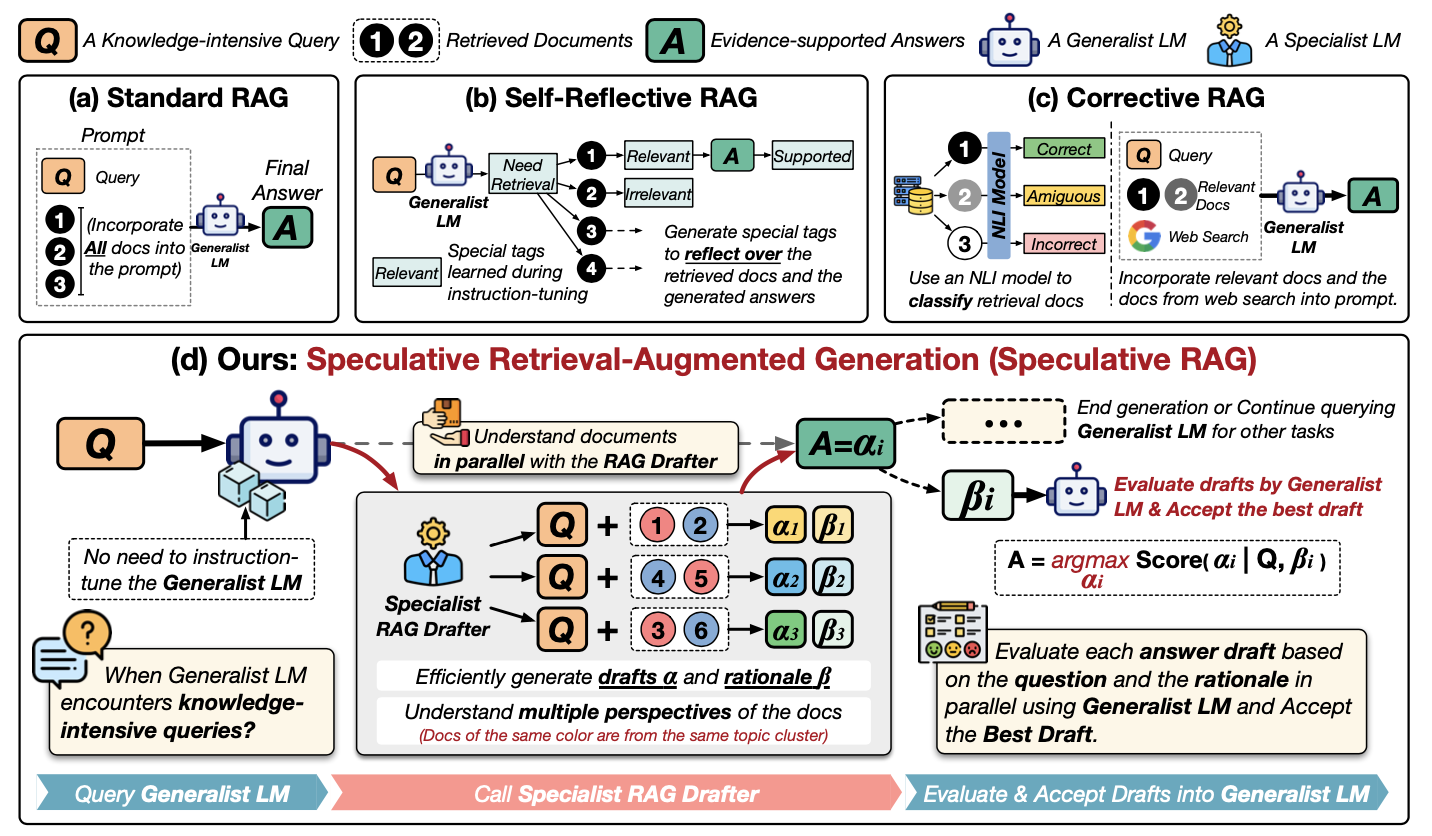
Let’s better understand speculative RAG by examining this diagram:
Source: Wang et al., 2024
Let's walk through this diagram step-by-step. It shows different ways to use external information to help an LLM answer questions, focusing on a new method called Speculative RAG. Let’s examine the methods in the first row:
- (a) Standard RAG: The simplest approach. All the relevant documents (1, 2... in the diagram) are directly given to the LLM (the "Generalist LM") along with the question (Q) to produce an answer (A).
- (b) Self-Reflective RAG: Here, the LLM is trained to analyze the documents and its own answer, generating special tags ("Need," "Relevant," "Supported") to improve its reasoning.
- (c) Corrective RAG: This uses a separate model (an "NLI model") to check if the retrieved documents are actually relevant to the question before giving them to the LLM.
Now, let’s a close look at (d) Speculative RAG:
- Specialist RAG Drafter: Instead of overwhelming the big LLM, a smaller "drafter" model takes the lead. It looks at the question (Q) and the documents (1, 2...) and creates multiple draft answers (α1, α2, α3...). Each draft is based on a different subset of the documents.
- Rationales: The drafter also provides explanations (β1, β2, β3...) for why it chose those specific documents for each draft. Think of it like showing its work.
- Evaluation: The main LLM (the "Generalist LM") now steps in. It looks at each draft answer and its explanation. It then picks the best answer (A) based on this evaluation.
Essentially, speculative RAG is like having a team of experts: the drafter creates options, and the generalist LLM makes the final decision. This makes the process faster and potentially more accurate.
Advantages of Speculative RAG
Speculative RAG offers several key advantages over traditional RAG systems:
1. Greater accuracy
By using a specialized RAG Drafter to generate multiple drafts from diverse document subsets, Speculative RAG improves the accuracy of the final output. This approach allows the system to consider multiple perspectives, reducing the chances of generating incorrect or biased answers. In experiments, Speculative RAG demonstrated up to a 12.97% improvement in accuracy on benchmarks like PubHealth compared to conventional RAG systems.
2. Reduced latency
One of the most significant challenges with traditional RAG systems is the increased latency caused by processing long and complex documents. Speculative RAG addresses this issue by offloading the drafting process to a smaller, more efficient LM, which can generate drafts in parallel. This approach reduces the overall processing time, with latency improvements of up to 51% in some cases.
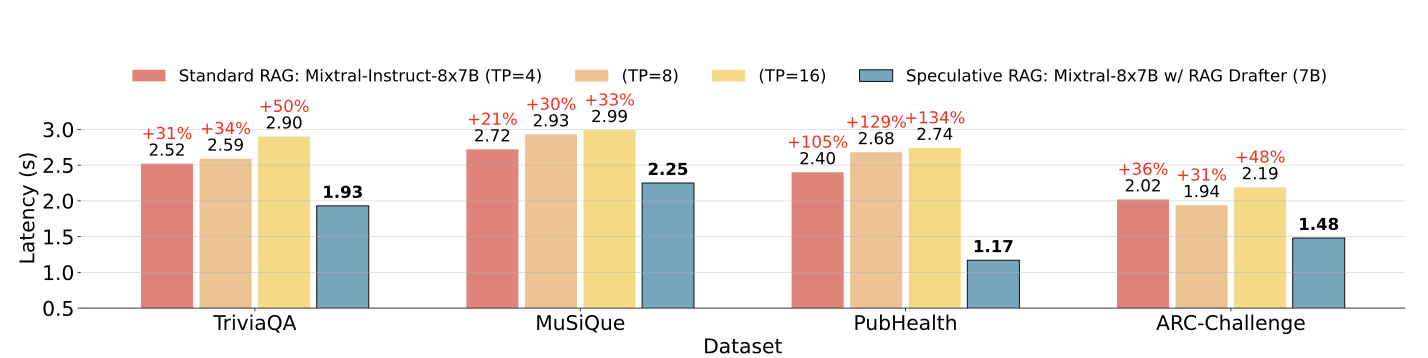
Speculative RAG latency vs Standard RAG latency on different datasets. Source: Wang et al., 2024
3. Resource efficiency
Speculative RAG optimizes resource usage by delegating the drafting task to a smaller LM, which is less computationally intensive than the larger generalist LM used in traditional RAG systems. This division of labor not only speeds up the generation process but also reduces the overall computational load, making it a more resource-efficient solution.
4. Scalability and flexibility
The Speculative RAG framework is highly adaptable and can be applied to various knowledge-intensive tasks without the need for extensive tuning. This scalability makes it an ideal solution for a wide range of applications, from question answering to complex document analysis.
How to Implement Speculative RAG
To implement a simplified version of Speculative RAG for a basic question-answering task, we'll use a small dataset and a simple setup with two models—a smaller model for drafting and a larger one for verification.
For simplicity, we’ll use the Hugging Face Transformers library. We'll demonstrate how to use a smaller language model to generate multiple drafts and a larger model to verify and select the best draft.
Step 1: Install the required libraries
First, let's install the necessary libraries. You’ll need to restart the session after installing the transformers library from HuggingFace. Make sure that you have added HuggingFace credentials under a secret key in Collab or any other editor.
!pip install transformers torch datasetsStep 2: Load the dataset
For this example, we'll use the SQuAD (Stanford Question Answering Dataset) available from the Hugging Face datasets library.
from datasets import load_dataset
# Load the SQuAD dataset
dataset = load_dataset("squad", split="train[:100]") # Using a small subsetStep 3: Initialize models
We'll use two pre-trained models from the Hugging Face library. A smaller model (distilbert-base-uncased-distilled-squad) will act as our RAG Drafter and a larger model (bert-large-uncased-whole-word-masking-finetuned-squad) will act as the RAG Verifier.
Then, we’ll build a Drafter and a verifier pipeline with the selected models.
from transformers import AutoModelForQuestionAnswering, AutoTokenizer, pipeline
# Initialize the smaller model (RAG Drafter)
drafter_model_name = "distilbert-base-uncased-distilled-squad"
drafter_model = AutoModelForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained(drafter_model_name)
drafter_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(drafter_model_name)
# Initialize the larger model (RAG Verifier)
verifier_model_name = "bert-large-uncased-whole-word-masking-finetuned-squad"
verifier_model = AutoModelForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained(verifier_model_name)
verifier_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(verifier_model_name)
# Set up pipelines
drafter_pipeline = pipeline("question-answering", model=drafter_model, tokenizer=drafter_tokenizer)
verifier_pipeline = pipeline("question-answering", model=verifier_model, tokenizer=verifier_tokenizer)Step 4: Define the drafting function
Next, we'll define a function to generate multiple drafts using the smaller model with the predefined Drafter pipeline.
def generate_drafts(question, context, num_drafts=3):
drafts = []
for _ in range(num_drafts):
draft = Drafter_pipeline(question=question, context=context)
drafts.append(draft)
return draftsStep 5: Define the verification function
We'll now define a verify_drafts() function that uses the larger model to verify and select the best draft based on confidence scores.
It works by mapping the start and end character positions of each draft to the corresponding token positions in the tokenized context using an offset mapping. The verifier model then scores each draft based on its confidence in these positions being the correct answer. The draft with the highest confidence score is selected as the best answer, ensuring that the final output is both accurate and reliable.
This function's careful handling of token alignment and scoring is key to the enhanced performance of Speculative RAG.
def verify_drafts(question, context, drafts):
best_draft = None
highest_score = 0
# Tokenize the context using the verifier's tokenizer, keeping track of offsets
inputs = verifier_tokenizer(question, context, return_tensors="pt", return_offsets_mapping=True)
offset_mapping = inputs['offset_mapping'][0] # This will give us the character-to-token mapping
input_ids = inputs['input_ids'][0]
for draft in drafts:
start_char = draft['start']
end_char = draft['end']
# Find the corresponding token positions using offset mapping
start_index = None
end_index = None
for idx, (start, end) in enumerate(offset_mapping):
if start_index is None and start_char >= start and start_char < end:
start_index = idx
if end_index is None and end_char > start and end_char <= end:
end_index = idx
if start_index is not None and end_index is not None:
break
# Ensure indices were found and are within bounds
if (start_index is None or end_index is None or
start_index >= len(input_ids) or end_index >= len(input_ids)):
print(f"Draft skipped: Out of bounds or no matching tokens. "
f"Start Index: {start_index}, End Index: {end_index}")
continue
# Get the confidence score using the larger model
outputs = verifier_model(input_ids=input_ids.unsqueeze(0))
score = (outputs.start_logits[0, start_index].item() +
outputs.end_logits[0, end_index].item())
if score > highest_score:
highest_score = score
best_draft = draft
if best_draft is None:
print("No valid draft found after verification.")
return best_draftStep 6: Run and evaluate the Speculative RAG process
Now, let's apply our Speculative RAG process to 10 sample questions from the dataset.
correct = 0
total = 10 # Evaluate on 10 samples for simplicity
for i in range(total):
sample = dataset[i]
question = sample['question']
context = sample['context']
drafts = generate_drafts(question, context)
best_answer = verify_drafts(question, context, drafts)
print(f"Q: {question}")
if best_answer is not None:
print(f"A: {best_answer['answer']}\n")
# For simplicity, compare with the first answer (gold) provided in the dataset
if best_answer['answer'].lower() in sample['answers']['text'][0].lower():
correct += 1
else:
print("No valid draft found.\n")
accuracy = correct / total * 100
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy}%")This code snippet evaluates the accuracy of a simplified speculative RAG implementation on 10 samples from a dataset. For each sample, it generates multiple answer drafts based on a given question and context and then selects the best draft using a verification function. If a valid answer is found, it compares this answer to the gold (correct) answer provided in the dataset. If the answer matches, the correct count is incremented.
Finally, the code calculates and prints the accuracy as a percentage of correct answers out of the total samples. This code yields an accuracy of 90% on this simplified dataset.
Challenges of Speculative RAG
While speculative RAG gives good results, it presents some challenges:
- Complexity in implementation:
- Requires coordination of multiple models.
- Adds complexity to integration into existing systems.
- Training overhead:
- Training the RAG Drafter introduces an extra step.
- Requires resources and time.
- Complicates deployment, especially in environments requiring rapid deployment.
- Dependency on high-quality retrieval:
- Effectiveness depends heavily on the quality of retrieved documents.
- Poor retrieval results lead to suboptimal drafts.
Applications of Speculative RAG
Speculative RAG can be applied across a wide range of domains where accurate and efficient information retrieval is critical. Here are some potential applications:
- Knowledge-intensive question answering:
- Speculative RAG is effective in tasks where accuracy and relevance are important.
- The framework can generate precise and well-supported answers to complex queries by leveraging diverse document subsets.
- Real-time information retrieval:
- Speculative RAG can enhance the speed and reliability of responses in scenarios where up-to-date information is crucial.
- The framework's ability to reduce latency while maintaining accuracy makes it ideal for real-time applications.
- Medical and legal text analysis:
- Speculative RAG can be used in fields where accurate interpretation of complex documents is essential.
- The framework ensures critical decisions are based on reliable information by generating multiple drafts and selecting the most accurate one based on a rationale.
- Educational tools:
- Speculative RAG can support the creation of accurate and context-rich content for e-learning platforms.
- This ensures that learners receive reliable and well-rounded information, enhancing the overall learning experience.
Conclusion
Speculative RAG enhances retrieval-augmented generation with improved accuracy, reduced latency, resource efficiency, and scalability. We demonstrated its implementation using Hugging Face Transformers.
While challenges exist, speculative RAG's potential in various domains makes it promising for further research.
If you want to learn more about RAG implementation, I recommend the following tutorials:
Develop AI Applications
Senior GenAI Engineer and Content Creator who has garnered 20 million views by sharing knowledge on GenAI and data science.

