Track
Whether you're just starting your programming journey, preparing for technical interviews, or aiming to build scalable software, understanding data structures and algorithms (DSA) is essential. But with so much information out there, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. Where do you begin? How do you stay motivated for the long haul? And how can you be sure you’re truly mastering these skills, not just memorizing facts for interviews?
This DSA roadmap is designed to guide you, step by step, through a full year of learning. We'll move from foundational programming skills to advanced algorithms, with each section building on what came before. Along the way, you’ll find practical tips, recommended resources, and ways to apply your knowledge through hands-on projects and real-world examples.
Let’s break down the path to DSA mastery, one stage at a time.
TL;DR – Your 12-Month DSA Roadmap
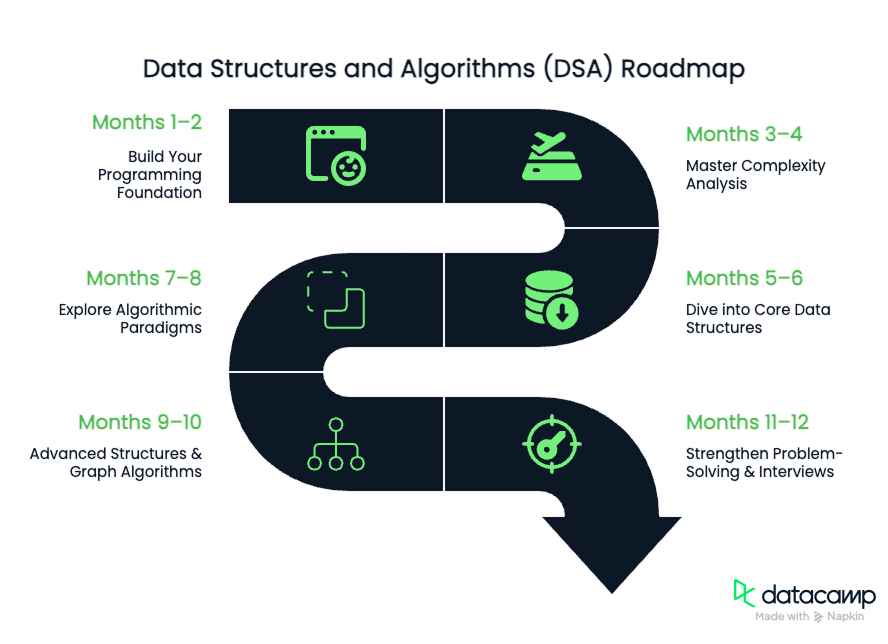
Here’s a quick overview of the journey ahead:
- Months 1–2: Choose a programming language and build a strong grasp of core programming constructs.
- Months 3–4: Learn how to analyze code performance using Big-O notation and related concepts.
- Months 5–6: Dive into foundational data structures; arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs.
- Months 7–8: Explore key algorithmic approaches, including divide and conquer, greedy methods, and dynamic programming.
- Months 9–10: Tackle advanced data structures and graph algorithms to solve more complex problems.
- Months 11–12: Practice effective problem-solving strategies, mock interviews, and review for mastery.
- Continual practice: Apply what you learn regularly and stay curious about new developments in tech.
Why DSA Skills Matter
Before we jump into the full learning plan, let’s take a moment to consider why DSA is so fundamental, not just for interviews, but for your growth as a developer.
- Interview readiness: Most major tech companies test DSA skills because they reveal how you solve problems and think logically.
- Building efficient software: The right algorithm can make a difference between a product that scales and one that stalls.
- Versatility: Once you understand DSA, picking up new languages or frameworks becomes much easier.
- Problem-solving confidence: The ability to break down and tackle unfamiliar challenges is crucial in any tech career.
Investing time in DSA isn’t just about landing your first job; it’s about building a toolkit you’ll use for years.
Months 1–2: Build Your Programming Foundation
The first step is to choose a primary programming language and get comfortable with its core features. Even the most advanced algorithms rely on solid fundamentals.
Choosing your language
The best language is one that aligns with your goals and is supported by active communities. Here are some considerations:
- Python: Great for beginners and widely used in data science, scripting, and automation.
- Java: Common in enterprise development; a strong choice for object-oriented programming and large systems.
- C++: Offers fine-grained control over memory and performance; preferred in competitive coding and systems programming.
Pick one language to focus on for DSA practice. If you’re unsure, Python is a friendly and versatile starting point.
Key language concepts to master
- Variables and data types: Understand how your language handles numbers, strings, and more.
- Control structures: Practice loops (for, while) and conditional logic (if/else).
- Functions and methods: Learn to break problems into reusable pieces.
- Basic data input/output: Read from and write to files or the console.
If you’re using C++ or Java, take some time to explore pointers (C++), object-oriented principles (Java), and how each language manages memory.
Laying the groundwork with projects
Use this time to build simple programs; a calculator, a to-do list, or a file reader. These projects reinforce your understanding and set you up for more complex work ahead.
Resources to get started
- Python Programming Fundamentals skill track: Build up your programming skills in Python. Discover how to create variables, work with various data types, and implement custom logic.
- Java Fundamentals skill track: Learn the fundamentals of Java and start building real-world applications with one of the most widely used programming languages in the world.
- Python Loops tutorial: earn and practice while and for loops, nested loops, the break and continue keywords, the range function, and more.
- OOP in Java tutorial: Learn Object-Oriented Programming in Java with practical examples. Master classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, and abstract classes
- Dashboard Design Concepts: Practice communicating your results clearly, even with basic code.
Months 3–4: Master Complexity Analysis
Now that you’re comfortable writing code, it’s time to learn how to analyze its performance, an essential skill for any engineer.
Understanding algorithmic complexity
Big-O notation is the standard way to reason about how your code scales with input size.
- O(1): Constant time. The operation doesn’t depend on input size.
- O(n): Linear time. Performance grows with input.
- O(n²), O(log n), O(2ⁿ): Recognize common patterns as you analyze new algorithms.
Get in the habit of asking, “How does my code perform as data grows?” For example, compare linear search (O(n)) with binary search (O(log n)).
Balancing time and space
Efficient programs often require tradeoffs between speed and memory use. Learn to:
- Identify when in-place algorithms are appropriate.
- Use memoization to optimize recursive solutions, a key step toward dynamic programming.
Putting theory into practice
Take simple problems like summing a list or reversing a string and analyze how different solutions affect performance. Write out best, worst, and average-case scenarios for your code.
Resources for complexity analysis
- Big O Notation and Time Complexity Guide: Learn the basics of Big O notation with this hands-on guide.
- Data Structures & Algorithms in Python course: Explore data structures such as linked lists, stacks, queues, hash tables and graphs; and the most common searching and sorting algorithms.
- Understanding Modern Data Architecture: See why performance matters in real systems.
- Data Governance Fundamentals Cheat Sheet: Learn to think about data quality and efficiency early on.
- Associate Data Engineer in SQL: Lay the foundation for working with structured data.
- Data Strategy: Discover how programming skills fit into broader data workflows.
Months 5–6: Dive into Core Data Structures
With programming basics and complexity analysis behind you, it’s time to master the classic data structures that form the heart of DSA.
Linear data structures
- Arrays/lists: Fast access, fixed or dynamic size. Practice inserting, deleting, and searching.
- Linked lists: Nodes linked by pointers; great for efficient insertions and deletions.
- Stacks: “Last in, first out” (LIFO); useful for undo functionality, parsing, and backtracking.
- Queues: “First in, first out” (FIFO); essential for scheduling and breadth-first algorithms.
Non-linear data structures
- Trees: Organize data hierarchically. Start with binary trees, then explore balanced trees (like AVL or red-black trees).
- Graphs: Model networks and relationships between entities. Learn to represent graphs as adjacency lists and matrices.
Hands-on projects for structure mastery
- Build a contacts app using linked lists.
- Implement a browser history feature using a stack.
- Create a simple scheduling system using a queue.
Resources for exploring data structures
- An Introduction to Graph Theory: Explore the essentials of graph theory and learn about vertices, edges, and various graph types to understand complex networks.
- Data Structures: A Comprehensive Guide with Python: This tutorial takes you through some worked examples.
- Database Design: Understand how data structures power robust storage systems.
- Data Skills for Business: See how structured data supports business workflows.
Months 7–8: Explore Algorithmic Paradigms
Now that you know the basic data structures, let’s focus on strategies for solving more complex problems.
Divide and conquer
Break problems down into smaller parts, solve them independently, and combine solutions.
- Examples: Merge sort, quicksort, binary search.
Greedy algorithms
At each step, make the best local choice. Fast and simple, but only work when a global optimum can be built from local decisions.
- Examples: Activity selection, coin change with certain denominations, Huffman coding.
Dynamic programming
When greedy methods fall short, dynamic programming (DP) helps by solving overlapping subproblems and storing results.
- Tabulation: Build up solutions iteratively.
- Memoization: Cache recursive results to avoid redundancy.
Practice problems
- Calculate the nth Fibonacci number using DP.
- Find the shortest path in a grid using greedy and then DP approaches.
- Solve the knapsack or longest common subsequence problem.
Resources to deepen your understanding
- Introduction to Network Analysis in Python course: This course will equip you with the skills to analyze and visualize networks such as Facebook and Twitter.
- Python Merge Sort Tutorial: Learn everything you need to know about the merge sort operation in Python and how to implement this critical algorithm for sorting large databases.
- Understanding Recursive Functions in Python: Learn about the different aspects of recursive functions and implement a recursive function in Python from scratch.
- Data Storytelling & Communication Cheat Sheet: Learn to explain your solutions clearly, an invaluable skill in interviews.
- Interactive Data Visualization in R: Visualize how algorithms work and compare their performance.
Months 9–10: Level Up with Advanced Structures and Graph Algorithms
By this stage, you’ve built a solid foundation. Now it’s time to explore advanced structures and algorithms you’ll encounter in real-world applications and interviews.
Specialized data structures
- Tries: Efficient for prefix searches, autocomplete, and spell checking.
- Segment trees and Fenwick trees: Enable fast range queries and dynamic updates; useful in analytics and gaming.
Essential graph algorithms
- Breadth-first search (BFS): Ideal for finding shortest paths in unweighted graphs and exploring networks layer by layer.
- Depth-first search (DFS): Useful for cycle detection, topological sorting, and exploring all possible paths.
- Shortest path algorithms: Dijkstra’s algorithm helps find optimal paths in weighted graphs.
- Minimum spanning trees (MST): Kruskal’s and Prim’s algorithms connect all nodes with the minimum total weight, which is great for network design.
Applying advanced concepts
- Implement a spell checker using tries.
- Analyze a social network or transportation map using graph algorithms.
Supplementary resources
- Implementing the Dijkstra Algorithm in Python: Learn how this popular shortest path algorithm works.
- Breadth-First Search in Python: A Guide with Examples: Discover how breadth-first search systematically explores nodes and edges in graphs.
- Depth-First Search in Python: Traversing Graphs and Trees: Discover the essentials of depth-first search for navigating graphs and trees.
Months 11–12: Strengthen Problem-Solving and Prepare for Interviews
You’re now equipped with the tools and techniques needed for DSA mastery. In these final months, focus on practice, reflection, and simulating real-world scenarios.
A systematic approach to challenges
- Understand the problem: Clarify requirements and constraints. Don’t rush into coding.
- Start with brute force: Build a basic, working solution first.
- Look for patterns: Map the problem to known techniques (such as two-pointer or sliding window approaches).
- Test edge cases: Think about unusual inputs to ensure your solution is robust.
Practice with intention
Target platforms and resources that mimic real interview environments. Focus on:
- Core data structure questions
- Algorithmic problem sets
- Timed practice and mock interviews
Building confidence for interviews
- Explain your reasoning aloud as you work through problems.
- Practice with friends or mentors who can ask follow-up questions.
- Review common interview topics and revisit challenging problems.
Resources for interview prep
- Data Science Interview Preparation: Gain practical tips on interview readiness and mindset.
- A Data Science Roadmap for 2025: Stay ahead of industry trends and emerging technical skills.
- Top 24 Programming Interview Questions for 2025: Discover essential programming interview questions with Python examples for job seekers, final-year students, and data professionals.
- 56 Java Interview Questions and Answers For All Levels: A list of 56 Java interview questions suitable for developers applying to junior, intermediate, and senior roles.
Final Thoughts
A year of focused, step-by-step study can transform how you approach technical problems and open many new doors. DSA mastery is more than an interview requirement; it’s a mindset that values efficiency, clarity, and adaptability.
Keep your learning active by:
- Revisiting core concepts regularly
- Building projects that stretch your skills (such as caching systems, recommendation engines, or network analyzers)
- Participating in hackathons, study groups, or online forums to stay engaged
Remember, your DSA journey doesn’t end here. Use your foundation to explore adjacent fields like cloud computing, data engineering, or machine learning. As you move forward, consider courses and resources that align with your professional interests and goals.
The tech landscape is always evolving, but a strong grasp of DSA will keep you prepared for whatever comes next. Keep practicing, stay curious, and enjoy the process.
DSA Roadmap FAQs
How can I practice DSA effectively?
Consistency beats cramming. Aim to solve a few problems each day, revisit past solutions for deeper understanding, and challenge yourself with contests or mock interviews. Keeping a log can help you track patterns and highlight areas for improvement.
What mistakes should I avoid?
Common pitfalls include:
- Jumping to advanced problems before solidifying fundamentals
- Focusing on rote memorization instead of true comprehension
- Skipping complexity analysis
- Neglecting to review and learn from mistakes
How long will it take to master DSA?
With steady effort, most learners achieve proficiency in 6–12 months. However, DSA is a long-term skill, so ongoing practice and exposure to new problem types will keep you sharp.
Which data structures should I prioritize first?
Start with arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, and hash tables. Once you’re comfortable, branch out to trees, heaps, and graphs. These form the basis for tackling more advanced topics.

A senior editor in the AI and edtech space. Committed to exploring data and AI trends.