Track
As AI systems become more integrated into critical applications, I've witnessed the challenges organizations face in ensuring models behave safely and reliably. A customer service chatbot leaking private information, a healthcare AI providing dangerous medical advice, or a financial assistant generating biased recommendations. These aren't hypothetical scenarios. There are real risks that damage trust, violate regulations, and harm users.
The fast adoption of large language models (LLMs) has intensified these concerns. While these powerful systems can generate human-like text and solve complex problems, they can also produce harmful content, leak sensitive information, or generate convincing but false information. Without proper safeguards, organizations expose themselves to significant legal, ethical, and reputational risks.
In this tutorial, I'll walk you through what AI guardrails are, why they matter, and how to implement them effectively. Whether you're building your first chatbot or deploying enterprise-scale applications, understanding guardrails is essential for creating systems users can trust.
If you are new to AI safety and development, I can recommend several of our courses, including AI Security and Risk Management, Understanding the EU AI Act, and Associate AI Engineer for Developers.
What Are AI Guardrails?
AI guardrails are safety mechanisms that monitor, validate, and control the behavior of AI systems throughout their lifecycle.
I like to think of them as the equivalent of safety features in a car: seat belts, airbags, and anti-lock brakes don't prevent you from driving, but they do protect you when things go wrong.
At their core, AI guardrails serve three primary purposes:
- Preventing harmful outputs before they reach users
- Ensuring compliance with ethical standards and regulations
- Maintaining consistent system behavior even in edge cases
Unlike simple content filters that just block certain words, guardrails operate at multiple levels, from validating input data to monitoring model outputs and enforcing business rules.
It's important to distinguish AI guardrails from related concepts.
Content moderation tools typically focus on post-generation filtering, while guardrails work proactively throughout the AI pipeline.
Similarly, prompt engineering guides model behavior through instructions, but guardrails provide enforceable constraints that the system cannot override.
With this understanding of what guardrails are, let's explore why they've become essential for modern AI deployment.
Why Are AI Guardrails Important?
Implementing AI without safeguards carries significant risks for both users and organizations.
For businesses
For businesses, regulatory fines for non-compliant systems, reputational harm from skewed outputs, and data breaches when models unintentionally release training data are all potential problems for many firms.
This importance is further enforced by regulatory frameworks, such as the EU AI Act and industry-specific requirements like HIPAA in healthcare or GDPR for data protection, as they create legal obligations.
Beyond compliance, there's an ethical imperative for organizations to deploy AI responsibly, ensuring systems don't perpetuate biases or generate harmful content.
For users
For end users, the risks are potentially even greater. An unprotected AI in the healthcare industry might literally put lives in peril by giving inaccurate medical information.
AI guardrails build trust. Users adopt AI systems when they know safeguards are in place to prevent errors and protect their interests. For organizations, this translates to user retention, brand reputation, and sustainable AI adoption. Without guardrails, one high-profile failure can undermine years of development effort.
The Basics of AI Guardrails in Action
AI guardrails work by constraining AI behavior through programmatic checks, validation rules, and monitoring systems that operate alongside AI models.
The evolution of guardrails mirrors AI's own development. Early rule-based systems relied on keyword filtering. As models grew sophisticated, so did guardrails. The emergence of large language models accelerated guardrail development, introducing new risks around hallucination and prompt injection.
Today's guardrails combine deterministic rules with machine learning, creating multilayered protection systems.
This has led to a rich taxonomy of guardrail types, each addressing specific aspects of AI safety. Let's examine these categories in detail.
Types of AI Guardrails
Understanding different types of guardrails helps you or your organization build comprehensive protection.
AI guardrails can be categorized based on where they operate in the system architecture and what specific risks they address. Some focus on protecting data privacy, others ensure appropriate model behavior, while others handle deployment and compliance concerns.
The following table outlines the major guardrail categories, each serving distinct but complementary purposes in creating safe AI systems:
|
Characteristic |
Focus |
Operation |
Example |
|
Data Guardrails |
Protect sensitive information |
Detect and redact PII |
Mask credit card numbers |
|
Model Guardrails |
Control model generation |
Toxicity filters block harmful content |
Factuality checks verify claims |
|
Application Guardrails |
Manage user interactions |
Manage conversation flow |
Prevent unauthorized comments |
|
Infrastructure Guardrails |
Ensure safe deployment |
Monitor system resources |
Implement access control |
|
Appropriateness Guardrails |
Maintain professional standards |
Filter inappropriate topics |
Adjust content based on age |
|
Hallucination Guardrails |
Ensure factual accuracy |
Cross-reference generated content |
Flag unverifiable claims |
|
Regulatory-Compliance Guardrails |
Support legal requirements |
Implement automated checks |
Document decision-making processes |
|
Alignment Guardrails |
Match user intent |
Enforce ethical guidelines |
Ensure consistency with company policies |
|
Validation Guardrails |
Verify output correctness |
Validate data quality |
Ensure output is in JSON format |
AI Guardrail Types Comparison
These guardrail types work together to create comprehensive protection for AI systems. Data, model, and application guardrails form the first line of defense, operating at different stages of the AI pipeline to catch issues before they reach users.
Infrastructure and appropriateness guardrails ensure the system operates safely and professionally at scale, while hallucination and validation guardrails focus on accuracy and reliability.
The final categories, regulatory compliance and alignment guardrails, address broader organizational needs. They ensure AI systems not only function correctly but also operate within legal boundaries and align with company values.
In practice, most production AI systems implement multiple guardrail types simultaneously, creating layered protection that addresses technical, ethical, and legal concerns.
Understanding these types is valuable, but to truly implement guardrails effectively, we need to examine the technical building blocks that make them possible.
Technical Architecture of AI Guardrails
The guardrail architecture typically consists of four key components working together to provide comprehensive protection.
The checker
The checker examines inputs or outputs against defined criteria: a toxicity classifier, data leak detector, or factuality verifier. Checkers can be deterministic rule-based systems or machine learning models trained to identify specific risks.
The corrector
When a checker identifies an issue, the corrector determines how to handle it. Correctors might mask sensitive data, rephrase problematic content, or reject the output and request regeneration. Simple correctors replace detected PII with placeholders, while advanced ones use language models to rewrite content while preserving meaning.
The rail
The rail defines the constraints and policies that checkers enforce. Rails are specified in structured formats such as YAML, JSON, or domain-specific languages, making them maintainable by non-technical stakeholders. A rail might specify that outputs must be under 500 words, cannot mention competitors, and must maintain a professional tone.
The guard
Finally, the guard orchestrates the process, determining when to apply which checkers, managing the correction workflow, and logging all actions for auditing.
Deterministic guardrails and probabilistic models
A critical distinction exists between deterministic guardrails and probabilistic models. Deterministic guardrails provide predictable behavior: a regular expression for email detection always produces the same result.
Probabilistic models offer nuanced detection but with uncertainty. Modern systems combine both approaches for optimal protection.
With these architectural components in place, let's see how they work together in practice when processing actual requests.
How Do AI Guardrails Work?
Understanding the guardrail workflow clarifies how these components operate in practice. When a user submits input to your AI application, the request first passes through input guardrails that validate the prompt for injection attacks, inappropriate content, or policy violations.
The model generates a response, but before reaching the user, output guardrails examine it. Multiple checkers run in parallel: one validates factual claims, another checks for sensitive data leakage, and a third ensures appropriate tone.
If any checker flags an issue, the corrector attempts remediation, perhaps masking PII (Personally Identifiable Information) or regenerating with stricter constraints.
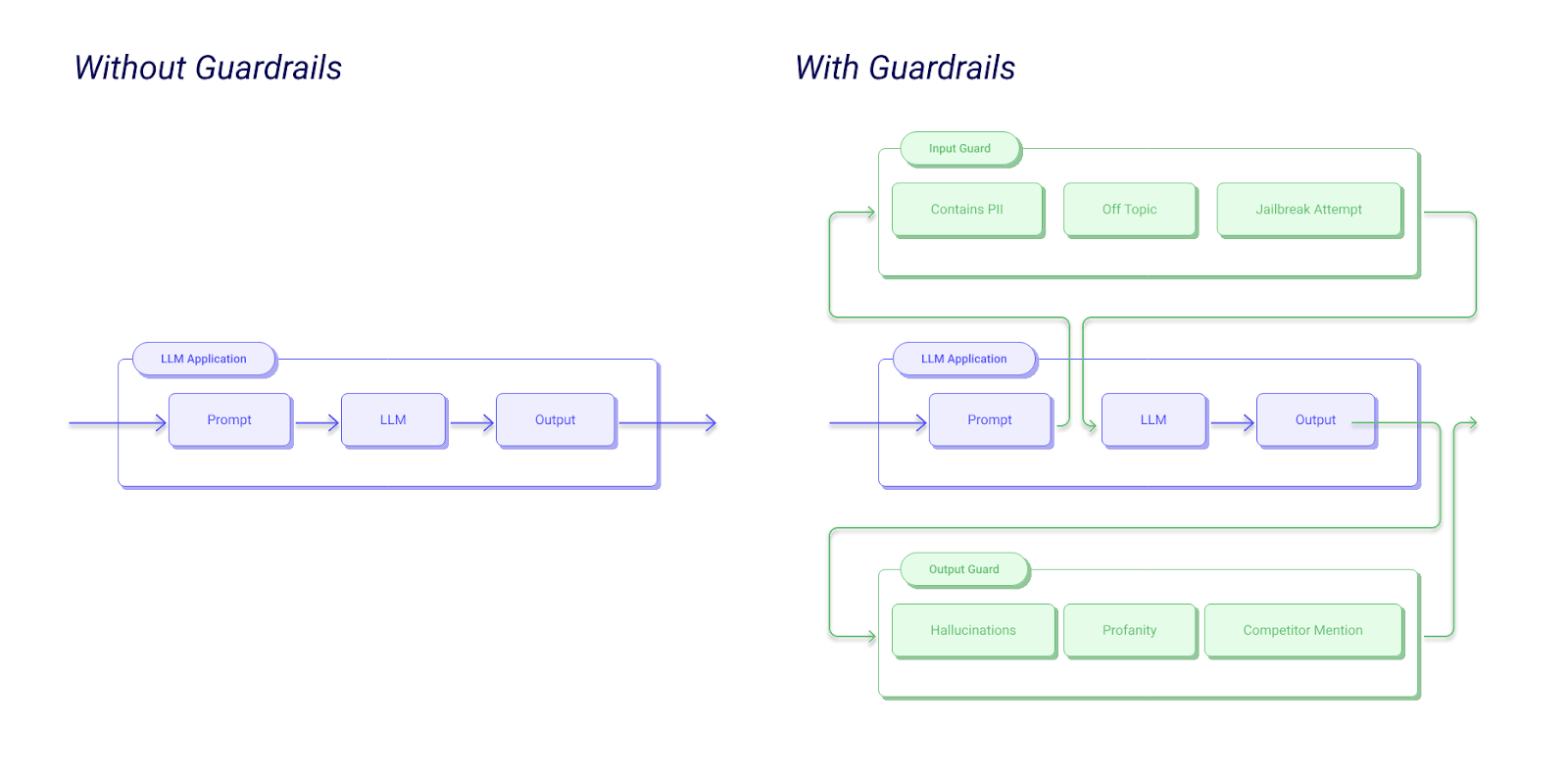
Guardrails AI Example Workflow
After correction, the response goes through final validation. If it passes, it's delivered to the user with metadata about applied guardrails. All steps are logged for monitoring and compliance. If validation fails after multiple attempts, the system returns a safe fallback response.
This multi-stage approach ensures comprehensive protection while maintaining acceptable latency. By parallelizing checks and optimizing models, modern guardrail systems add only 50-200 milliseconds to response times.
AI Guardrail Implementation Approaches
There are three primary approaches to implementing guardrails, each with distinct advantages and limitations:
- Rule-based systems use predefined patterns, regular expressions, and deterministic logic. They're highly interpretable. You know exactly why the content was flagged. They're also fast and cheap to run. However, they struggle with nuance and require constant maintenance as language evolves.
- Machine learning classifiers offer sophisticated detection by learning patterns from training data. A transformer-based toxicity classifier can understand context and catch subtle harmful content that rules miss. The downside is reduced interpretability and the possibility of false positives. ML classifiers also require more computational resources.
- Hybrid approaches combine the strengths of both methods. You might use rules for clear-cut cases like PII detection and ML models for nuanced judgments like appropriateness or factuality. This is what I typically recommend for production systems.
Beyond technical approaches, successful implementation requires assembling multidisciplinary teams including domain experts, ethicists, legal counsel, and engineers.
Benefits of AI Guardrails
By now, I’ve hopefully made it clear why AI guardrails are important, but let’s recap.
Privacy and security
Guardrails provide more than simply avoiding problems. They enhance user privacy and security by preventing data leaks before they occur, detecting when models might reproduce training data, and catching attempts to extract sensitive information through prompt injection.
For organizations handling personal health information or financial data, these protections are essential.
Compliance
Regulatory compliance becomes manageable with guardrails. Systems automatically enforce GDPR's right to explanation by logging decision rationales.
HIPAA-compliant applications use guardrails to ensure protected health information never appears in outputs. The EU AI Act's requirements for high-risk AI systems explicitly call for technical measures to mitigate identified risks.
Trust in AI
Most importantly, guardrails foster user trust. When users know systems have safeguards, they're more willing to engage authentically. Trust translates to higher adoption rates, more valuable feedback, and sustainable growth.
Leading AI Guardrail Platforms and Tools
Several platforms have emerged to simplify guardrail implementation. Understanding your options helps you choose the right tools for your specific requirements and technical environment.
Guardrails AI
Guardrails AI is an open-source framework that has gained quite a bit of notice in the developer community. I think this is largely because it provides an extensive library of pre-built validators covering common risks like PII detection, toxicity filtering, and hallucination prevention.
The framework uses a specification language called RAIL (Reliable AI Markup Language) that allows you to define custom guardrails in a declarative manner.
What makes Guardrails AI particularly attractive in my eyes is its flexibility and extensibility.
You can use one of the many validators from their Guardrails Hub, integrate them with popular LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Cohere, and deploy them anywhere your applications run.
The open-source nature means you can inspect the code, contribute improvements, and avoid vendor lock-in. The active community continuously adds new validators and shares implementation patterns for common use cases.
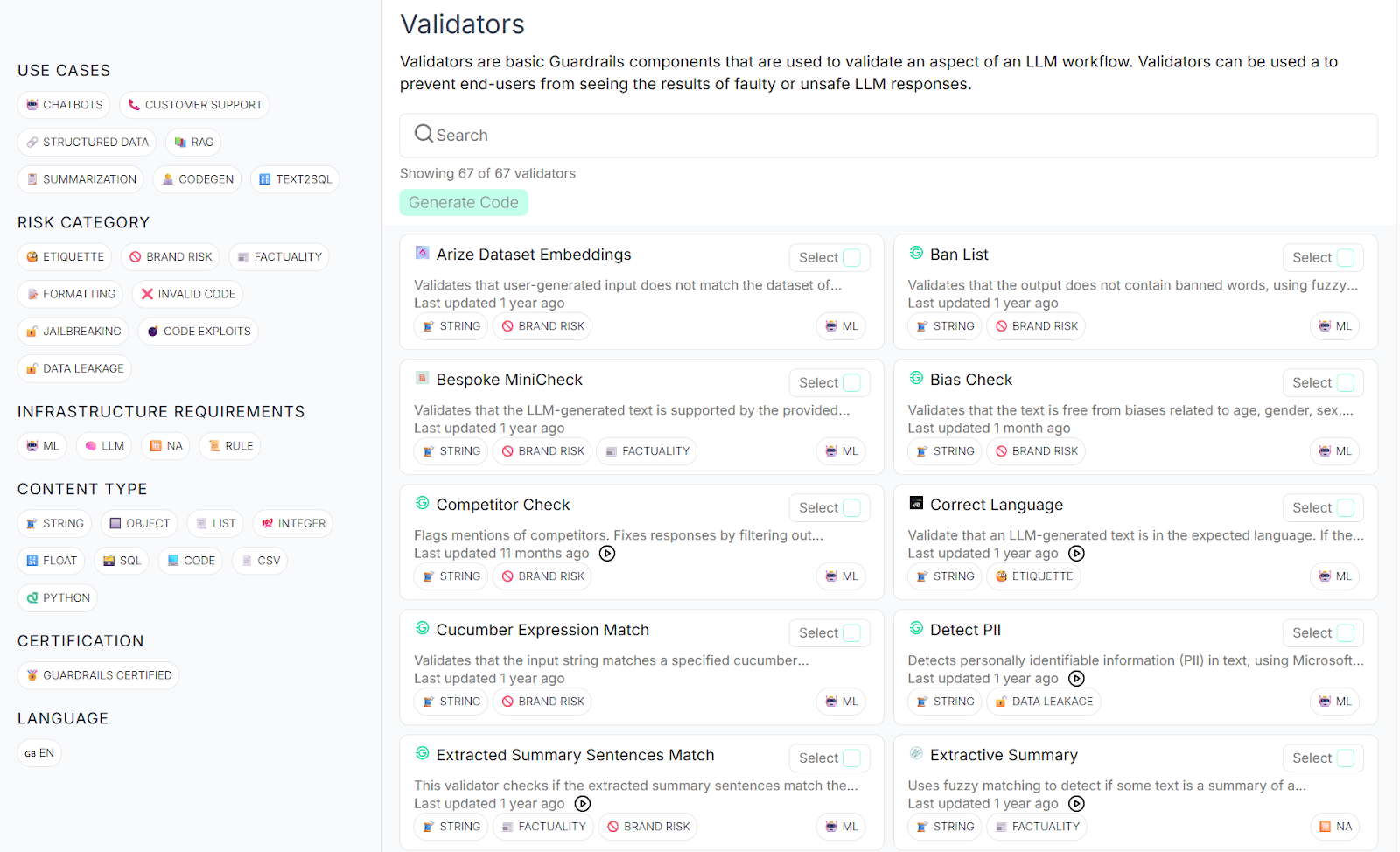
Guardrails AI Hub
Amazon Bedrock Guardrails
Amazon Bedrock Guardrails takes a managed, cloud-native approach that integrates seamlessly with AWS services. It offers pre-configured policies for content filtering, PII detection, denied topics, and word filters, among others.
The platform handles the infrastructure complexity, automatically scaling guardrails based on your traffic patterns.
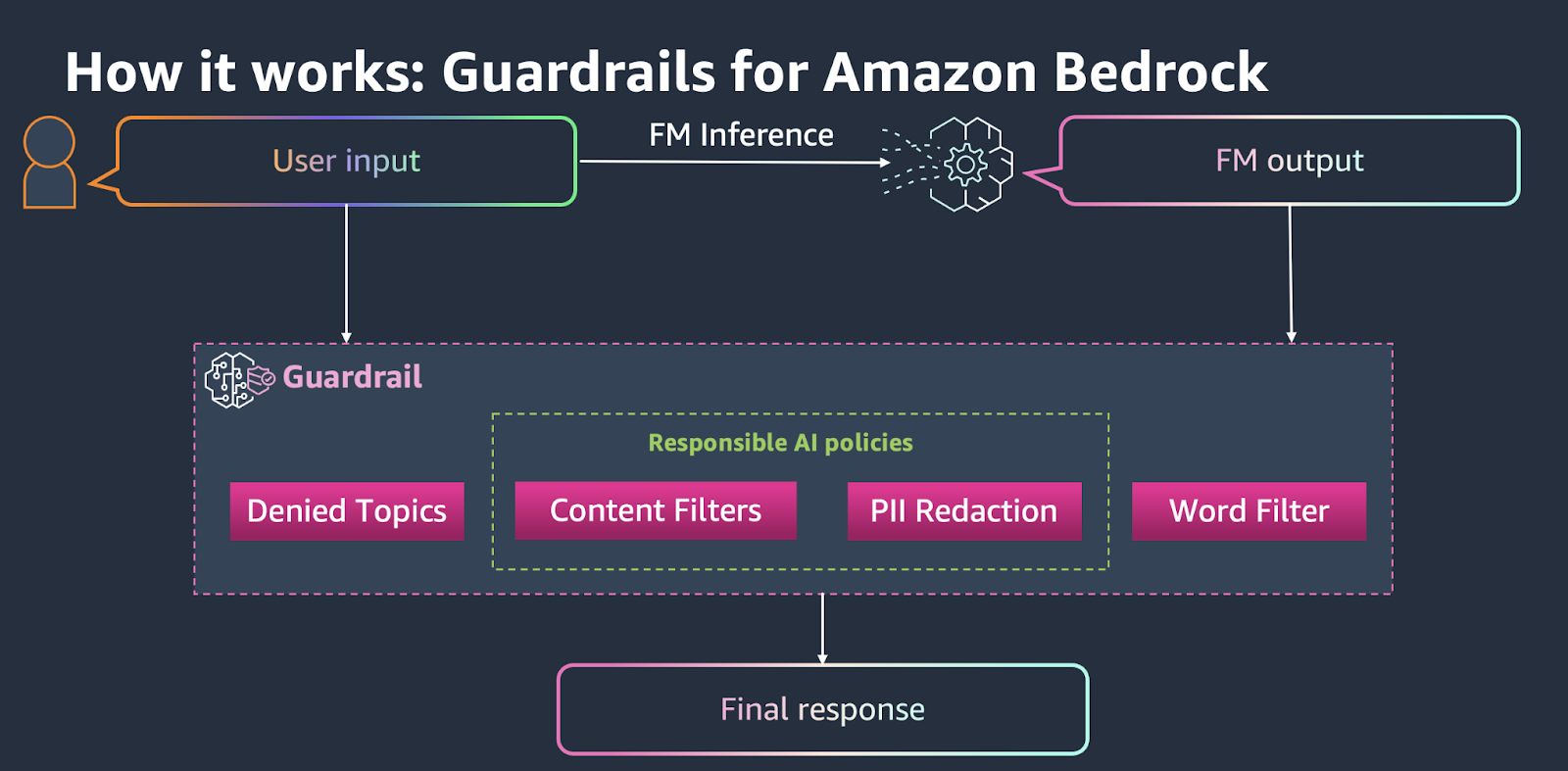
For teams already invested in the AWS ecosystem, you might find Bedrock Guardrails provide the lowest friction path to production. You can configure guardrails through the AWS console or API, apply them to any foundation model on Bedrock, and monitor their performance through CloudWatch.
The trade-off is reduced customization compared to open-source alternatives, but the ease of deployment and enterprise support make it compelling for organizations prioritizing time-to-market.
NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails
NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails takes a unique approach by focusing specifically on conversational AI through a dialogue-centric state machine model. Rather than just filtering inputs and outputs, NeMo manages entire conversation flows, ensuring multi-turn interactions follow defined paths and constraints.
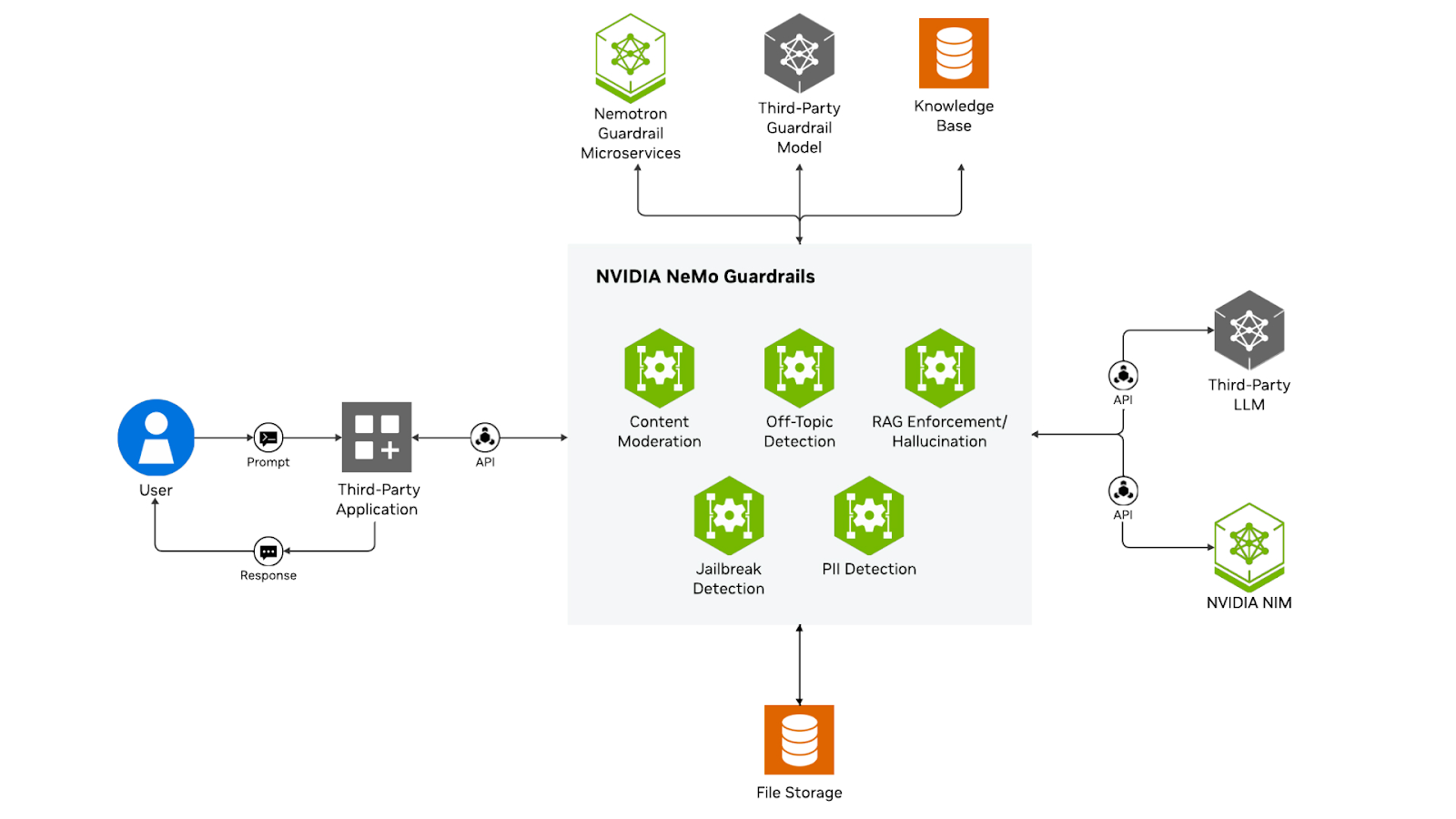
The platform uses Colang, a modeling language designed specifically for controlling dialogue behavior. This allows you to define conversation rails that guide interactions, handle context across turns, and enforce business logic throughout extended conversations.
NeMo's approach excels particularly for chatbots, virtual assistants, and customer service applications where maintaining coherent, policy-compliant conversations matters more than single-turn filtering.
Microsoft Azure AI Content Safety
Microsoft's Azure AI Content Safety provides enterprise-grade content moderation specifically tuned for text, images, and multi-modal content. The platform offers customizable severity thresholds across categories like hate speech, violence, sexual content, and self-harm. It includes specialized capabilities for detecting jailbreak attempts and protecting against prompt injection attacks.
Azure AI Content Safety integrates naturally with Azure OpenAI Service and other Azure AI offerings, making it a strong choice for organizations using Microsoft's cloud platform. The service provides detailed risk scores rather than binary decisions, allowing you to implement nuanced moderation policies based on your risk tolerance.
LlamaGuard
LlamaGuard, developed by Meta, represents a new generation of open-source safety models. It's a fine-tuned LLaMA model specifically trained to classify AI-generated content for safety risks. LlamaGuard provides safe/unsafe output for its safety assessments, together with the categories it violates.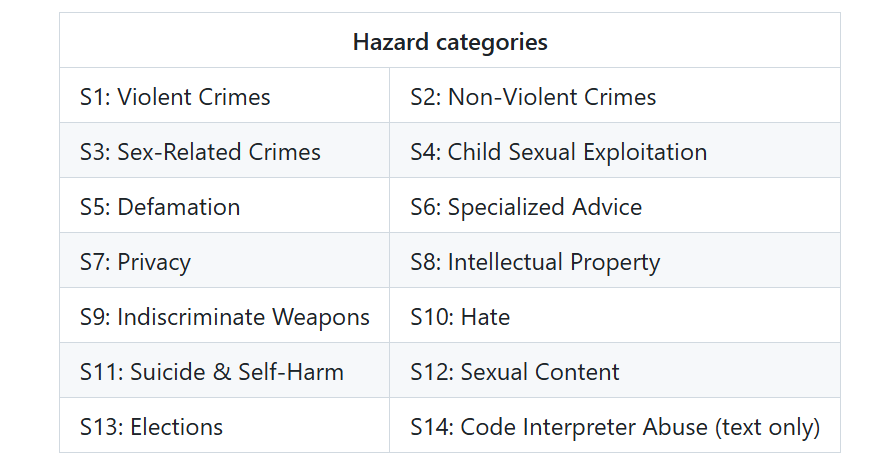
With these platforms available, let's explore how organizations across different industries are putting guardrails to work in real-world scenarios.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases of AI Guardrails
Seeing guardrails in action across industries illustrates their practical value.
Customer service
In customer service, guardrails ensure AI agents maintain a professional tone, never make unauthorized commitments, and escalate appropriately when facing complex issues. A telecommunications company implemented guardrails that detect angry customers and automatically route conversations to human agents.
Healthcare
Healthcare applications face particularly stringent requirements. Guardrails in medical AI systems prevent diagnosis claims from unlicensed systems, validate that recommended treatments align with evidence-based guidelines, and ensure patient data privacy. A clinical trial matching system uses guardrails to verify that patient information never leaks into explanations.
Research
In academic research, guardrails balance safety with academic freedom. Research assistants must avoid plagiarism, properly cite sources, and maintain a scholarly tone without being overly restrictive.
Cybersecurity
For cybersecurity and enterprise workflows, guardrails protect against prompt injection attacks, prevent execution of unsafe code, and maintain audit trails for compliance. A financial services firm uses guardrails to ensure AI assistants never expose proprietary trading strategies while still providing useful analysis.
Regulatory Compliance and Governance
Understanding the regulatory landscape helps you design guardrails that meet legal requirements. The EU AI Act categorizes AI systems by risk level and mandates technical safeguards for high-risk applications in employment, education, law enforcement, or critical infrastructure. The Act specifically requires risk mitigation measures, human oversight capabilities, and transparency mechanisms.
Data protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA create specific guardrail requirements. GDPR's data minimization principle demands guardrails that prevent unnecessary data collection and processing. HIPAA's security rule requires safeguards for electronic protected health information.
Emerging governance frameworks emphasize continuous monitoring and adaptation. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework encourages organizations to implement technical controls as part of a broader governance strategy.
Conclusion
As I've tried to demonstrate, AI guardrails represent an essential component of responsible AI deployment. They transform AI from unpredictable systems into reliable tools that organizations and users can trust. Throughout this tutorial, I've explored what guardrails are, why they matter, and how to implement them effectively.
The key takeaway is that guardrails aren't about limiting AI's capabilities. They're about channeling those capabilities safely and productively. As you build AI systems, I encourage you to make guardrails a first-class consideration from the beginning. Start with clear policies, implement modular protections, and continuously refine based on real-world feedback.
The field continues evolving, with new tools, techniques, and best practices emerging regularly. Stay engaged with the community, experiment with different approaches, and share your learnings. Together, we can build AI systems that are not only powerful but also safe, reliable, and trustworthy.
To keep learning, I can recommend the following resources:
AI Guardrails FAQs
What are AI guardrails?
AI guardrails are safety mechanisms that monitor, validate, and control AI system behavior throughout their lifecycle, preventing harmful outputs and ensuring compliance with ethical standards.
What types of AI guardrails exist?
The main types include data guardrails (protecting sensitive information), model guardrails (controlling generation), application guardrails (managing interactions), infrastructure guardrails (ensuring safe deployment), and regulatory-compliance guardrails (supporting legal requirements).
Which platforms offer AI guardrail solutions?
Leading platforms include Guardrails AI (open-source), Amazon Bedrock Guardrails (cloud-native), NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails (dialogue-focused), Microsoft Azure AI Content Safety, and LlamaGuard.
How do guardrails impact AI system performance?
Guardrails add 50-200 milliseconds of latency and increase computational costs, but intelligent caching, asynchronous validation, and tiered checking minimize performance impact while maintaining protection.
Are AI guardrails required by law?
Yes, in many cases. The EU AI Act mandates guardrails for high-risk AI systems, while regulations like GDPR and HIPAA require specific safeguards for data protection and privacy compliance.
As the Founder of Martin Data Solutions and a Freelance Data Scientist, ML and AI Engineer, I bring a diverse portfolio in Regression, Classification, NLP, LLM, RAG, Neural Networks, Ensemble Methods, and Computer Vision.
- Successfully developed several end-to-end ML projects, including data cleaning, analytics, modeling, and deployment on AWS and GCP, delivering impactful and scalable solutions.
- Built interactive and scalable web applications using Streamlit and Gradio for diverse industry use cases.
- Taught and mentored students in data science and analytics, fostering their professional growth through personalized learning approaches.
- Designed course content for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) applications tailored to enterprise requirements.
- Authored high-impact AI & ML technical blogs, covering topics like MLOps, vector databases, and LLMs, achieving significant engagement.
In each project I take on, I make sure to apply up-to-date practices in software engineering and DevOps, like CI/CD, code linting, formatting, model monitoring, experiment tracking, and robust error handling. I’m committed to delivering complete solutions, turning data insights into practical strategies that help businesses grow and make the most out of data science, machine learning, and AI.


