Track
Structured Query Language (SQL) is at the heart of data management, powering analytics and applications across every major industry. Whether you’re setting out to become a data analyst, data scientist, or database administrator, SQL is a foundational skill that opens countless doors.
But with so much to learn, from basic syntax to advanced analytics and cloud platforms, the path can feel overwhelming. Many learners bounce between tutorials without a clear plan, missing key skills along the way.
I’ve created this month-by-month SQL roadmap to provide learners with a structured, practical path. You’ll build your expertise step by step, supported by proven learning strategies and curated resources. The goal is to give you the confidence, skills, and adaptability you need to succeed with your SQL learning.
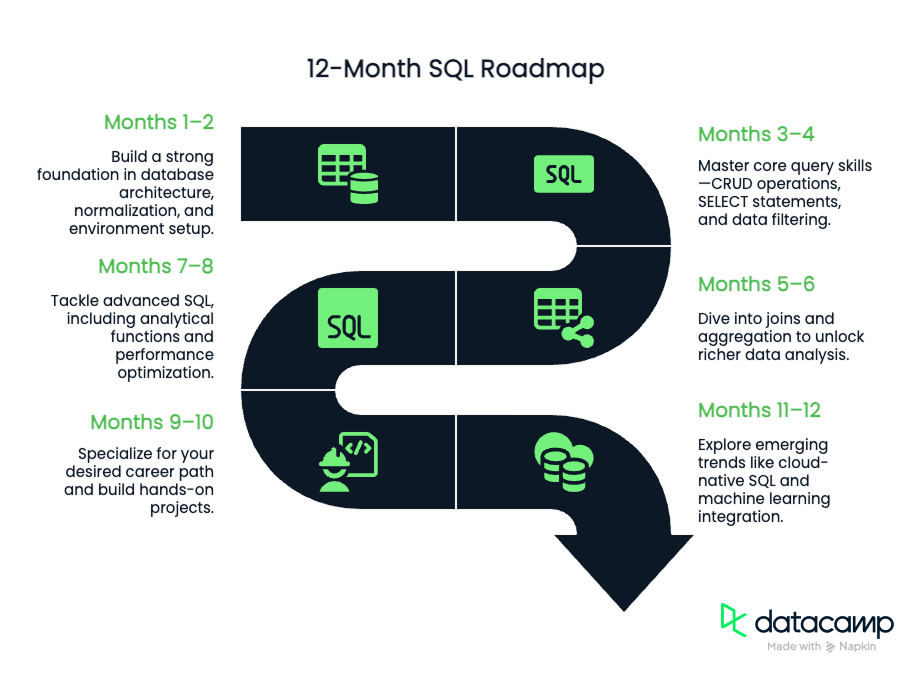
TL;DR: Your 12-Month SQL Roadmap
If you need a quick glance at what the roadmap covers, check out the details and diagram below.
- Months 1–2: Build a strong foundation in database architecture, normalization, and environment setup.
- Months 3–4: Master core query skills; CRUD operations, SELECT statements, and data filtering.
- Months 5–6: Dive into joins and aggregation to unlock richer data analysis.
- Months 7–8: Tackle advanced SQL, including analytical functions and performance optimization.
- Months 9–10: Specialize for your desired career path and build hands-on projects.
- Months 11–12: Explore emerging trends like cloud-native SQL and machine learning integration.
- Ongoing: Keep practicing, benchmarking, and learning with the SQL community.
Months 1–2: Building a Strong Foundation
A successful SQL journey starts with a clear understanding of how data is organized and managed in relational databases. These basics set the stage for everything you’ll do with SQL.
Understanding relational database architecture
Relational databases store data in structured tables, with each table defined by columns and relationships to other tables. Learning about these relationships helps you ensure data consistency, reduce redundancy, and query data efficiently.
Key concepts
- Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS): Platforms like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server structure, secure, and manage your data.
- Normalization: Organizing data to reduce duplication and promote logical relationships. Focus on the first three normal forms (1NF, 2NF, 3NF) to design efficient schemas.
- Primary and foreign keys: Use primary keys to uniquely identify records and foreign keys to connect related tables.
If you’re not sure where to start, both MySQL and PostgreSQL are beginner-friendly, open-source choices with strong community support. PostgreSQL is known for advanced data types, while MySQL is widely used in web applications. Oracle and SQL Server are common in large enterprises.
Setting up your SQL environment
Getting hands-on is the best way to learn SQL. Here’s how to set up:
- Choose your platform: Pick one (like MySQL or PostgreSQL) that aligns with your goals.
- Install locally or use the cloud: Tools such as MySQL Workbench or cloud-hosted services (like AWS RDS) let you create and manage databases easily.
- Explore the interface: Learn the basics; how to create databases, add users, and manage permissions.
Introduction to data definition language (DDL)
Start by learning to define and structure your data.
- Create schemas and tables: Use DDL statements such as CREATE TABLE to design your database.
- Understand data types: Familiarize yourself with types like VARCHAR, INT, and DATE, and when to use each.
- Apply constraints: Use PRIMARY KEY, UNIQUE, NOT NULL, and FOREIGN KEY constraints to maintain data quality.
Resources for months 1–2
- SQL Fundamentals skill track: Learn the SQL fundamentals you need to level up your data skills. Through hands-on exercises, you'll discover SQL basics.
- SQL Basics Cheat Sheet: A handy reference guide to basic querying tables, filtering data, and aggregating data.
- Database Design course: Learn to design databases using star and snowflake schemas, and OLTP and OLAP. You will gain essential skills for creating and managing databases in SQL.
- Types of Databases: Relational, NoSQL, Cloud, Vector: Explore the array of database types, including relational, NoSQL, cloud, vector and more.
- PostgreSQL vs. MySQL: Choosing the Right Database for Your Project: Explore the key differences and similarities between PostgreSQL and MySQL to find the best database solution for your project's needs.
- Analyzing Industry Carbon Emissions project: Once you’ve mastered some of the basics, you can test your skills with a hands-on project.
Months 3–4: Core Query Mechanics
With your environment ready, it’s time to interact with your data. This phase focuses on the essential query and data manipulation skills that every SQL user needs.
CRUD operations: the backbone of data work
CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, and Delete—the four basic ways you interact with any database.
- Create: Insert new data into tables.
- Read: Retrieve data with SELECT statements.
- Update: Change existing records.
- Delete: Remove records you no longer need.
Writing simple queries and filtering results
Start by writing queries to pull out the data you need. The SELECT statement is your primary tool.
- Filter with WHERE: Focus your results on rows that meet specific conditions.
- Sort with ORDER BY: Arrange your output for easier analysis.
- Limit with LIMIT: Control the number of rows returned.
- Use conditional logic: Operators like AND, OR, NOT, and BETWEEN help you refine your searches.
Try extracting practical insights—such as finding customers from a certain region or transactions above a set value.
Resources for months 3–4
- Associate Data Analyst in SQL career track: In this hands-on track, you'll learn how to extract, analyze, and communicate data-driven insights using real-world datasets.
- SQL for Business Analysts: Boost your business SQL skills. Learn how you can use SQL to quickly analyze data and build powerful reports to overcome business problems.
- SQL: Reporting and Analysis: Master SQL for data reporting and daily data analysis by learning how to select, filter, and sort data, customize outputs, and more.
- SQL Order of Execution: Understanding How Queries Run tutorial: Understand the SQL order of execution and how its different from the order of writing.
- Introduction to the WHERE Clause in SQL tutorial: Get an introduction to filtering rows in SQL using the WHERE clause.
- Using ORDER BY Keyword in SQL tutorial: Learn how to use and apply the ORDER BY keyword in SQL.
- How to Use the SQL LIMIT Clause in Combination with SELECT tutorial: Learn the application of the SQL LIMIT clause to filter data.
- What and Where are the World's Oldest Businesses project: With an intermediate project, you can test your skills and find out areas you need to work on.
Months 5–6: Intermediate Query Techniques
Now that you’re comfortable with basic queries, it’s time to expand your skills and answer more complex questions.
Joining tables for richer insights
Data is often spread across multiple tables. Learning to join them unlocks deeper analysis.
- INNER JOIN: Combine records with matching values in both tables.
- LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN: Keep all records from one table, and pull in matching records from the other.
- FULL OUTER JOIN: Get all records when a match exists in either table.
By joining tables, you can link sales with customer details or orders with shipping information—all in a single query.
Aggregating and grouping data
Aggregate functions let you summarize and analyze your data:
- COUNT: Tally the number of records.
- SUM and AVG: Calculate totals and averages.
- GROUP BY: Organize results into categories, like sales by region.
- HAVING: Filter groups based on summary values.
Use these tools to spot trends, track key metrics, or answer business questions.
Resources for months 5–6
- Joining Data in SQL Course: Supercharge your SQL queries by learning to join tables together, apply relational set theory to table joins, and work with subqueries.
- SQL INNER JOIN vs. OUTER JOIN: Key Differences tutorial: Understand SQL INNER JOIN vs. OUTER JOIN with examples and visual aids to enhance your database management skills.
- SQL LEFT JOIN vs. LEFT OUTER JOIN: What You Need to Know tutorial: Explore practical examples and discover how to apply these joins effectively in your queries.
- Aggregate Functions in SQL tutorial: Learn how to use aggregate functions for summarizing results and gaining useful insights about data in SQL.
- Intermediate SQL: Learn how to filter, compare, and summarize data with SQL. You'll also get a taste of aggregate functions, sorting, grouping, and how to present data neatly.
- SQL Joins Cheat Sheet: With this SQL Joins cheat sheet, you'll have a handy reference guide to joining data in SQL.
- SQL Subquery: A Comprehensive Guide: Discover how to master SQL subqueries to enhance your database queries. Learn about correlated, non-correlated, and recursive subqueries.
- Analyze International Debt Statistics project: Get more hands-on experience as you investigate international debt data collected by The World Bank.
Months 7–8: Advanced SQL Concepts
With intermediate skills in place, you’re ready to tackle advanced SQL techniques that unlock new levels of analysis and performance.
Analytical (window) functions
Window functions let you perform calculations across sets of rows without losing row-level detail. They’re essential for time-based analysis, financial modeling, and complex reporting.
- Ranking and windowing: Functions like RANK(), DENSE_RANK(), ROW_NUMBER(), and LAG() help analyze sequences, trends, and group behavior.
- Partitioning data: Use PARTITION BY to apply functions within subgroups of your data.
These skills help you deliver insights that go beyond basic reporting.
Optimizing queries for performance
Fast, efficient queries matter as data grows. Performance optimization helps your analyses and applications run smoothly.
- Understand execution plans: See how the database processes your queries and find bottlenecks.
- Leverage indexes: Speed up queries by indexing frequently searched columns.
- Choose the right join strategies: Write queries that minimize resource usage and return results quickly.
Regular optimization can make a huge difference as your projects scale.
Resources for months 7–8
- SQL Window Functions Cheat Sheet:
- With this SQL Window Functions cheat sheet, you'll have a handy reference guide to the various types of window functions in SQL.
- PostgreSQL Summary Stats and Window Functions: Learn how to create queries for analytics and data engineering with window functions, the SQL secret weapon.
- Improving Query Performance in PostgreSQL: Experience firsthand how changes in filtering methods and using subqueries impact query performance.
- SQL Materialized View: Enhancing Query Performance tutorial: Understand how materialized views improve query performance in SQL databases.
- Analyzing Unicorn Companies project: With this advanced project, you’ll figure out how many companies reached a valuation of over 1 billion dollars across different industries in a given time period.
Months 9–10: Professional Development and Specialization
At this point, you’ve developed robust SQL skills. Now, it’s time to tailor your expertise to your career goals and showcase your abilities through real-world projects.
Aligning SQL skills with your career path
SQL is used differently depending on your role. Consider focusing on:
- Database Administrator: Dive into backup and restore, managing users, replication, and high availability.
- Data Analyst: Emphasize ad-hoc queries, building reports, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines, and analytics.
- Data Engineer: Deepen your knowledge of data modeling, automation, and complex performance tuning.
Explore industry certifications like Oracle OCP, Microsoft MCSE, or AWS Database Specialty to validate your expertise.
Building projects and benchmarking skills
Hands-on projects are the best way to solidify knowledge and show employers what you can do.
- Real-world projects: Analyze sales funnels, predict customer churn, or aggregate IoT sensor data.
- Benchmarking: Use tools like EXPLAIN ANALYZE to measure and improve your queries.
Projects not only reinforce your skills but also build a portfolio to demonstrate your capabilities.
Resources for months 9–10
- SQL for Business Analysts track: Boost your business SQL skills. Learn how you can use SQL to quickly analyze data and build powerful reports to overcome business problems.
- Associate Data Engineer in SQL: Accompanied at every step with hands-on practice queries, this course teaches you everything you need to know to analyze data using your own SQL code.
- When Was the Golden Age of Video Games? SQL project: In this advanced project, you’ll analyze the top 400 best-selling video games released since 1977 to identify whether or not the gaming market has improved with time and when its most flourishing epoch was.
- The Best SQL Jobs in 2025: Career Paths and Opportunities: Discover the top jobs that use SQL in 2025. Learn why SQL is essential, how to get started, and explore high-demand career paths with SQL skills.
- SQL Developer Salaries: Benchmarks for 2025: Learn what an SQL developer does, what factors impact SQL developer salaries, how the average SQL developer salary compares to the average salaries of other developer profiles.
Months 11–12: Future Trends and Advanced Topics
As SQL evolves, so should your skills. This final phase introduces you to the cutting-edge areas shaping the future of data.
Embracing cloud-native SQL and serverless databases
With more data moving to the cloud, SQL platforms have adapted to offer greater scalability and flexibility.
- Serverless databases: Services like AWS Aurora automatically handle scaling, making them ideal for variable workloads.
- HTAP systems: Hybrid Transactional/Analytical Processing platforms enable real-time analytics alongside traditional transaction processing.
Stay up to date with new SQL standards, such as SQL:2023, which bring features like native JSON support and advanced pattern matching.
Integrating machine learning with SQL
Modern SQL engines often support in-database machine learning, letting you analyze and predict without moving data.
- Embedded ML functions: Run predictive analytics directly in SQL—for example, to segment customers or forecast trends.
- Handling semi-structured data: Use SQL to work with JSON, arrays, and other flexible data types, which are increasingly common.
Keeping pace with these trends ensures your SQL skills remain in demand.
Resources for months 11–12
- Amazon Aurora: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Get Started tutorial: This practical guide walks you through setting up, managing, and optimizing Amazon Aurora, with insights on performance tuning, security, and cost management.
- PostgresML Tutorial: Doing Machine Learning With SQL: Learn how to perform machine learning using SQL statements in PostgresML.
- 10 Portfolio-Ready SQL Projects for All Levels: Practice your SQL skills, develop new ones, and create an outstanding professional portfolio.
- Top 85 SQL Interview Questions and Answers for 2025: Get interview-ready with this comprehensive overview of essential SQL questions and answers for job hunters, hiring managers, and recruiters.
- Top 30 SQL Server Interview Questions (2025): A curated list of SQL Server interview questions and answers, covering topics from basic concepts to advanced techniques
- Top 34 MySQL Interview Questions and Answers For 2025: Master MySQL with this guide to interview questions, with real-world examples and expert tips to help you excel in your next database interview
Conclusion
Learning SQL is a rewarding process when approached with structure and curiosity. This 12-month roadmap is designed to guide you from foundational knowledge to advanced expertise, supporting your growth every step of the way.
Keep practicing, build real projects, and stay engaged with the SQL community. As the world of data evolves, SQL remains a vital tool, one that will continue to open doors in your data career. Get started today with the SQL Fundamentals skill track.
SQL Roadmap FAQs
What’s the difference between SQL and NoSQL databases?
SQL databases are relational; they use structured tables and are great for complex queries and consistent data. NoSQL databases handle unstructured data with high flexibility. While both have advantages, SQL remains a go-to for analytical and reporting needs.
How do I optimize complex SQL queries?
Start by reviewing your query’s execution plan. Index columns you search often, avoid unnecessary joins or subqueries, and use features like materialized views to speed up results. DataCamp’s query performance tutorials offer step-by-step tips.
What are some common SQL mistakes to avoid?
Watch out for missing indexes, using inefficient queries like SELECT *, mishandling NULL values, and skipping input validation. Stay on top of best practices and seek out feedback from the SQL community to improve.
How can I effectively practice SQL queries?
Work with real-world datasets and challenges. Set up your own SQL environment to experiment, or try DataCamp’s interactive projects. Frequent practice, especially on practical tasks like building dashboards or analyzing sales data, builds skill and confidence.

A senior editor in the AI and edtech space. Committed to exploring data and AI trends.