Course
In this tutorial, I will show you how Excel version history works in modern Excel, how to view, restore, and recover earlier file versions, and the common pitfalls to avoid when recovering your files.
If you are getting started in Excel, our Introduction to Excel course covers skills like navigating the interface, understanding data formats, and working with basic functions. Also, I find the Excel Formulas Cheat Sheet, which you can download, is a helpful reference because it has all the most common Excel functions.
When Excel Version History Works (and When It Doesn’t)
Before you try to restore your file, it’s important to understand when Excel version history is actually available. The feature’s availability depends on where the file is stored and how it was saved. Let’s look at the following differences:
- Cloud: Excel provides full version history for files saved to OneDrive or SharePoint. In these locations, Excel automatically tracks changes and stores earlier versions that especially when AutoSave is turned on, since Excel continuously saves snapshots as you work.
- Local files: If your file is saved directly to your Desktop, Documents folder, or a USB drive, Excel’s built-in Version History feature is usually disabled. However, you might still recover unsaved work using the AutoRecover option, but that’s different from true version history and offers far less flexibility.
- Excel for Windows, Mac, and Web: Excel for Windows and Mac support version history for cloud files, while Excel for the web relies entirely on cloud storage and always tracks version changes.
Always remember that if your Excel file isn’t saved to OneDrive or SharePoint, version history will be limited or unavailable.
How to Check If Your Excel File Has Version History
To confirm if your Excel supports version history, use the following steps:
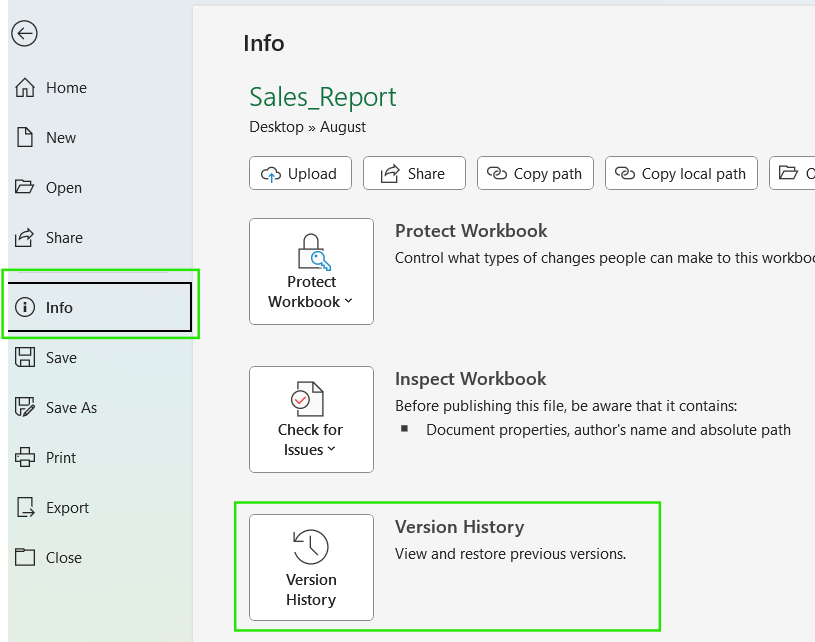
If you are using Excel for Windows:
- Open the Excel file
- Click File → Info
- Look for Version History
- Look for the Version History button. Check whether versions are listed or if the option is missing or disabled
If you are using Excel for Mac:
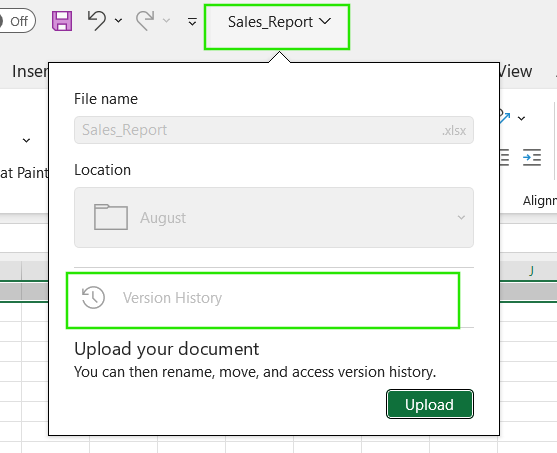
- Open your workbook.
- Click the File menu in the top Apple menu bar.
- Select Browse Version History.
Alternatively, you can click the filename in the center of the top title bar and select Version History from the dropdown menu.
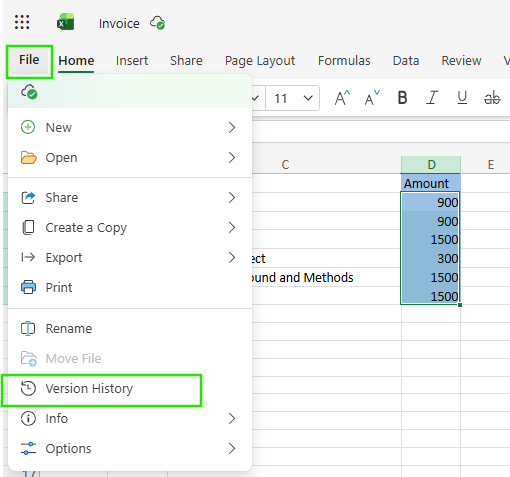
If you are using Excel for the Web:
- Open the file in your browser via OneDrive or SharePoint.
- Click the File → Info → Version History.
When you don't see the Version History option, or it is grayed out, it can be a result of any of the following:
- The file is stored locally: Move it to OneDrive to enable the feature.
- You are offline: Excel needs a connection to the cloud to retrieve the history list.
- Permissions: You may not have the necessary permissions to view version history, especially if you are viewing shared files.
How to View Previous Versions of an Excel File
Once you have confirmed that your file is saved to the cloud, accessing its history is straightforward. You can view your previous versions using the following steps:
- Open the Excel file
- Go to File → Info → Version History
- Review the list of available versions
- Select a version to open it
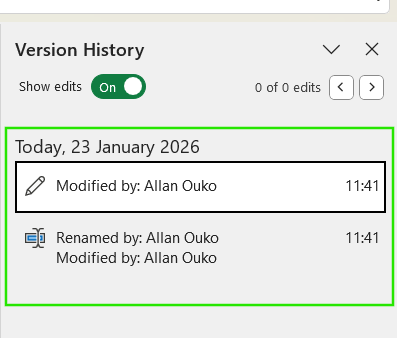
The version list usually shows timestamps, the name of the editor, and whether the version was created automatically or saved manually. The file versions created by AutoSave often appear more frequently and may not have descriptive labels, while manual saves are typically spaced farther apart and easier to identify.
When you open a previous version, Excel opens it in read-only mode in a separate window. This allows you to review formulas, data, and structure without overwriting the current file. If you need to compare versions, you can switch between windows or copy specific cells from the older version into the current one. You can also use the View > View Side by Side tool to safely compare the files before deciding to restore, as we will see in the next section.
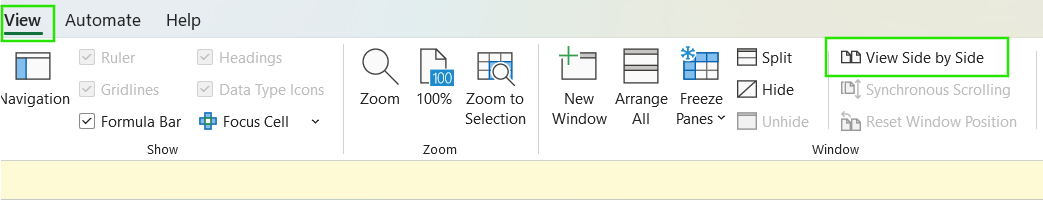
How to Restore a Previous Version of an Excel File
Now that you have seen how to view previous file versions, let me show you how to recover the file. You can restore your desired file version using the following steps:
- From the file, open File > Info > Version History.
- Select the version you want to recover
- Click Restore
- Confirm the action if prompted
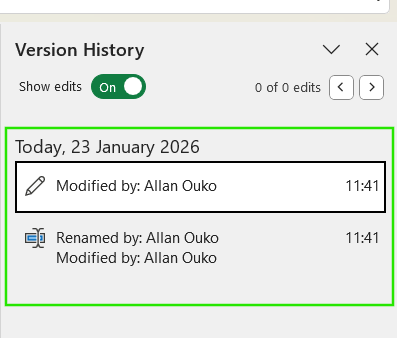
When you restore a previous version, Excel replaces the current version with the selected one. However, this does not permanently delete newer file versions. Excel keeps the version history intact, meaning you can restore any file version from the available list if needed.
As a best practice, I recommend you avoid restoring the entire file unless you’re sure. If only a few formulas or rows are affected, open the older version in read-only mode and copy the needed data into the current file instead.
How to Restore a Previous Version Using OneDrive or SharePoint
If you access Excel files through a browser using OneDrive and SharePoint, you can also restore the previous file version using the following steps:
- Open OneDrive or SharePoint in your browser
- Locate the Excel file
- Right-click the file and select Version history
- Preview or restore the desired version
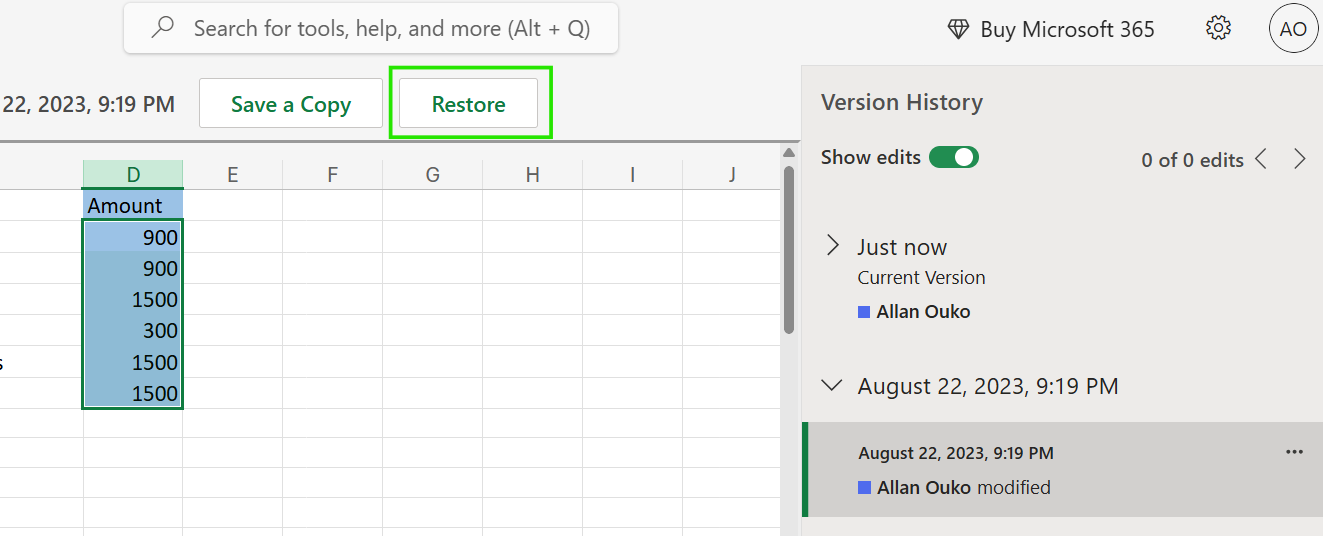
This method is often better when Excel won’t open properly or when you need a quick overview of multiple versions. It also works across devices, hence useful when working in collaborative environments.
How to Recover an Unsaved or Accidentally Closed Excel File
If you closed a file without hitting save, or if Excel suddenly quit, then you're looking for a temporary backup and not a previous file version.
Excel has the AutoRecover feature, which periodically saves temporary copies of open workbooks so Excel can restore them after a crash, power outage, or forced shutdown. These files are stored locally and are meant for short-term recovery only. They are not full versions and may not capture every recent change.
To recover an unsaved workbook:
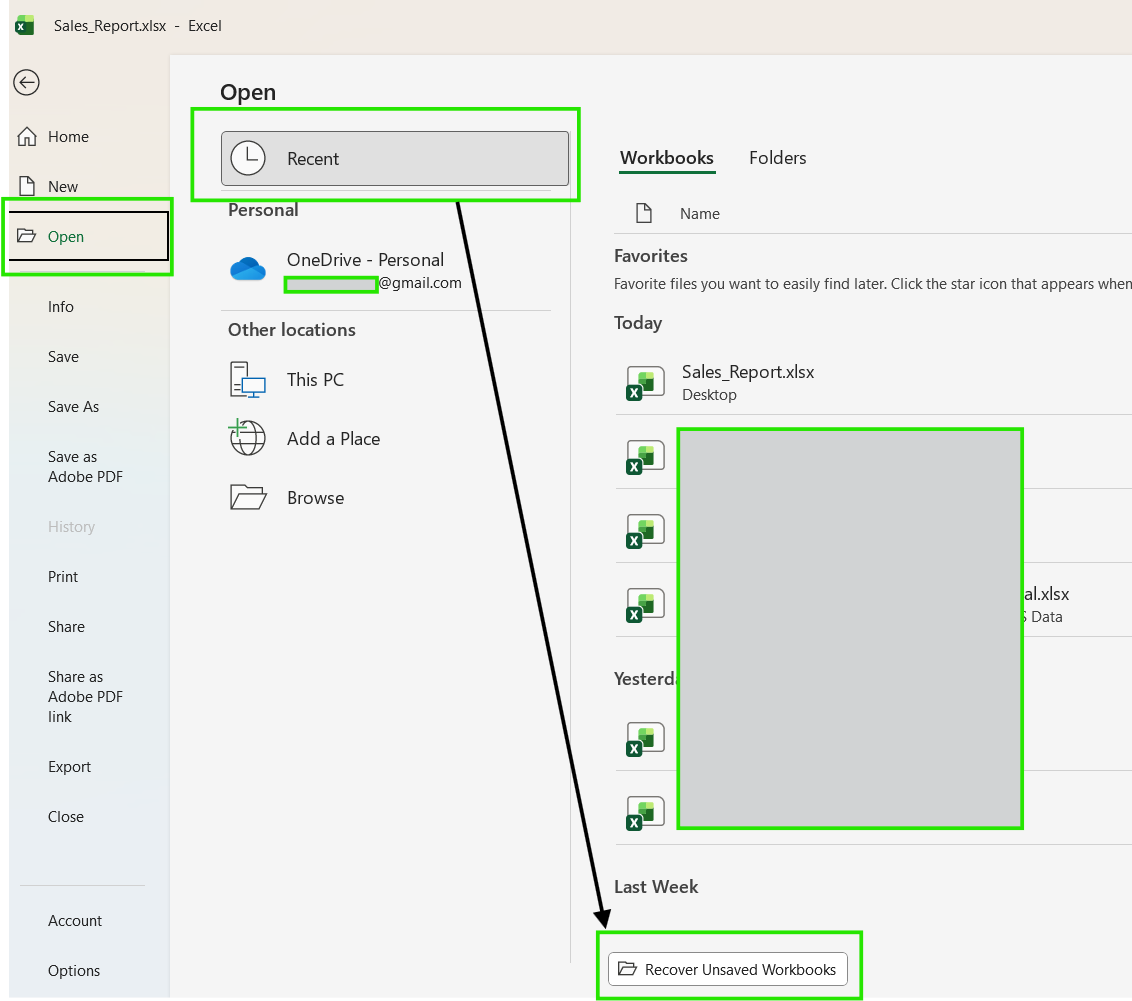
- Open Excel
- Go to File → Open
- Select Recover Unsaved Workbooks or Recent → Recover Unsaved Workbooks
- Open the recovered file and save it immediately
You should note that if your app crashes before saving your file, Excel often shows a Document Recovery pane automatically when you reopen the app. If you close this pane without saving, the recovered files may be deleted.
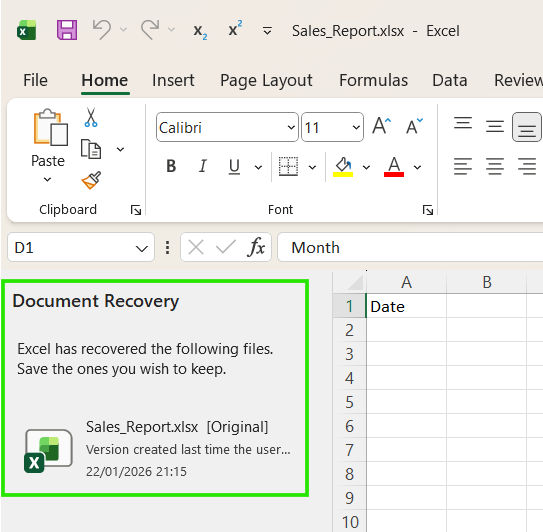
Depending on which platform you use, take note of the following differences.
- Windows: AutoRecover files are usually stored in a temporary system folder linked to Excel.
- Mac: Recovered files may appear when reopening Excel or in the AutoRecovery folder under user libraries
What AutoSave Does (and What It Doesn’t Do)
AutoSave is often misunderstood. It doesn’t just save your file; it continuously saves changes and creates frequent versions, but only when you save it in OneDrive or SharePoint. You also need to turn on the AutoSave toggle. In this way, Excel will frequently save your file as you work on it, and the saves will appear in the version history list.
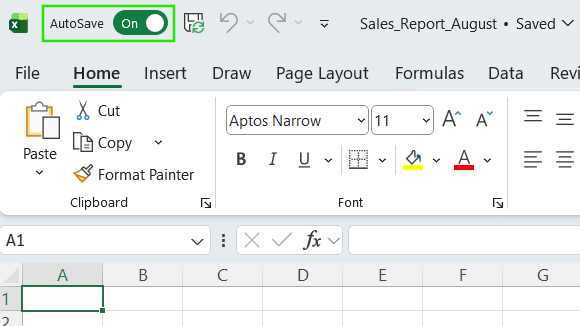
However, AutoSave does not create version history for files stored locally. Instead, it will behave like a normal save and overwrite a file from its previous state.
If you are unsure when to apply a specific method, use the AutoSave when working in the cloud and manual save when working locally or before making major structural changes.
Check out the Excel Shortcuts Cheat Sheet to learn how to improve productivity by learning the shortcuts for different Excel features.
How Version History Works with Shared and Co-Authored Files
Version history is valuable when multiple people are editing the same Excel file. When a workbook is shared through OneDrive or SharePoint, Excel tracks edits from each collaborator and associates changes with user accounts. If two people edit different cells, Excel merges those changes automatically. If the same cell is edited at the same time, Excel resolves the conflict by keeping the most recent save and recording earlier states in version history.
You can use version history to identify who made a change by checking the editor name and timestamp for each version. This makes it easier to undo accidental overwrites or recover data changed by another collaborator without disrupting the entire workbook.
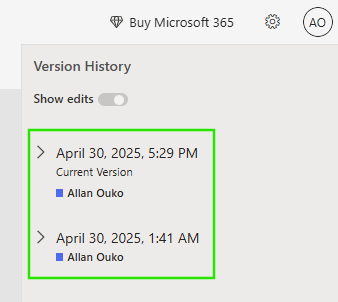
In team environments, version history acts as a safety net. Instead of guessing what changed or when, you can review past versions, restore specific data, or roll back confidently, even when multiple editors are involved.
Common Problems with Excel Version History (and How to Fix Them)
Sometimes, the version history may not behave as expected or be unavailable in your workbook. The following are some of the methods to troubleshoot these issues:
-
Version history not appearing: This issue occurs when the file is saved locally. To solve the problem, try moving the file to OneDrive or SharePoint, reopening it from there, and then checking File → Info → Version History again.
-
File saved as
.xlsinstead of.xlsx: Older Excel formats don’t fully support modern version history features. Solve this issue by saving the file as.xlsxor.xlsmif macros are required. -
Macro-enabled files behaving differently: Macro-enabled files (
.xlsm) support version history, but AutoSave may be disabled when macros are running. Try to save the file manually after major changes and confirm AutoSave is enabled when possible. -
The file was moved: If you move a file out of your OneDrive folder and onto your local desktop, the connection to its cloud-based history is lost. To fix this problem, try opening the original file directly from the cloud location instead of a local copy.
-
Permissions blocking access to history: Read-only access or restricted permissions can hide version history. Always confirm you have edit access to the file, then reopen it to access the version history.
Best Practices for Managing Versions in Excel
To maintain good version management, you need to set up a workflow that minimizes mistakes. Here are some best practices I recommend to keep your file versions safe:
-
Save important Excel files to OneDrive or SharePoint from the start, especially anything you’ll revisit or share.
-
Leave AutoSave on for collaborative files so changes are captured automatically and appear in version history.
-
Avoid using the manual version, like saving files as
final_v7_REAL_FINAL.xlsx. When working in the cloud, rely on version history instead of creating duplicate backups whenever possible. -
Restore versions selectively by opening an older version and copying out what you need instead of rolling back the entire workbook. This method is safer, faster, and far less disruptive, especially in shared environments.
Conclusion
Excel version history is one of the most practical safety features Excel offers, but it only works well when your files are saved in the right place. Storing workbooks in OneDrive or SharePoint, keeping AutoSave on, and knowing where to find version history gives you a reliable way to undo mistakes without starting over.
If you want to advance your Excel skills, I recommend taking our Data Analysis in Excel course. This course will help you master advanced analytics and propel your career. I also recommend taking our Intermediate Power Query in Excel course to learn about data transformation and using the M language for creating dynamic functions.
Advance Your Career with Excel
Gain the skills to maximize Excel—no experience required.
FAQs
How do I access version history in Excel?
Open the file, go to File → Info → Version History, and select a version to view or restore.
Does Excel version history work for locally saved files?
No. Local files have limited recovery options and do not support full version history.
What should I do if version history is missing or disabled?
Check that the file is saved to OneDrive or SharePoint, is in a modern format (.xlsx or .xlsm), and that you have edit permissions.
What’s the difference between AutoSave and version history?
AutoSave creates frequent saved states, while version history lets you review and restore those states later.
How long is the Version History kept?
Version History is kept indefinitely in OneDrive/SharePoint. For Microsoft 365 subscribers, it stores up to storage limits, while older versions may auto-archive but remain accessible.
