Track
dbt Cloud has emerged as the leading managed service for data transformation, powering modern analytics teams with scalable, reliable, and collaborative workflows.
It extends the power of dbt Core, offering a hosted environment that automates deployments, orchestrates jobs, manages credentials, and provides collaboration features for data teams.
This enables organizations to manage SQL-based transformations in a secure, automated, and team-friendly environment.
In this introductory tutorial, we’ll go through what dbt Cloud is, how to set it up, and examples of how it can be used.
If you are new to the framework and prefer a structured learning path, I recommend starting with our Introduction to dbt course.
What Is dbt Cloud and How Does It Work?
Let’s first start with an overview of what dbt Cloud is and some of its features.
Overview of dbt Cloud
At its core, dbt Cloud empowers teams to follow the ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) approach. Unlike traditional ETL processes, where transformations happen before loading data into the warehouse, dbt performs transformations inside the warehouse using its compute power and scalability.
Source: dbt
dbt Cloud simplifies the data transformation process, as it:
- Provides a managed service for SQL transformations using dbt.
- Fits into modern pipelines by shifting transformations into the warehouse.
- Standardizes analytics engineering through shared workflows and practices.
Core concepts and workflow
dbt Cloud consists of the same concepts as dbt Core.
These include:
- Models: SQL files that define transformations.
- Sources: Definitions of raw data tables.
- Tests: Assertions on data quality.
- Documentation: Auto-generated lineage and model docs.
- Exposures: Define downstream BI or reporting dependencies.
A typical dbt Cloud workflow looks like this: Develop models > Test transformations > Commit to Git > Deploy via dbt Cloud jobs > Monitor runs on dbt Cloud.
Setting Up Your dbt Cloud Environment
To explain how dbt Cloud works, let’s look at a practical example of how to set up an environment yourself.
Getting started with dbt Cloud is simple, as it is designed for fast onboarding. Here are the steps you need to take:
Account creation and setup
- Sign up for dbt Cloud to access a 14-day free trial of the starter plan.
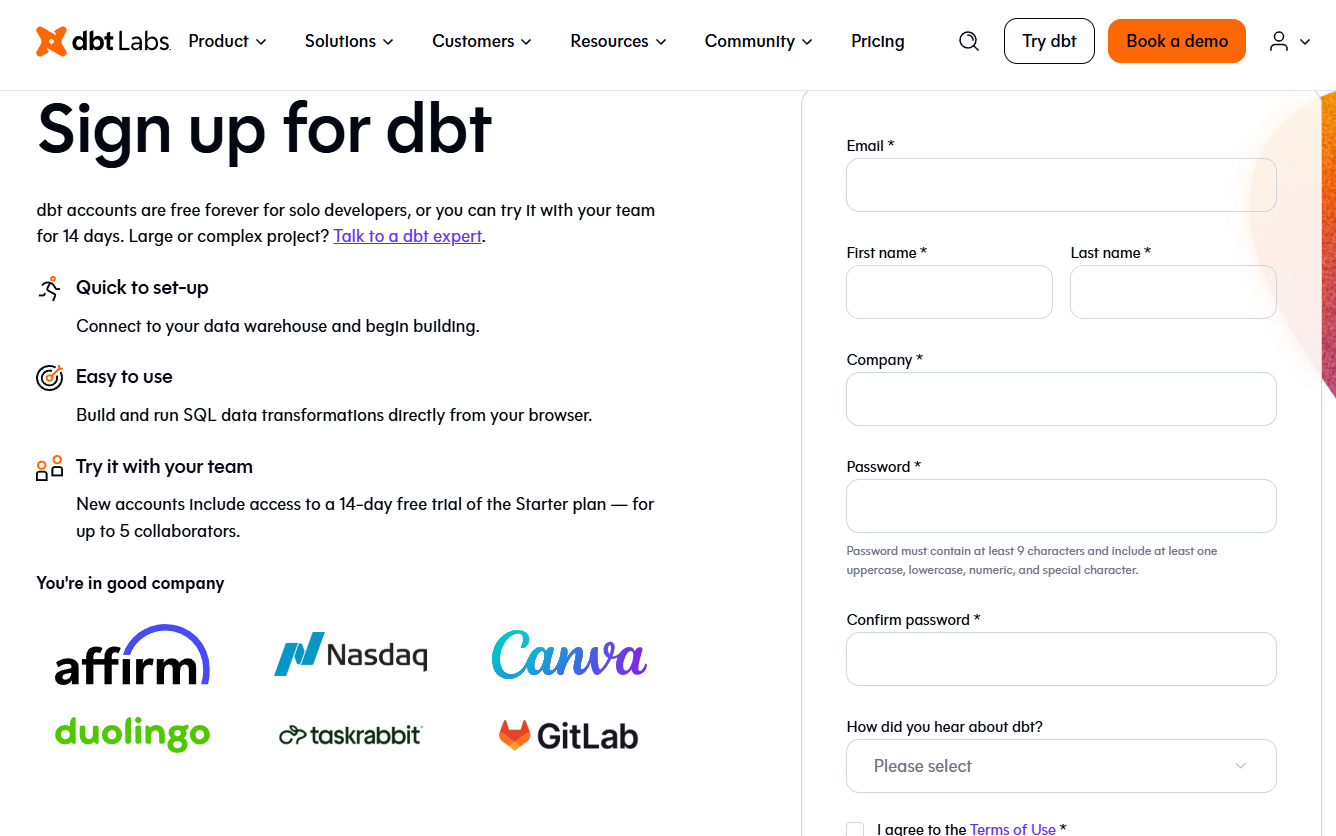
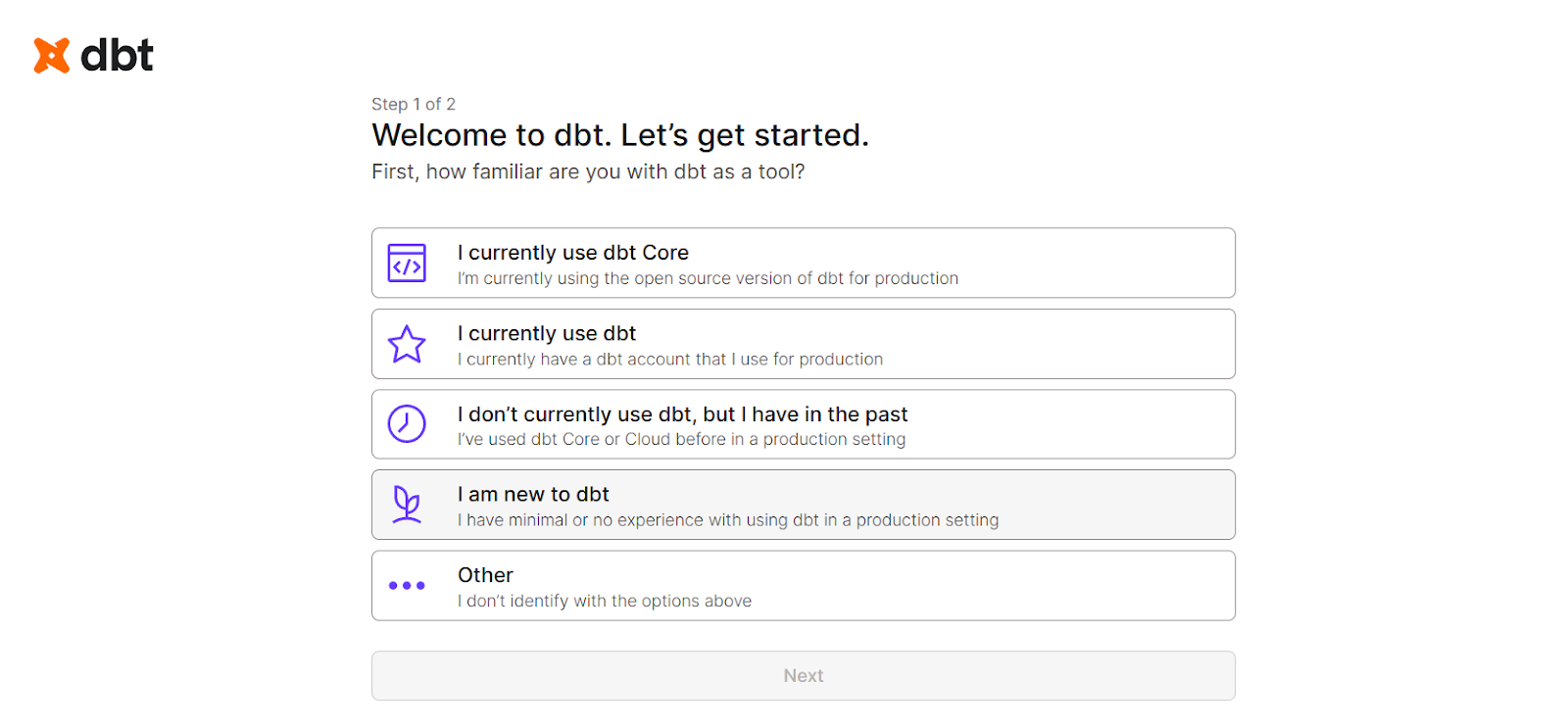
- Select the starting options according to your experience with dbt.
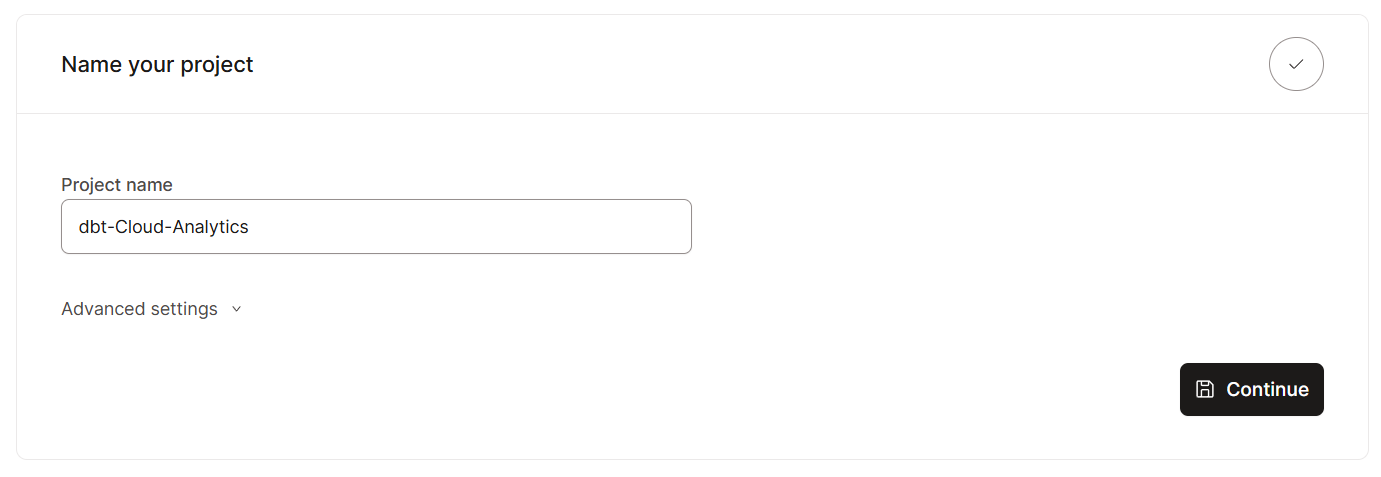
- Name your project, for example, dbt-Cloud-Analytics.
- Add a new connection.
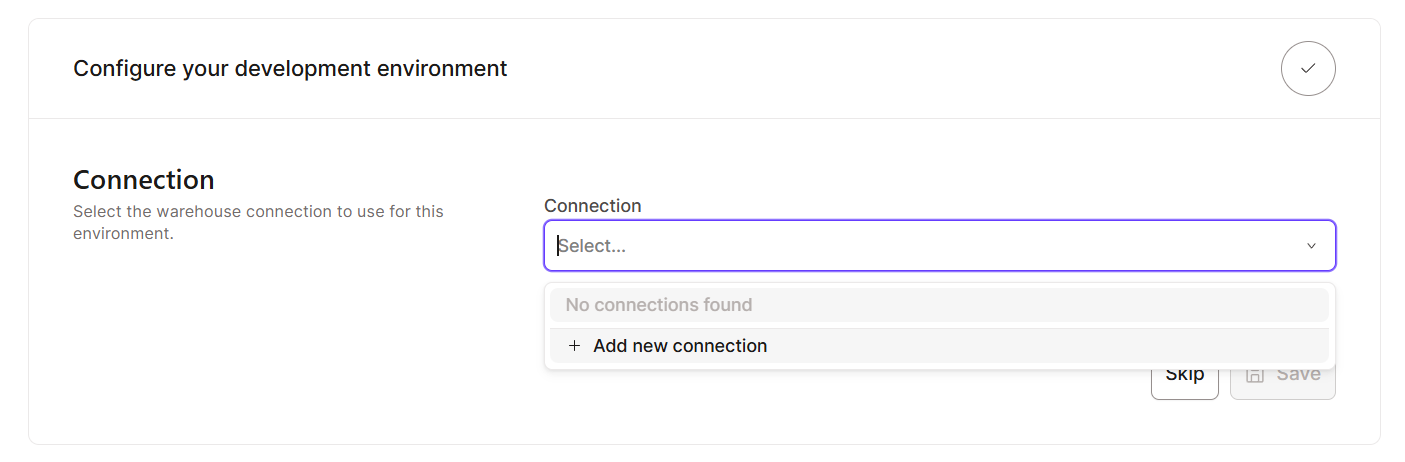
- Connect to a data warehouse (such as Snowflake, BigQuery, PostgreSQL, Redshift, or Databricks) of your choice. I will be using a local PostgreSQL database.
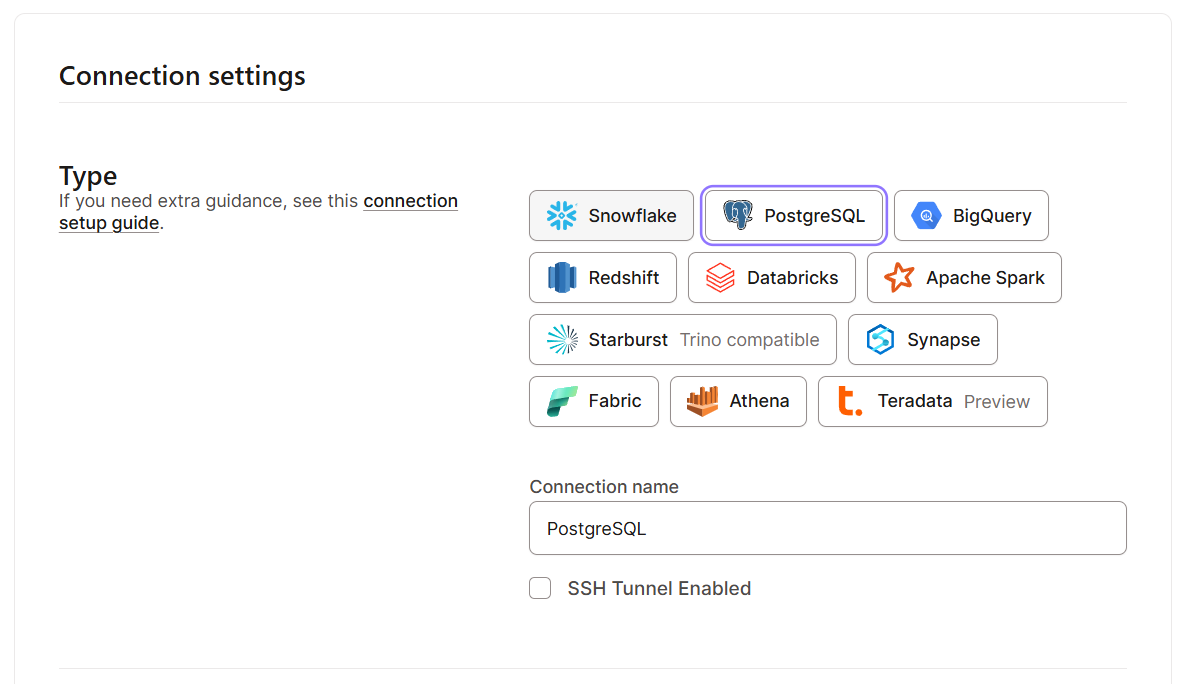
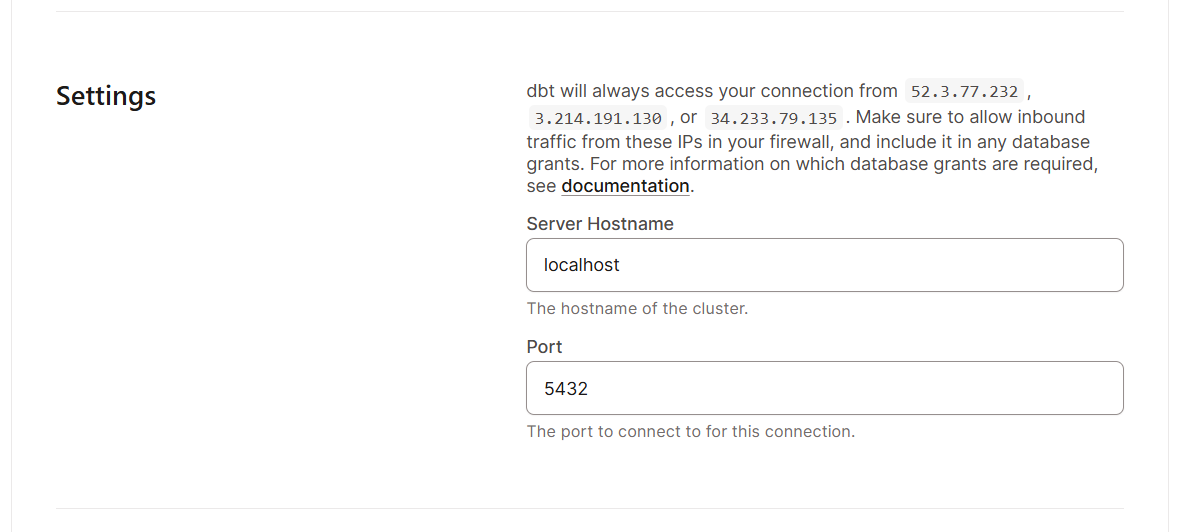
- Configure connection settings.
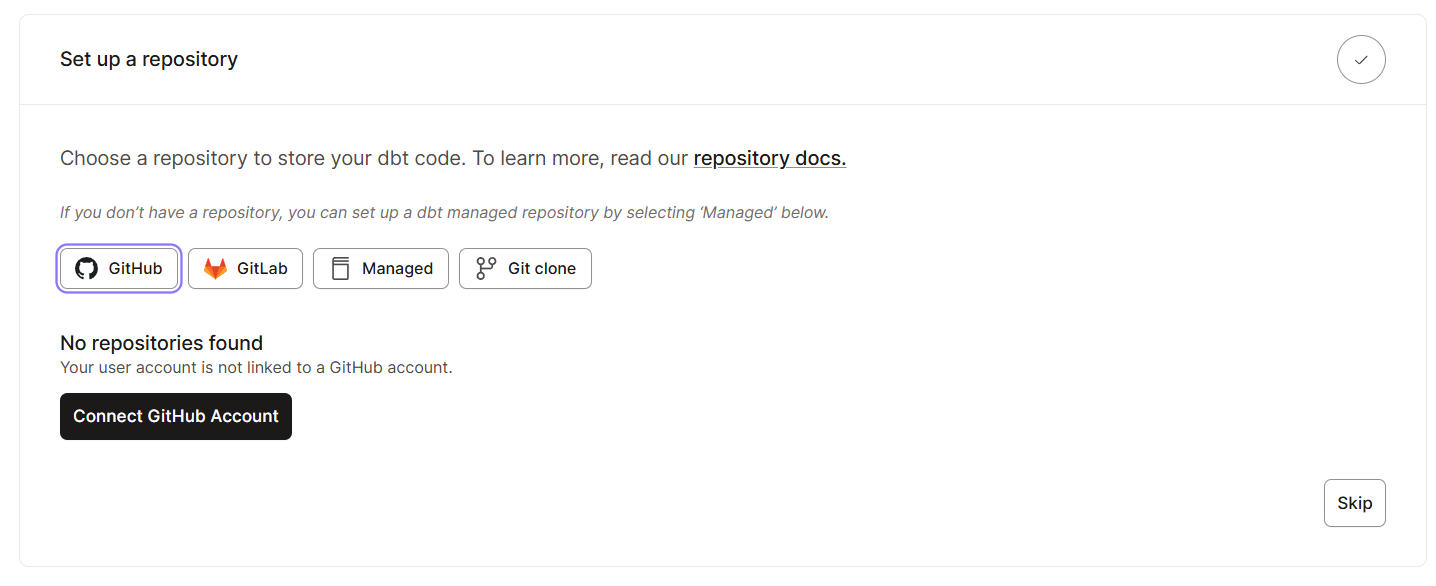
- Set up a Git repository.
Understanding the user interface
Once you have all the basic setups in place, let’s explore the interface. Here’s what you should expect to see in the dbt Cloud interface:
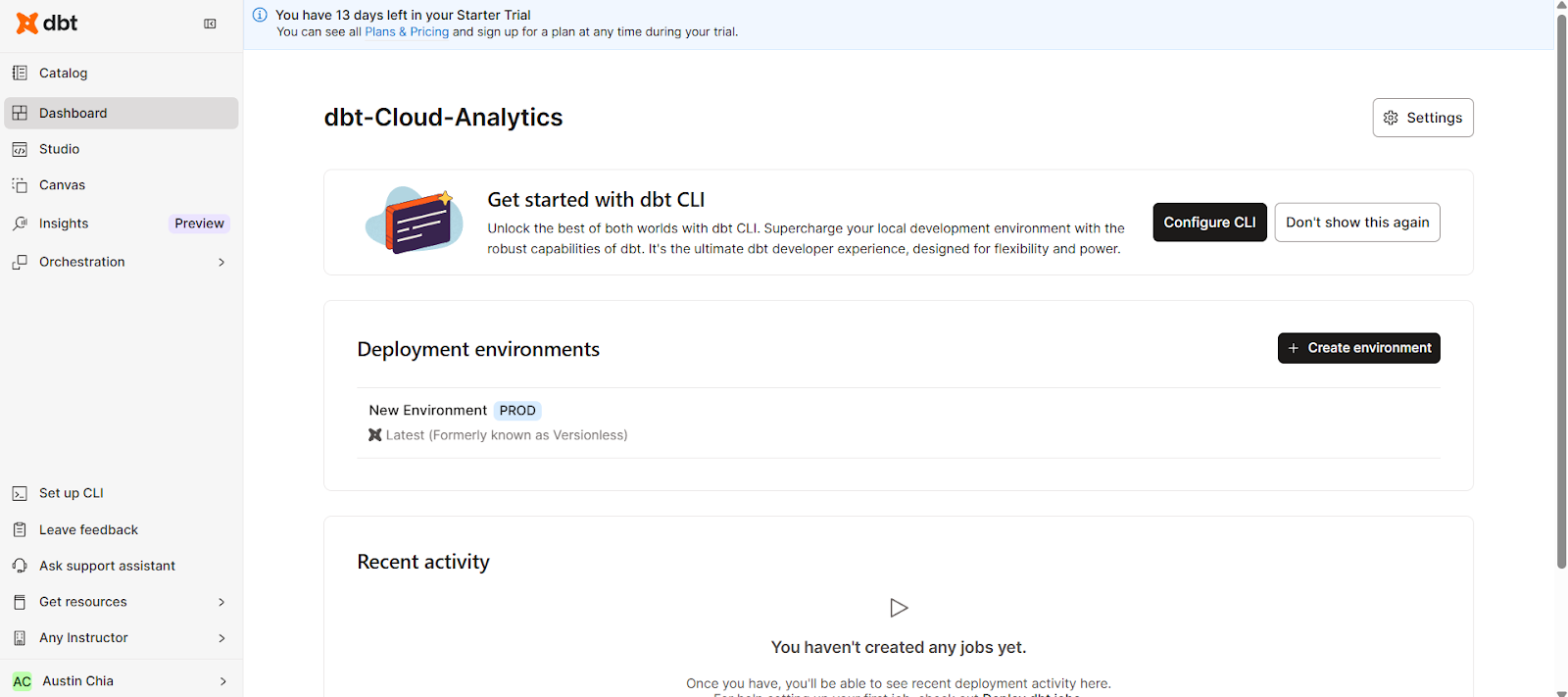
The dbt Cloud UI organizes your workflow efficiently. By using the navigation bar, you can access the following key areas:
- Catalog: Displays projects and models.
- Studio: Serves as the working interface to write code files.
- Dashboard: Provides a central overview of jobs and activity.
- Canvas: Enables drag-and-drop creation of models (Enterprise-tier feature).
- Insights: Offers additional information on deployed environments.
- Orchestration: Configures and schedules dbt runs.
This consolidates all necessary information, coding studio, and configuration settings in one web interface.
Developing in the dbt Cloud IDE
dbt Cloud also provides a browser-based IDE purpose-built for analytics engineering with GitHub integration. It was made to build, run, test, and version control dbt projects from your browser.
Navigating the Cloud IDE
The dbt Cloud IDE requires no local setup, easing onboarding for analysts. To access it, you can click on the Studio tab on the left side of the interface.
This should bring up a simple interface for writing, compiling, and running code.
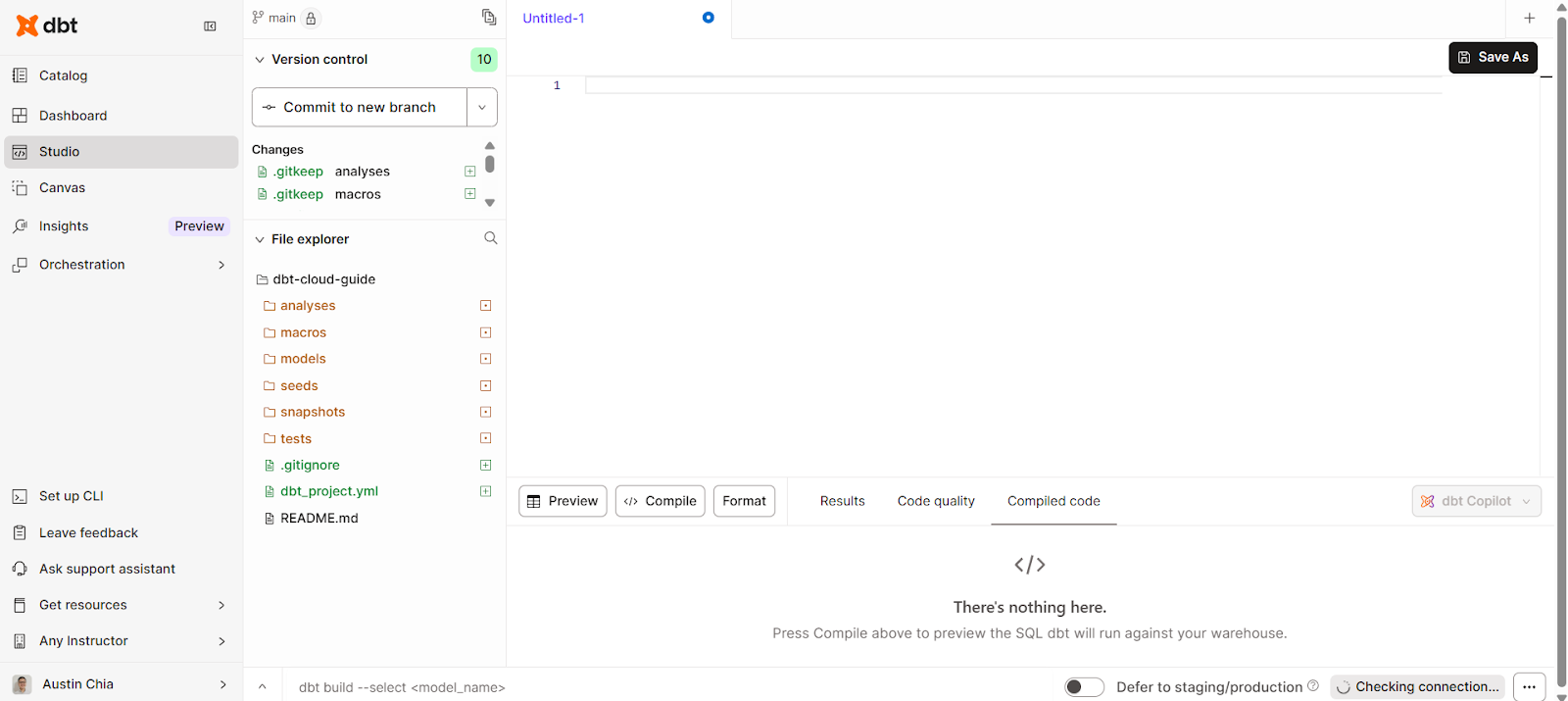
The dbt Cloud IDE allows you to perform these tasks:
- Real-time query execution with results preview.
- SQL autocomplete and Jinja templating.
- Error highlighting and debugging tools.
Version control integration
Additionally, dbt Cloud also allows you to integrate with GitHub for version control integration.
This feature allows you to:
- Connect dbt Cloud to GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket.
- Manage branches directly from the IDE.
- Commit and sync code changes with your central repo.
- Streamline collaborative workflows with pull requests and reviews.
Building and Testing Data Models in dbt Cloud
Just like in dbt Core, you’ll also be able to build and test data models from within dbt Cloud. Let’s look at some ways that can be done.
Writing SQL transformations
When working with data models, you’re likely going to need to do some transformations. In the dbt Cloud IDE, we can write SQL statements within the Studio.
You can create a data model to transform like this:
with source as (
select * from {{ source('raw', 'orders') }}
)
select
id as order_id,
user_id,
order_date,
status
from sourceThis is how the interface looks:
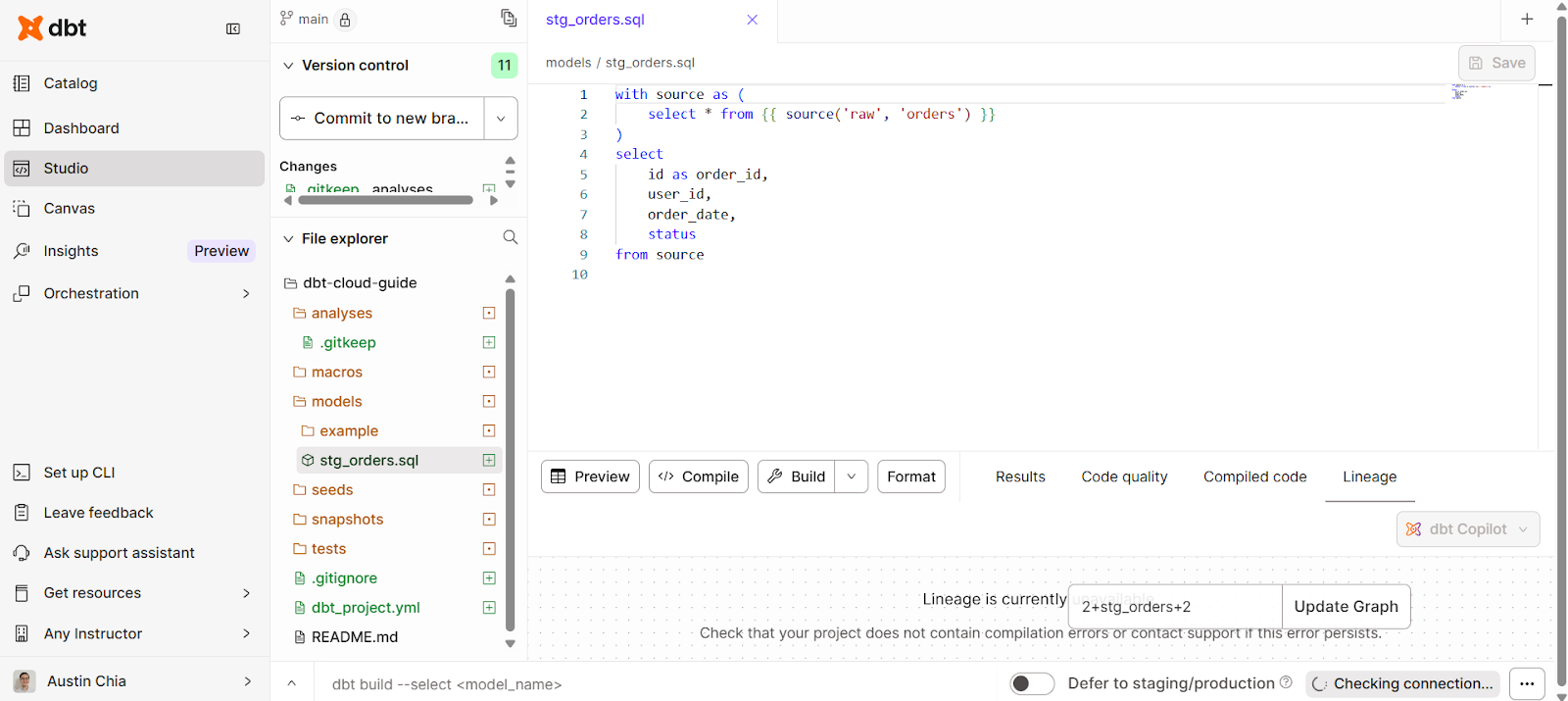
Some best practices you should take note of:
- Organize models by layers (staging, intermediate, marts).
- Use consistent naming conventions.
- Reuse logic via macros.
Automated testing and validation
In addition, you can also define tests in YAML for automated checks:
models:
- name: stg_orders
columns:
- name: order_id
tests:
- not_null
- unique
- name: status
tests:
- accepted_values:
values: ['completed', 'pending', 'cancelled']Testing your data enforces trust in transformations. This ensures that any jobs you run will have tests built into them to maintain integrity.
If you’re an advanced user, you can also define custom tests using Jinja and SQL.
Scheduling and Orchestration in dbt Cloud
In dbt Cloud, job scheduling and orchestration help support analytics automation. They ensure that your transformations run consistently, on time, and in the right environment with minimal manual intervention.
This section covers how to schedule jobs, trigger them automatically, and monitor their performance in real time.
Job scheduling
Within the dbt Cloud interface, you can:
- Create jobs for dev, staging, or production environments.
- Configure cron schedules or event-driven triggers.
- Chain tasks (run, test, snapshot).
To create a job schedule in dbt Cloud:
- Navigate to the Orchestration tab, then Jobs in your project.
- Click Create Job > Deploy Job and give it a descriptive name (e.g., “Daily Production Run” or “Staging Incremental Refresh”).
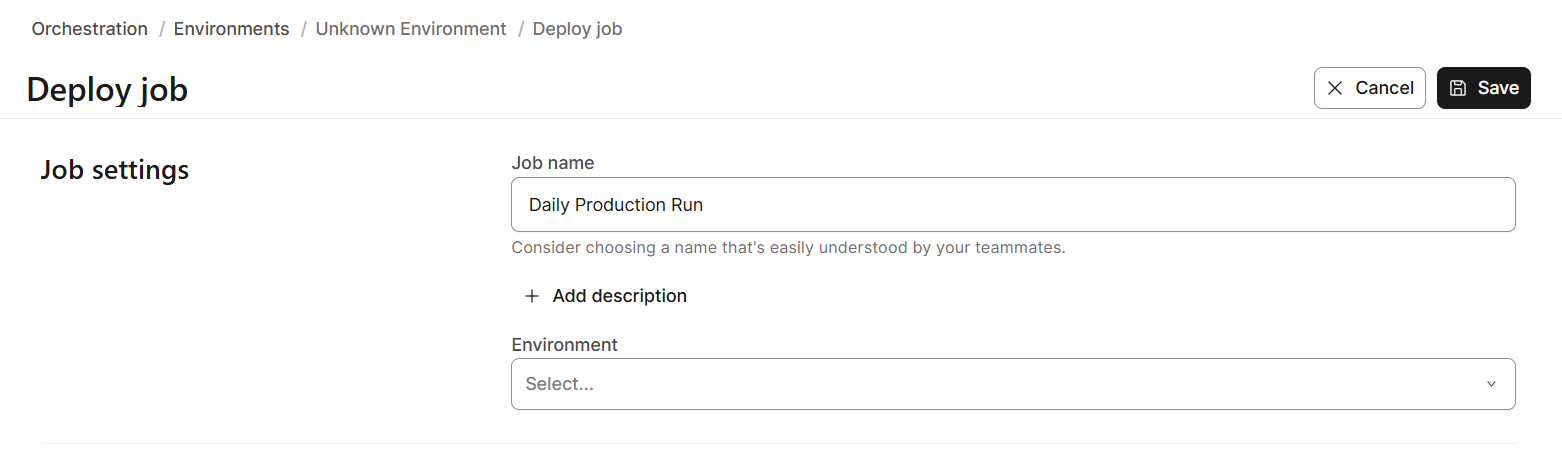
- Choose the environment where the job should run — typically development, staging, or production.
- Add one or more commands, such as dbt run --models stg_orders.
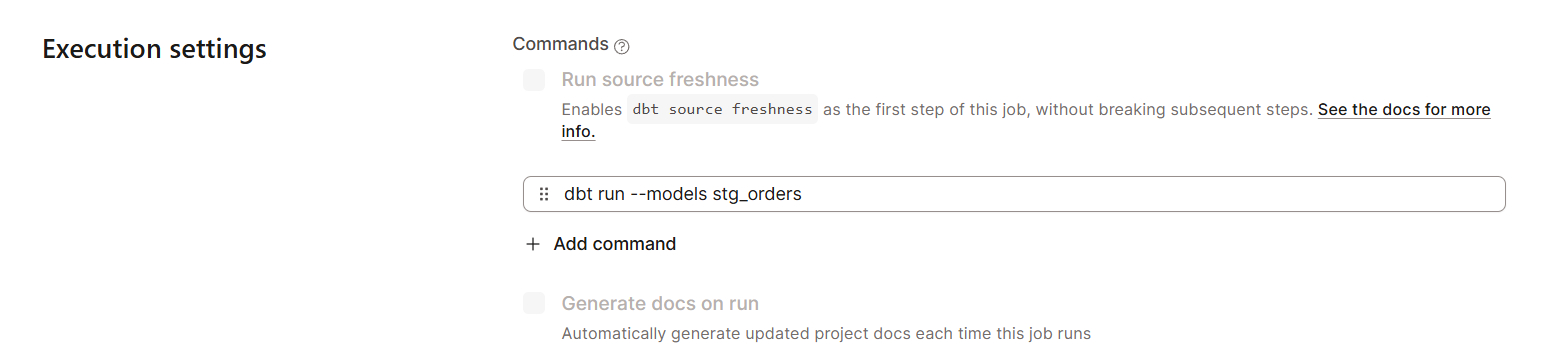
- Under Schedule, select cron syntax or use the visual time selector to define when the job should execute (e.g., every night at 2 AM, every Monday morning).
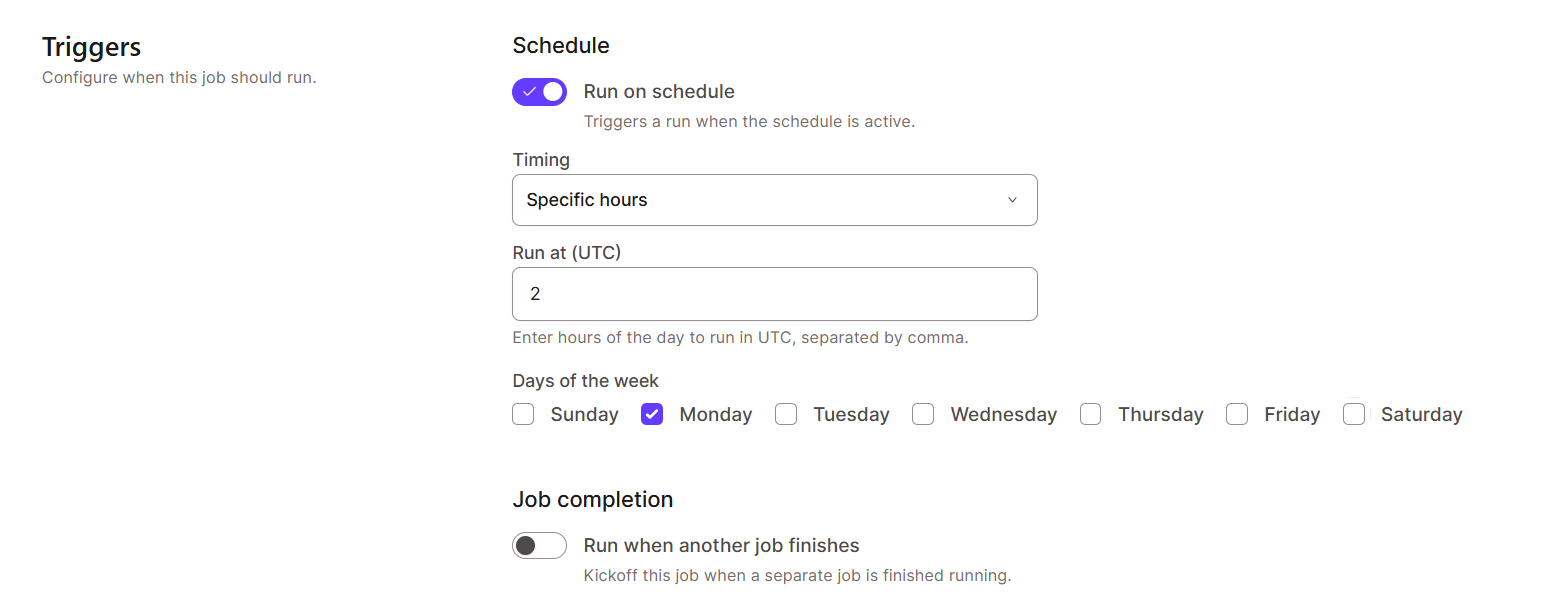
- Save the job and enable email or Slack notifications for run status updates.
Real-time monitoring and logging
dbt Cloud supports monitoring and logging features for better data observability. This is essential for troubleshooting failures and optimizing performance.
It enables you to:
- View run logs directly in the UI.
- Export logs for external monitoring.
- Send notifications to Slack, email, or PagerDuty.
Advanced Features of dbt Cloud
Beyond its core modeling and orchestration capabilities, dbt Cloud offers advanced features that bring intelligence, consistency, and automation to modern analytics workflows.
They can be found in two main features: the dbt Semantic Layer and AI-powered tools like dbt Copilot and Fusion.
Using the dbt Semantic Layer
The dbt Semantic Layer provides a central, governed layer where teams can define, manage, and serve business metrics in a consistent and version-controlled way.
It helps:
- Define and manage business metrics centrally.
- Ensure consistency across BI and analytics tools.
- Prevent metric drift by enforcing a single source of truth.
This unified layer bridges the gap between data transformation and visualization through its connections with common BI tools.
For a hands-on example, check out this tutorial on implementing a semantic layer with dbt.
Integrating AI with dbt Copilot and Fusion
One of dbt’s latest features, dbt Copilot, is an AI assistant built directly into dbt Cloud’s IDE. It helps developers write, debug, and optimize dbt code using natural language prompts and context-aware suggestions.
With dbt Copilot, you can:
- Generate SQL models or Jinja macros from plain-language descriptions.
- Receive autocomplete suggestions for dbt commands, tests, and configurations.
- Automatically document models with generated descriptions and metadata.
- Identify and fix common syntax or dependency issues before running jobs.
The Fusion engine is a new engine written in Rust to replace dbt Core, with many more features.
It brings some use cases, such as:
- Catching incorrect SQL code in your dbt models
- Allows inline CTEs to be previewed for faster debugging
- Model tracing across your dbt project
Security and Compliance in dbt Cloud
In data transformation workflows, security and governance are non-negotiable. That’s why dbt Cloud is also built with enterprise-grade security controls to protect sensitive information, maintain compliance, and ensure accountability across teams.
Role-based access control
dbt Cloud uses role-based access control (RBAC) to manage user permissions and restrict access to critical assets like projects, environments, and credentials.
Possible roles include:
- Developer
- Reviewer
- Admin
To configure access control in dbt Cloud:
- Navigate to the Account Settings section, then Users.
- Assign users to pre-defined roles or create custom roles for more granular control.
- Define whether users can manage environments and job schedules, modify warehouse credentials or API tokens, and/or approve code deployments or merge requests.
- Use project-level permissions to separate access across multiple teams or departments.
Audit logging and compliance
dbt Cloud includes comprehensive audit logging and compliance features designed to help organizations meet stringent data governance requirements, which comply with standards such as SOC 2, GDPR, and others.
Audit logs also enable the investigation of issues, and SCIM support improves identity management integration.
Integration and Connectivity of dbt Cloud
One of dbt Cloud’s greatest strengths lies in its ability to connect seamlessly with the broader data ecosystem. It integrates effortlessly with leading data warehouses, APIs, orchestration tools, and monitoring platforms.
This makes it a good choice for building a unified and automated analytics workflow, from ingestion to visualization. Let’s explore these aspects below:
Data platform connectivity
dbt Cloud supports all major cloud data warehouses and lakehouses, allowing teams to run transformations natively within the environments where their data already resides.
This eliminates the need for data movement or duplication, using each platform’s performance and scalability instead.
dbt Cloud integration options include:
You can also have multiple authentication options per platform, such as key pair authentication, OAuth, or username/password.
API and webhook integration
For organizations that require extensibility and automation, dbt Cloud also provides a powerful REST API and webhook framework.
The dbt Cloud API enables developers to:
- Programmatically trigger and monitor job runs.
- Retrieve run artifacts such as logs, manifest files, or compiled SQL.
- Automate deployment workflows by integrating dbt Cloud into CI/CD pipelines (e.g., GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Azure DevOps).
- Manage users, environments, and projects at scale.
dbt Cloud webhooks provide event-based integration, allowing external systems to respond to key dbt events such as job completion, run failures, or deployment updates.
The webhooks can be used for:
- Sending real-time alerts to Slack or Microsoft Teams when jobs fail.
- Triggering incident management workflows.
- Forwarding run metrics and performance data to monitoring systems.
- Updating dashboards or metadata catalogs automatically when new models are built.
Performance Optimization in dbt Cloud
As data pipelines grow in scale and complexity, observability becomes essential for maintaining reliability, performance, and trust.
But what does dbt Cloud have to offer? It comes down to two aspects: monitoring pipelines and model optimization.
Monitoring data transformation pipelines
Every job run is logged, tracked, and visualized within the platform, allowing you to understand the end-to-end state of your transformations.
For example, within the Run History dashboard, dbt Cloud displays detailed information like:
- Run duration: Total time taken for the job, broken down by model and step.
- Status tracking: Real-time indicators showing whether a run is queued, running, completed, or failed.
- Execution logs: Detailed logs showing SQL queries, timestamps, and row counts.
dbt Cloud is also easily integrated with data monitoring tools like Datadog.
Optimizing model performance
Large monolithic transformations are difficult to maintain and optimize. dbt promotes modular development, where complex logic is broken into smaller, reusable models and each performing a focused task.
To optimize performance, you can follow these best practices:
- Using Common Table Expressions (CTEs) sparingly and refactoring repeated logic into staging models.
- Implementing naming conventions (
stg_,int_,fct_,dim_) to clarify the model's purpose. - Running
dbt depsanddbt docs generateregularly to validate dependencies and documentation.
You can also use incremental materializations to reduce compute costs, as shown in the following example.
{{ config(materialized='incremental') }}
select *
from {{ source('raw', 'events') }}
{% if is_incremental() %}
where event_timestamp > (select max(event_timestamp) from {{ this }})
{% endif %}Using dbt Mesh for Multi-Project Collaboration
As data teams require more sharing of data within an organization, you’ll also need to consider the collaboration options dbt Cloud has.
Managing multi-project environments
dbt Mesh enables scalable collaboration across large organizations through centralized governance of the entire data lineage. It enables your team to create multiple interdependent projects, with each owned by different business units or data domains.
Key benefits of dbt Mesh include:
- Scalability: Each team can own and deploy its own dbt project without dependency bottlenecks.
- Cross-project references: Teams can safely reference models from other projects using well-defined public interfaces.
- Governance and discoverability: Shared models are catalogued with clear ownership, documentation, and versioning, promoting accountability and transparency.
- Autonomy with alignment: Teams can innovate independently while adhering to company-wide data standards and governance rules.
At its core, dbt Mesh allows teams to reference models across projects while preserving autonomy.
For example, a finance team might maintain a “core financial metrics” project, while the marketing team builds a separate project that references those financial models without duplicating code or logic.
dbt Mesh enables cross-project references through the ref() function, extended with project namespaces. For instance:
SELECT *
FROM {{ ref('finance_project', 'fct_revenue') }}This enables the marketing model to query the fct_revenue model from the finance project directly, using the canonical version defined by that team.
Versioning and contracts for data models
To guarantee backward compatibility and trust across projects, dbt Mesh introduces two essential mechanisms: model versioning and model contracts.
Model versioning
Model versioning is one of the methods that allows teams to modify their models without breaking existing dependencies. You can define multiple versions of the same model using the versions: property in the model’s YAML file.
For example:
models:
- name: fct_revenue
versions:
- v: 1
description: "Initial revenue aggregation"
- v: 2
description: "Includes new discount and refund logic"Model contracts
Model contracts define the structure, data types, and constraints of a model. It acts as an agreement between data producers and consumers.
When a model includes a contract, dbt validates it before execution, ensuring that schema changes (like column deletions or type mismatches) don’t propagate unintended errors downstream.
Example of a simple contract:
models:
- name: fct_revenue
contract:
enforced: true
columns:
- name: customer_id
data_type: string
- name: total_revenue
data_type: numeric
- name: report_date
data_type: dateIf someone attempts to remove or alter a contracted column, dbt will raise an error, protecting dependent models and dashboards.
Conclusion
dbt Cloud extends the functionality of dbt Core by providing an end-to-end managed platform for analytics engineering.
Throughout this guide, we explored how it centralizes development through the Studio IDE, handles orchestration, and supports newer tools like dbt Mesh and the Semantic Layer.
By integrating these tools into a single platform, dbt Cloud allows teams to handle the entire data lifecycle, from ingestion to documentation, without needing to manage underlying infrastructure.
If you’re interested to get hands-on experience using dbt, our dbt Fundamentals skill track offers a practical way to start building your first project.
dbt Cloud FAQ
What are the main differences between dbt Cloud and dbt Core?
dbt Core is the open-source command-line tool you install locally to build, test, and run dbt projects manually.
dbt Cloud, on the other hand, is a hosted platform that includes a web-based IDE, job scheduling, collaboration tools, and integrations for CI/CD, making it easier to manage dbt projects at scale without complex setup.
How does dbt Cloud handle version control and collaboration?
dbt Cloud integrates directly with Git platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket. It allows developers to edit code, create branches, and submit pull requests from within the web IDE, ensuring version control and team collaboration through familiar Git workflows.
What are the key features of dbt Cloud's CI/CD capabilities?
dbt Cloud automates testing and deployment by running jobs on every pull request or code merge. It includes pre-merge checks, continuous integration to validate models, and automated deployments to production environments, ensuring reliable and consistent data transformations.
How does dbt Cloud's job scheduling work?
dbt Cloud lets you schedule jobs through an intuitive interface, where you can define run times, environments, and dependencies. It supports time-based scheduling (like cron) and job chaining, enabling automated pipeline runs and routine model updates without manual intervention.
What are the benefits of using dbt Cloud's web-based IDE?
The web-based IDE simplifies development by allowing users to write, test, and run dbt models directly in the browser without local software installation. It provides instant feedback, integrated documentation, and easy Git versioning

I'm Austin, a blogger and tech writer with years of experience both as a data scientist and a data analyst in healthcare. Starting my tech journey with a background in biology, I now help others make the same transition through my tech blog. My passion for technology has led me to my writing contributions to dozens of SaaS companies, inspiring others and sharing my experiences.
