Track
In an increasingly digital world, data security has become a must-have for businesses of all sizes. With the rise in remote work and increasing adoption of cloud computing, protection of sensitive information is becoming more challenging and important by the day.
Beyond operational concerns, data security plays a crucial role in meeting regulatory compliance requirements and preserving a company's brand reputation. Loss of data security may bring with it not only legal or financial repercussions but also destroyed customer relations.
This guide will explore essential topics such as data security compliance, developing a robust data security policy, effective management strategies, and best practices for securing both on-premises and cloud environments.
You can also check out our Data Ethics and GDPR for Data Practitioners webinar to learn more.
Strengthen Your Data Privacy & Governance
Ensure compliance and protect your business with DataCamp for Business. Specialized courses and centralized tracking to safeguard your data.

Key Data Security Principles
Confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA Triad)
The CIA Triad—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—is the foundation of any secure data strategy.
- Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals. Techniques such as encryption, access control mechanisms, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are commonly used to protect confidentiality.
- Integrity focuses on maintaining the accuracy and consistency of data, ensuring it is not altered during storage or transmission. Practices like digital signatures and checksums verify that data remains unchanged.
- Availability ensures that authorized users can access data whenever needed. This principle emphasizes reliable systems, robust backup solutions, and disaster recovery plans to minimize downtime.
Understanding and applying the CIA Triad helps data practitioners design systems that balance protection with usability, ensuring business operations remain efficient and secure.
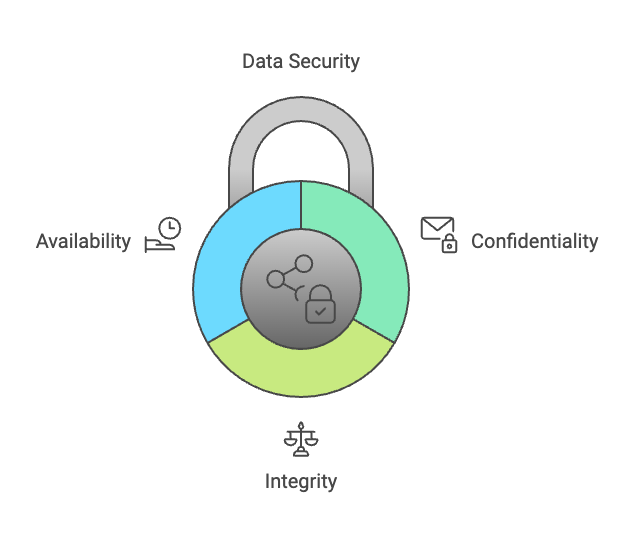
Image created with Napkin.ai
Data privacy vs. data security
While closely related, data privacy and data security serve distinct purposes.
- Data security focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage through technical measures like firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection.
- Data privacy governs how personal information is collected, shared, and used, ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
Successful privacy and security practices are essential for maintaining compliance and ensuring customer trust. Customers expect organizations to protect their personal information, and failures in security can lead to privacy breaches that damage both brand reputation and consumer confidence.
Common Data Security Threats and Risks
There are several potential threats when it comes to securing data, and awareness of these risks can help your organization mitigate them.
Cyber attacks and insider threats
Top on the list of organizational concerns are cyber threats—ransomware and phishing attacks—that exploit system vulnerabilities and user behaviors in order to steal or encrypt data. Insider threats, whether malicious or accidental, also represent serious risks; employees with access to sensitive systems can accidentally or maliciously disclose information.
Strong access management practices, such as RBAC and continuous monitoring of user activity, must be in place to mitigate these risks. These measures contribute to the alleviation of potential threats and the enforcement of accountability within the organization.
Cloud security vulnerabilities
With more reliance on cloud computing, unique security challenges arise. One of the top causes of breaches in cloud data is misconfigurations, such as unsecured storage buckets. Other vulnerabilities include data loss, inadequate encryption, and unauthorized access to cloud resources.
These would require, among other things, routine security audits and the setting of secure configurations. Additionally, the use of tools like CSPM and encryption for data at rest and in transit will be beneficial in ensuring that these practices really help in securing a cloud environment to store and process sensitive data.
Human error and accidental exposure
Human error remains the leading cause of data breaches. Errors, such as sending sensitive files to the wrong recipients, losing a device, or falling for phishing attacks, could easily compromise critical information.
Investment in security awareness training is necessary for any organization to educate employees on risks and preventive measures. Further, automation tools such as DLP solutions can help identify and block the accidental exposure of sensitive data.
Best Practices for Maintaining Data Security
While we’ve touched on some of the ways you can minitage risk, there are several core principles that you need to establish when creating your data security policy:
Implementing robust access controls
Effective access control is critical for minimizing unauthorized access to sensitive data. The principle of least privilege ensures that users only have the access necessary for their roles, reducing the risk of accidental or intentional misuse.
Additionally, multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification for access.
To enforce access control policies effectively, regularly review user permissions and revoke unnecessary access promptly. Use identity and access management (IAM) tools to automate processes and maintain a clear audit trail of access changes. These steps help ensure that only authorized individuals interact with sensitive data.
Regular security audits and monitoring
Continuous monitoring and regular security audits are essential for maintaining a proactive data security posture. Tools such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) platforms can help identify unusual activity and potential threats in real-time.
Conduct routine audits to assess vulnerabilities in your systems and ensure compliance with security policies. Addressing weaknesses before they are exploited reduces the risk of breaches and ensures awareness of evolving threats. More robust solutions for Data Security with AI are increasingly being adopted.
Data encryption and masking
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to protect data both at rest and in transit. By converting information into an unreadable format, encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains inaccessible without the appropriate decryption keys. Common encryption methods include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for data storage and TLS (Transport Layer Security) for secure communication over networks.
For sensitive data used in testing or development environments, data masking provides an additional layer of protection. Masking replaces real data with fictitious but realistic values, preventing unauthorized access while maintaining usability for analysis and testing. You can learn the fundamentals of Data privacy and anonymization in Python through our course.
Data Security in Cloud Computing
One of the latest frontiers of data security is that of cloud computing. This environment is developing rapidly, so it’s important to stay abreast of developments to remain compliant.
Cloud security challenges
Cloud computing introduces unique security challenges, such as multitenancy (multiple organizations sharing the same infrastructure) and the shared responsibility model, where providers manage infrastructure security while customers handle their data and applications. Misconfigurations, weak access controls, and lack of visibility can expose sensitive data in cloud environments.
To address these challenges, implement access management with role-based permissions and multi-factor authentication (MFA). Use tools like cloud security posture management (CSPM) to identify and correct misconfigurations. Encrypt data at rest and in transit, and ensure a clear delineation of responsibilities between your organization and cloud providers.
You can learn the key principles of cloud security in Azure with our online course.
Data resilience and redundancy
Resilience and redundancy are key to maintaining security and business continuity in the cloud. Regular data backups, disaster recovery plans, and redundant systems minimize the impact of data breaches or system failures. Backups should be automated, encrypted, and stored in multiple locations to prevent single points of failure.
For disaster recovery, consider strategies like geo-redundancy and failover systems to ensure uptime even during critical events. Tools such as cloud-based disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) can provide fast recovery times and reduced downtime, helping businesses maintain operations without compromising data integrity.
Security in hybrid and multi-cloud environments
Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies allow organizations to leverage multiple cloud providers or integrate cloud and on-premises systems. However, these approaches introduce complexity in maintaining consistent security policies and controls across environments.
Centralized security management tools, such as cloud access security brokers (CASBs) and unified policy management platforms, can ensure consistency across different providers. Regularly audit configurations and apply the principle of least privilege to all systems. Balancing security requirements across providers involves clear communication, standardized protocols, and diligent monitoring.
Data Security Compliance and Regulatory Standards
One of the key areas to bear in mind is that of regulatory standards. Keeping informed of the latest legislation is crucial for organizations working on their data security.
Key compliance frameworks
Compliance with data security regulations is essential for businesses handling sensitive information. Frameworks like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in healthcare, and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) in payment processing set strict requirements for data protection.
These standards emphasize practices such as limiting data access, encrypting sensitive information, and maintaining detailed logs for auditing purposes. To stay compliant, data practitioners should regularly monitor data access, use encryption technologies to safeguard information and establish clear reporting practices to demonstrate adherence to regulations.
New legislation, such as the AI EU Act, is also coming into effect, and organizations must be familiar with these laws.
Prepare Your Team for the EU AI Act
Ensure compliance and foster innovation by equipping your team with the AI literacy skills they need. Start building your AI training program with DataCamp for Business today.

Implementing automated compliance reporting
Automation can simplify compliance by streamlining reporting and auditing processes. Tools like compliance management platforms and real-time monitoring solutions allow organizations to continuously track their adherence to regulatory requirements. These tools can identify and flag potential issues, generate audit-ready reports, and provide actionable insights for maintaining compliance.
By automating these tasks, organizations reduce the risk of human error and free up resources to focus on strategic improvements. Automated systems also ensure faster responses to potential breaches, minimizing compliance risks and penalties.
Building a data security policy
A well-crafted data security policy is a cornerstone of regulatory compliance. This policy serves as a blueprint for how an organization handles, protects, and responds to security incidents involving sensitive data.
To create a comprehensive policy, include key components such as:
- Access controls: Define who has access to specific types of data and how permissions are granted or revoked.
- Data handling procedures: Outline protocols for storing, processing, and transmitting sensitive information.
- Breach response: Establish a clear plan for identifying, reporting, and mitigating data breaches.
- Employee training: Provide regular education on security best practices and regulatory requirements.
Understanding Data Ethics and new compliance policies like GDPR is essential to tailoring your policy to meet industry-specific standards, ensuring that all employees understand their roles in maintaining compliance and protecting sensitive information.
Tools and Technologies for Data Security
When it comes to implementing data security measures, there are several areas you should focus on:
Security information and event management (SIEM)
SIEM solutions provide centralized visibility into security events across an organization’s network, making them invaluable for threat detection and response. By aggregating and analyzing logs from multiple sources, SIEM platforms can identify suspicious patterns, enabling proactive responses to potential breaches.
SIEM tools also play a vital role in compliance by generating audit-ready reports and maintaining detailed logs required by frameworks like GDPR and PCI DSS. Features like real-time alerts and dashboards help organizations monitor their security systems continuously and respond effectively to threats.
Data loss prevention (DLP) solutions
DLP tools help prevent unauthorized data transfers or accidental exposure of sensitive information. These solutions monitor and control data flows within an organization, ensuring compliance with security policies.
In B2B environments, where cloud-based collaboration and data sharing are common, DLP tools safeguard customer information and proprietary data. They enable secure sharing by applying encryption or restricting access to specific users, reducing the risk of data breaches while maintaining operational efficiency.
Encryption and key management solutions
Encryption is fundamental to securing sensitive information, converting data into unreadable formats to prevent unauthorized access. Modern encryption methods, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for storage and TLS (Transport Layer Security) for data in transit, ensure protection against interception or compromise.
Key management governs how encryption keys are generated, stored, and accessed. Without proper key management, even encrypted data can be vulnerable to misuse. Tools like hardware security modules (HSMs) or cloud-based key management services provide secure storage and centralized control over encryption keys, ensuring only authorized parties can decrypt sensitive data.
Creating a Data Security Culture in Your Organization
The starting point for maintaining data security in your business is to create a culture where the concept is a focus point at all levels of the organization. There are several ways you can achieve this:
Employee training and awareness
Regular training sessions can equip staff with the knowledge to recognize phishing attacks, identify social engineering tactics, and follow proper data handling procedures. DataCamp for Business is a great solution to keep all employees up to date on important data security and data privacy topics. DataCamp for Business allows organizations to create custom tracks for any data topic.
To make training effective and engaging, incorporate interactive elements such as simulations of phishing emails or role-playing scenarios. Use gamification to incentivize participation and reward employees who demonstrate strong security practices. Keeping the content practical and updated ensures employees stay prepared against evolving threats.
Leveraging a platform like DataCamp for Business allows organizations to build a strong culture of data privacy and security while also driving data literacy in many other areas through our extensive data course library.
Empower Your Team with Data Literacy
Enhance your team's data literacy and decision-making capabilities with DataCamp for Business. Access diverse courses, hands-on projects, and centralized insights for teams of 2 or more.

Establishing a culture of security by design
A security-by-design approach ensures that data protection is integrated into every process and decision. This mindset encourages employees and teams to prioritize security from the outset, whether they are handling data, developing software, or setting up systems.
Strategies to embed security into your organization include:
- Incorporating security checkpoints at every stage of software development, such as code reviews and vulnerability scans.
- Requiring security assessments before launching new projects or services.
- Promoting the use of secure tools and technologies for data handling, such as encrypted storage and secure communication platforms.
Conclusion
Data security is a critical pillar of success for businesses and individuals working with sensitive information. By understanding foundational principles, addressing common threats, and leveraging effective tools and practices, data practitioners can help build secure systems that protect data, ensure compliance, and maintain trust. Building a culture of security within organizations further reinforces these efforts, making data protection an integral part of every process and decision.
For those new to the topic, our Introduction to Data Security course helps to establish the basics with interactive and hands-on examples.
Data Security FAQs
What is the difference between data privacy and data security?
Data privacy focuses on how personal information is collected, shared, and used, while data security involves the technical measures used to protect data from unauthorized access or breaches. Both are essential for safeguarding sensitive information.
What is the CIA Triad in data security?
The CIA Triad stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. It is a foundational model in data security that ensures sensitive data is accessible only to authorized users, remains accurate, and is available when needed.
What are data loss prevention (DLP) solutions, and how do they work?
DLP solutions prevent unauthorized access or accidental sharing of sensitive data by monitoring and controlling data movement. They are especially effective in cloud and B2B environments to ensure secure collaboration.
How does encryption protect sensitive information?
Encryption converts data into unreadable formats, ensuring that only authorized users with the correct decryption keys can access it. It protects data both at rest and in transit.
How can organizations create a culture of data security?
Organizations can build a security-first culture by conducting regular employee training, embedding security practices in workflows, and emphasizing security-by-design in data handling and software development.