Track
Python’s clarity, versatility, and expansive ecosystem have established it as a foundational language in modern programming. Whether you aspire to launch a career in data science, web development, automation, or machine learning, having a clear roadmap is crucial to turning curiosity into expertise. Yet, with such a wealth of resources and directions available, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed or unsure where to start.
This 12-month Python roadmap brings structure and focus to your learning, guiding you step by step from the fundamentals to advanced techniques and specializations. You’ll know not only what to learn, but when and why, enabling you to build real-world projects, meet industry standards, and evolve alongside Python itself. If you’re looking for a detailed guide on how to learn Python, be sure to check out our separate guide.
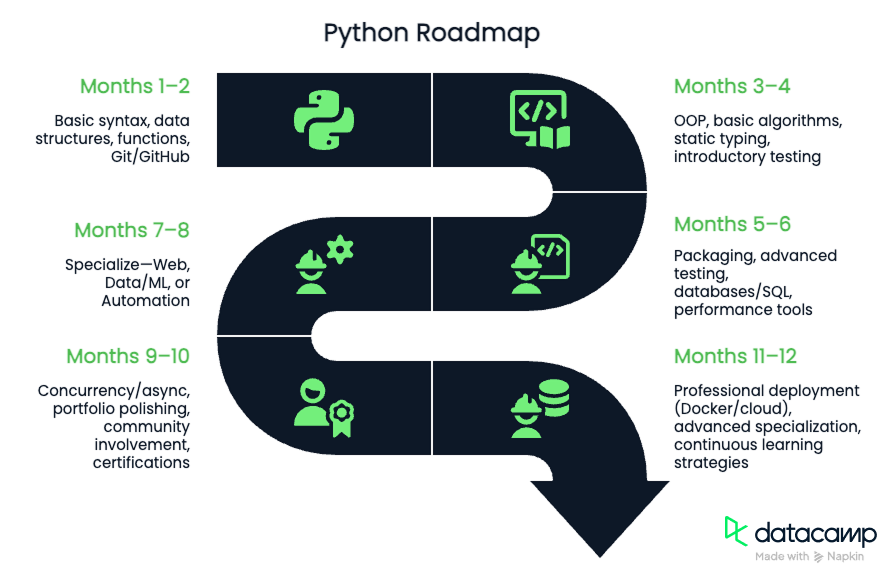
TL;DR: Python Roadmap Milestones
- Months 1–2: Basic syntax, data structures, functions, Git/GitHub.
- Months 3–4: OOP, basic algorithms, static typing, introductory testing.
- Months 5–6: Packaging, advanced testing, databases/SQL, performance tools.
- Months 7–8: Specialize—Web (Django/Flask/FastAPI), Data/ML (pandas/scikit-learn), or Automation (Selenium/API).
- Months 9–10: Concurrency/async, portfolio polishing, community involvement, certifications.
- Months 11–12: Professional deployment (Docker/cloud), advanced specialization, continuous learning strategies.
Months 1–2: Foundational Python Proficiency
Your Python journey starts by building a solid foundation, one that emphasizes practical coding skills over memorizing syntax. By the end of this initial phase, you’ll be confident enough to write, debug, and manage small scripts and projects independently.
Core syntax and computational logic
Start by learning how Python “thinks” and behaves. Focus on:
- Declaring variables and understanding data types: integers, floats, strings, and booleans.
- Conditional logic (if, elif, and else) for decision-making.
- Loops (for and while) to automate repetitive tasks.
Don't just read; code actively. Write small scripts, like number-guessing games or calculators, to internalize these concepts deeply.
Data structures and basic operations
Python excels at handling data efficiently. Master these core structures early:
- Lists: Flexible, ordered collections.
- Tuples: Immutable sequences used for fixed data.
- Sets: Ideal for unique-item tracking.
- Dictionaries: Key-value pairs for efficient data retrieval.
Practice common operations, such as adding, removing, sorting, and filtering data. Work with real-world scenarios, such as simple inventory management or data categorization tasks. Use basic error handling (try-except) to gracefully manage exceptions in your code.
Functions and modular design
Organizing your code into reusable functions is crucial for maintainability:
- Learn to define and invoke functions, passing arguments, and handling return values.
- Experiment with Python's built-in tools (map(), filter(), list comprehensions) for concise data transformations.
- Build simple projects (a calculator or to-do list) by breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable modules.
Essential developer workflow: Git and GitHub
Version control isn’t optional; it's foundational for modern programming. By Month 2, learn how to:
- Initialize repositories, track changes, and commit your work.
- Understand basic branching (main, feature) and merging workflows.
- Publish your early projects to GitHub to showcase your progress and collaborate easily.
Getting comfortable with Git early simplifies your future learning and positions you as a professional from day one.
For data-focused learners
If your long-term goal is data analysis or machine learning, consider exploring these additional libraries by the end of Month 2:
- NumPy: Start working with arrays and basic vectorized operations.
- pandas: Load, clean, and explore simple datasets like CSVs.
- Matplotlib: Create your first line charts, bar plots, or histograms.
Once you’re comfortable with loops, functions, and dictionaries, trying a small real-world dataset can boost your confidence and make Python feel immediately applicable.
Months 1–2: Top resources
- Introduction to Python Course: Interactive primer on variables, basic data types, conditional logic, and loops
- Python Programming Fundamentals skill track: Build up your programming skills in Python. Discover how to create variables, work with various data types, and implement custom logic.
- Python Fundamentals for Data Analysts skill track: Learn the Python basics you need to start on your data analytics journey, including how to clean real-world data ready for analysis.
- Intermediate Python course: Builds on core syntax with more logic control-flow drills and introduces pandas DataFrames for light data manipulation. It’s a smooth bridge between foundational scripts and small projects.
- Introduction to Git Course: A practical walk-through of initializing repos, committing changes, and rolling back mistakes—exactly the version-control basics you want learners to master by Month 2.
- Python Cheat Sheet for Beginners: This cheat sheet provides beginners and intermediate users with a guide to using Python.
- Investigating Netflix Movies Data Science Project: Explore Netflix movie data and perform exploratory data analysis for a production company to uncover insights about movies from a particular decade.
- Introduction to NumPy Course: Get to know Python's popular data science package; NumPy. In four hours, you'll create, sort, filter, and update arrays using New York City's tree census.
- Data Manipulation with pandas Course: This data manipulation with pandas course will show you how to manipulate DataFrames as you extract, filter, and transform real-world datasets for analysis.
- Introduction to Plotting with Matplotlib in Python Tutoiral: Learn how to use Matplotlib, a powerful data visualization library in Python, to create line, bar, and scatter plots with stock market data.
Months 3–4: Intermediate Development Techniques
Now that you've internalized Python’s basics, it’s time to build upon them with intermediate-level skills. You'll start designing structured, maintainable code, reinforcing your foundation with critical development practices and algorithmic thinking. This phase prepares you for collaborative coding and lays the groundwork for more advanced topics down the road.
Object-oriented programming (OOP)
OOP allows you to write code that's both modular and scalable. Begin mastering:
- Defining classes and creating objects to bundle related data and behaviors.
- Core OOP principles: encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism for better organization.
- Special methods (dunder methods like __init__ and __str__) to create intuitive, self-explanatory classes.
- Basic decorators such as @staticmethod and @classmethod.
Practice by designing classes for everyday scenarios, such as an online store system or banking transactions, to internalize these principles naturally.
Algorithmic thinking and efficiency
Efficiency matters, especially as your projects grow. Gain a practical understanding of algorithm fundamentals by learning:
- Big-O notation basics, enabling you to analyze the time and space complexity of your code.
- Fundamental algorithms, including linear search, binary search, and basic sorting techniques (bubble sort, insertion sort, merge sort).
- Practical exercises to compare the performance of various algorithms and appreciate their real-world implications.
Static typing and clean interfaces
Static typing, though optional, dramatically enhances readability and maintainability:
- Understand PEP 484 type annotations and the benefits of strongly typed interfaces.
- Adopt tools like mypy or modern linters (Ruff) to check your code proactively.
- Clearly annotate functions and classes, which will pay dividends as your codebases grow more complex.
Basic testing: Assert and Pytest fundamentals
Reliable code requires testing. At this stage, establish good habits early without overwhelming yourself:
- Use simple assertions to test core logic.
- Start with the basics of pytest: automatic test discovery, test naming conventions, and writing your first tests.
- Learn the value of automated tests in catching bugs early.
Hold off on advanced testing techniques like fixtures and mocks; you'll encounter these naturally as your projects become more sophisticated.
Months 3–4: Top resources
- Intermediate Object-Oriented Programming in Python Course: Goes beyond the basics with multilevel inheritance, operator overloading, dunder methods, and built-in type hints. Perfect for the “encapsulation → polymorphism” stretch goal.
- Data Structures and Algorithms Course: Covers linked lists, stacks/queues, DFS/BFS, and compares bubble vs. merge/quick sort complexities so learners can benchmark code speed.
- Writing Efficient Python Code Course: Teaches timeit, line/memory profiling, and vectorized patterns that slash runtime; an ideal follow-up to algorithm lessons.
- Type Checking in Python Tutorial: A quick, code-heavy guide to PEP 484 annotations, running mypy, and spotting bugs early. Great bridge into Ruff or other linters.
- Introduction to Testing in Python Course: Walks through assertions, pytest discovery, and basic test structuring so learners can start writing reliable code immediately.
- Building a Retail Inventory Management System Project: Design classes for stock, orders, and deliveries, mirroring an “online store” example. Finish with a working CLI app you can show off.
Months 5–6: Advanced Programming Practices and Data Management
In Months 5–6, you’ll elevate your Python skills by focusing on professional-level development practices, packaging your code for sharing and reuse, managing project environments effectively, and working confidently with databases. You'll also level up your testing capabilities, making your applications more robust and maintainable.
Packaging, distribution, and environment management
Writing good code is just half the battle—sharing it with others matters too. In this stage:
- Master Python’s modern packaging ecosystem using pyproject.toml, along with tools such as build, Hatch, or Poetry.
- Understand semantic versioning, dependency management, and publishing packages to PyPI.
- Confidently manage virtual environments, ensuring project dependencies remain isolated and reproducible across different machines.
Practice by creating and distributing your own small libraries or utilities, giving you practical experience that directly aligns with real-world workflows.
Advanced testing: Fixtures, parametrization, and mocking
As your codebase expands, basic tests alone won’t suffice. Learn advanced testing techniques to scale your reliability:
- Use pytest fixtures to manage common test setups, improving test readability and maintainability.
- Employ parametrization to efficiently test multiple inputs and outputs without redundant code.
- Utilize mocking techniques to isolate individual components and test them independently.
You'll practice these skills through targeted mini-projects—like testing a library that interacts with APIs—preparing you for complex real-world scenarios.
Database fundamentals and SQL integration
Almost every Python project interacts with data storage. In this phase, you’ll acquire fundamental database skills:
- Understand core SQL concepts: querying (SELECT), modifying (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE), and joining tables.
- Integrate Python with relational databases using libraries such as SQLite (built-in), SQLAlchemy (ORM), or basic connectors like psycopg2 for PostgreSQL.
- Learn to design efficient database schemas and execute common database operations programmatically from Python.
Solidify your knowledge by building a database-backed application, such as a small inventory management system or a personal finance tracker.
Performance fundamentals: Profiling and debugging
Before diving deep into concurrency later, first become comfortable measuring and optimizing your code:
- Use profiling tools (cProfile, line_profiler) to identify bottlenecks.
- Understand basic memory management with tools like tracemalloc.
- Benchmark critical code paths using timeit.
These techniques help you write efficient code proactively, saving effort later when complexity increases.
Months 5–6: Top resources
- Developing Python Packages Course: Walks you through project scaffolding, pyproject.toml, semantic versioning, setuptools + twine, and the full PyPI publish flow, so learners actually ship a library instead of keeping code on their laptop.
- Python Poetry: Modern And Efficient Python Environment And Dependency Management Tutorial: Step-by-step guide to creating locked virtual envs, adding dependencies, and pushing releases with just poetry build && poetry publish. Perfect practice for isolated, reproducible setups.
- pytest-mock Tutorial: A Beginner’s Guide to Mocking in Python: Builds on basic asserts by introducing reusable fixtures, parametrized tests, and the mocker fixture for isolating API/database calls.
- Introduction to Databases in Python Course: Teaches core SQL queries and then jumps into SQLAlchemy for building schemas, running joins, and writing data back to SQLite/MySQL/PostgreSQL—all from Python.
- Discover SQLAlchemy: A Beginner Tutorial With Examples: Article that reinforces the course with concrete patterns for engine creation, table reflection, and CRUD operations.
- Performing a Code Review Project: Review and make changes on a code project, including logic to ingest, clean, and visualize smartphone data to make sure it follows Python best practices, such as adhering to PEP-8 and DRY principles, as well as readability and documentation.
Months 7–8: Deepen Your Specialization
With foundational and intermediate skills firmly in place, from months 7-8 onwards, you have the opportunity to deepen your expertise. It’s best to choose one specialization aligned with your interests or career goals. Focusing clearly now helps you gain job-ready fluency and confidently build a strong project for your portfolio. Throughout the rest of our Python roadmap, we’ve given several examples for the different paths.
Data science and machine learning specialization
If you’re fascinated by data analysis, modeling, and AI, immerse yourself in:
- Data manipulation using pandas for cleaning, transforming, and analyzing real-world datasets.
- Visualization techniques with libraries like Matplotlib or Seaborn to communicate insights effectively.
- Machine learning workflows using scikit-learn, from preprocessing data to evaluating and optimizing predictive models.
- Deep learning basics with PyTorch or TensorFlow for tackling more complex challenges and working with neural networks.
Complete a well-structured data science project, such as predictive analytics on public datasets, sentiment analysis, or forecasting, clearly documenting your methodologies and conclusions.
Web development specialization
If creating web applications or APIs excites you, dive deep into:
- Django: A robust, full-stack framework ideal for comprehensive applications, complete with built-in authentication, admin panels, and a rich ORM.
- Flask: Flexible and lightweight, perfect for customized APIs and microservices with more explicit control.
- FastAPI: Modern and efficient, best suited for async APIs and high-performance services.
Build a meaningful web project, such as a personal blog, e-commerce site, or a RESTful API that integrates databases and third-party services. Emphasize clear documentation, code structure, and deployment considerations.
Automation specialization (scripting and integrations)
If streamlining processes and building efficiency interests you, focus on practical scripting and automation tasks:
- Master automation libraries such as Selenium (web automation), Requests (API integration), and scheduling tools like Airflow or cron-based automation.
- Integrate external APIs for workflow improvements, like syncing data between platforms or automating reporting.
- Utilize configuration management tools (PyYAML, JSON handling) to automate setup and deployments.
Develop a comprehensive automation project, like a data synchronization tool or automated workflow dashboard, emphasizing clarity, reusability, and real-world utility.
Months 7–8: Top resources
- Machine Learning Scientist in Python Career Track: Discover machine learning with Python and work towards becoming a machine learning scientist. Explore supervised, unsupervised, and deep learning.
- Associate Data Scientist in Python Career Track: Learn data science in Python, from data manipulation to machine learning.
- Python Data Associate Certification: Prove your Python skills are ready for real-world application. Demonstrate your ability to manage data in Python and answer common analysis questions.
- Django Tutorial: Python Web Development: A concise, code-first guide to spinning up models, views, templates, the admin panel, and built-in auth.
- Introduction to FastAPI Course: Walks through async endpoints, validation with Pydantic, and testing; learners end by shipping a fully working REST API.
- Introduction to APIs in Python Course: Hands-on practice with requests, authentication flows, and building simple bots—exactly what you need before orchestrating bigger automations.
- Facial Recognition with Supervised Learning Project: A guided project that walks through building an end-to-end scikit-learn pipeline on a real image dataset.
Months 9–10: Advanced Techniques and Career Readiness
In this phase, your Python skills reach the advanced practitioner level. You'll refine your technical skills, address concurrency if relevant to your specialization, and focus on turning your projects into a coherent portfolio narrative. This stage also introduces important soft skills to position yourself as a collaborative, professional developer ready for career opportunities.
Concurrency and async programming
Concurrency significantly improves your application's responsiveness and scalability. Depending on your chosen specialization, here’s how you can deepen your expertise:
- Data science and ML: Utilize multiprocessing or concurrent execution for intensive data transformations, model hyperparameter tuning, or parallel processing of large datasets.
- Web development: Implement asynchronous endpoints in FastAPI or Django Channels for real-time applications such as chat platforms or streaming dashboards.
- Automation: Use asyncio to concurrently manage API requests, web scraping tasks, or scheduled automation jobs that handle large workloads efficiently.
Master threading versus multiprocessing clearly by identifying I/O-bound versus CPU-bound tasks, and learn to build scalable solutions using Python’s asynchronous capabilities.
Portfolio polishing
Convert your accumulated projects into a cohesive and compelling narrative:
- Data analysis and machine learning: Present comprehensive analysis notebooks, dashboards, or deployed ML models highlighting data-driven decision-making and business impact.
- Web development: Deploy a complete web application with clear documentation, intuitive UI/UX, and CI/CD pipeline integration.
- Automation: Showcase scripts and tools with clear practical utility, such as an automated workflow dashboard, API integration service, or data synchronization tool.
Ensure your GitHub profile is organized, with each project containing informative READMEs and consistent documentation. Additionally, create short articles or blog posts explaining your project methodologies, technical decisions, and key lessons learned.
Soft skills, community, and open source contribution
Effective communication, collaboration, and community involvement significantly boost your professional profile:
- Engage actively in open-source communities, contributing code, submitting improvements, or participating in Python Enhancement Proposals (PEPs).
- Practice conducting code reviews and providing constructive feedback in collaborative environments to sharpen your teamwork skills.
- Attend Python meetups, webinars, conferences, or local tech community events, fostering your professional network and staying up-to-date on industry trends.
Career mapping and certification
Clearly align your skills and projects with potential career opportunities:
- Assess your proficiency clearly using industry-standard skill matrices (Beginner → Intermediate → Advanced → Expert).
- Identify relevant certifications such as AWS Machine Learning Specialty, TensorFlow Developer Certificate, Certified Associate Python Developer, or specific vendor certifications aligned with your chosen specialization.
- Strategically target job roles explicitly aligned with your specialization, such as Python Developer, Data Analyst, Machine Learning Engineer, or Automation Engineer, tailoring your portfolio and narrative to clearly meet job descriptions and market needs.
Months 9–10: Top resources
- Python Multiprocessing: A Guide to Threads and Processes: Contrasts the GIL-bound threading model with true multi-process execution, giving clear benchmarks and code patterns so learners know when to choose each approach.
- Asyncio Tutorial For Beginners: Walks through async/await, event loops, and coroutine design; ideal for building concurrent API aggregators or high-throughput automations.
- Parallel Programming with Dask in Python Course: Shows how to push workloads across cores and clusters while measuring speed-ups, reinforcing the “profile then optimize” habit you introduced earlier.
- Build Your Portfolio By Contributing to Open Source Webinar: Practical guidance on finding “good first issues,” submitting PRs, and showcasing contributions during interviews
- The 8 Best Python Certifications For All Levels in 2025: Compares industry-recognized certs (AWS ML, PCPP, DataCamp Associate, TensorFlow Developer, etc.), making it easy to align your new skills with credible credentials.
- Efficient AI with PyTorch Project: Build and optimize a CNN while learning about model compression and performance profiling—perfect for showing employers you can scale DL models responsibly.
Months 11–12: Advanced Deployment & Professional Readiness
At this advanced stage, you’ll solidify your Python expertise and practical readiness by diving deeper into your chosen specialization. The goal is to prepare yourself for professional roles by mastering deployment techniques, continuous learning strategies, and industry-recognized best practices.
Specialized Path Deep-Dive
Tailor your learning to professional-level readiness based on your chosen specialization:
- Data analysis and machine learning:
- Deepen your expertise in specialized libraries and frameworks, such as advanced pandas techniques, visualization tools, and powerful ML frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch).
- Master model deployment using cloud solutions like AWS SageMaker, Azure ML, or Google AI Platform.
- Understand model monitoring, retraining workflows, and basic MLOps best practices.
- Web development:
- Master Docker and containerization to package and deploy web apps consistently.
- Establish continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines with GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Jenkins.
- Deploy applications on popular cloud platforms (AWS, Heroku, Render) and understand infrastructure management basics.
- Automation:
- Advance your scripting and automation skills, building complex automation workflows with scheduling (Airflow, Prefect), task orchestration, and robust error handling.
- Learn advanced API integration and authentication techniques (OAuth2, JWT).
- Deploy automation solutions using Docker and container orchestration tools to ensure reliability and maintainability.
Optional DevOps and engineering deep-dive
If your goals align specifically with software engineering or DevOps roles, consider:
- In-depth exploration of cloud infrastructure management (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
- Advanced container orchestration with Kubernetes.
- Comprehensive CI/CD pipeline setups for complex applications, covering testing, security scanning, and deployment automation.
Continuous learning and portfolio enhancement
- Regularly revisit and update your portfolio projects, ensuring they're aligned with current industry standards and trends.
- Engage in ongoing professional development through targeted certifications, such as AWS certifications, Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA), or industry-specific Python certifications.
- Stay actively engaged with industry communities, following relevant blogs, podcasts, or technical publications to ensure your Python skills and knowledge remain current and competitive.
By refining your skills strategically in these final months, you’ll emerge fully prepared for professional roles and continuous growth as an advanced Python practitioner.
Months 11–12: Top resources
- MLOps Fundamentals Skill Track: This track covers topics such as MLOps concepts, deployment and life cycling of MLOps, fully automated MLOps, and developing machine learning models.
- Working with APIs in Python Code-Along: Shows how to authenticate, paginate, and automate data pulls, giving you production-ready scripting patterns for everything from ETL jobs to Slack bots.
- Introduction to TensorFlow in Python Course: Moves beyond scikit-learn into neural networks, batching, and GPU-ready workflows—perfect if your next goal is a deep-learning certification or portfolio piece.
- Introduction to Docker Course: Covers the Docker engine, CLI, Dockerfiles, image-hardening best practices, and container orchestration basics, so you can package any Python app for reproducible deployment.
- Introduction to Kubernetes Course: Learn the fundamentals of Kubernetes and deploy and orchestrate containers using Manifests and kubectl instructions.
- CI/CD for Machine Learning Course: Builds full GitHub Actions pipelines, uses DVC for data versioning, and shows true “train → test → deploy” automation—the core of modern CI/CD.
- AWS Concepts Course: Introduces cloud economics, core AWS services, and common deployment models, giving you the cloud vocabulary and hands-on labs you’ll need before shipping a containerized app to production
Conclusion
Your Python learning journey can sometimes feel overwhelming, but with a structured roadmap, it becomes manageable, rewarding, and practical. This 12-month Python roadmap provides clear milestones, essential skills, and guidance tailored to real-world needs. By following this structured approach, you'll not only learn Python effectively but also develop projects and skills employers value most.
But remember: the roadmap is only the beginning. True mastery comes from curiosity, practice, and continuous learning. So choose your path, stay consistent, and start building. Your journey to Python proficiency begins now. Get started with either Python Programming Fundamentals or Python Fundamentals for Data Analysis.

A senior editor in the AI and edtech space. Committed to exploring data and AI trends.