Track
Meta recently released Meta Movie Gen, which is both a significant and somewhat unexpected event in the text-to-video generation landscape—I don’t think Meta was on many people’s radar when it comes to video generation.
Given the competitive environment, with several high-profile companies such as OpenAI already working on robust models like Sora, Meta's release is noteworthy.
The model performs well across various tasks, outperforming or matching the quality of offerings from established players like Runway Gen3, LumaLabs, and, notably, OpenAI's Sora.
In this blog, I'm going to cover what Meta Movie Gen is, how it works, its capabilities and limitations, and the safety considerations surrounding its use.
If you want to get an overview of the video generation field, I recommend going over this article on top AI video generators.
What Is Meta Movie Gen?
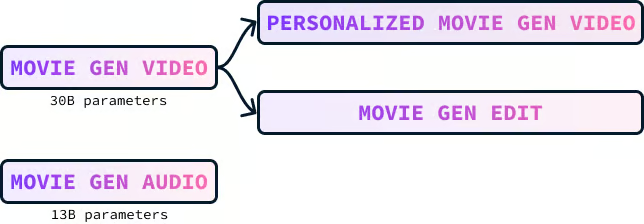
Meta Movie Gen is a collection of foundational models for generating various types of media, including text-to-video, text-to-audio, and text-to-image. It consists of four models:
- Movie Gen Video
- Movie Gen Audio
- Personalized Movie Gen Video
- Movie Gen Edit
Movie Gen Video model
Movie Gen Video is a 30-billion-parameter model designed to create images and videos based on text descriptions. The model can generate high-quality videos up to 16 seconds long that match the given text prompt. It can produce content in different sizes, resolutions, and lengths.
Here’s an example of a video generated with the prompt:
“A sloth with pink sunglasses lays on a donut float in a pool. The sloth is holding a tropical drink. The world is tropical. The sunlight casts a shadow.”
The water reflections in the video are remarkable. I also found the shadows on the face of the sloth to be quite interesting. These small details, when executed well, often go unnoticed. However, they are striking and disrupt the illusion when done poorly.
Movie Gen Audio model
Movie Gen Audio is a 13-billion-parameter model that can create video soundtracks that match the content of a video. It can also generate audio from a text prompt.
It generates high-quality, 48kHz audio that syncs with videos of different lengths, even several minutes long. The model can also produce ambient sounds, matching unseen sources in the video, sound effects that sync with actions, and fitting background music.
Here’s an example of the music and sound effects generated for one of the videos using the prompt:
“Rustling leaves and snapping twigs, with an orchestral music track.”
Note that the mood of the music track wasn’t present in the prompt. The model was able to pick up the mood from the video's content.
Personalized Movie Gen Video model
The Movie Gen Video model can generate videos of a chosen person based on a text description and an image of that person. The video keeps the person's identity intact while following the text prompt.
The following example was generated by combining the selfie of the person with the prompt:
“A woman DJ spins records on a rooftop in LA. She is wearing a pink jacket and giant headphones. There is a cheetah next to the woman. The background is a cityscape.”
In my opinion, this model stands out as their crown jewel because it shows huge potential if incorporated into their other products, such as Instagram. Imagine users creating videos featuring themselves in various scenarios, all generated from a single image and a text prompt. This could lead to an explosion of creative and engaging content.
Movie Gen Edit model
The Movie Gen Edit model lets us easily make detailed and creative changes to real and made-up videos using just text instructions.
The model has the potential to revolutionize video editing workflows across various industries. Its ability to accurately understand and execute text-based editing instructions could significantly improve the editing process, making it faster, more efficient, and accessible to a wider range of users. This technology could benefit filmmakers, content creators, educators, and anyone who works with video content.
How Does Movie Gen Video Work?
The training of the Movie Gen Video model involved several key components: data collection and preparation, the training process itself, fine-tuning for enhanced quality, and the upsampling techniques used to achieve high-resolution outputs.
Data and pre-processing
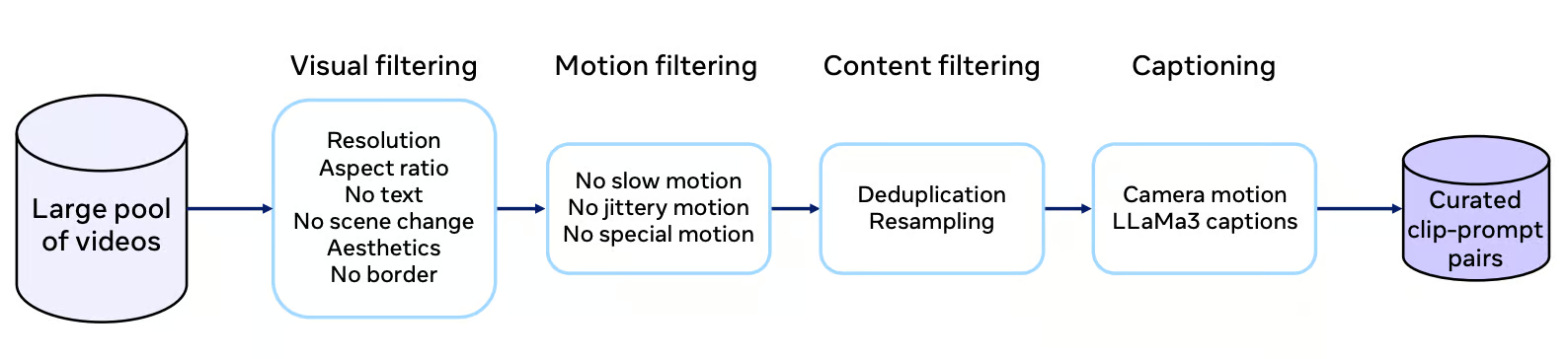
The Movie Gen Video model was trained on a massive dataset containing hundreds of millions of video-text pairs and over a billion image-text pairs.
Each video in the dataset undergoes a rigorous curation process that involves filtering for visual quality, motion characteristics, and content relevance. The filtering process aims to select videos with non-trivial motion, single-shot camera work, and a diverse range of concepts, including a significant portion featuring humans.
Source: Movie Gen research paper
High-quality captions are very important for effectively training the model. Movie Gen Video uses the LLaMa3-Video model to generate detailed captions that accurately describe the video content. These captions go beyond simply labeling objects; they include descriptions of actions, camera movements, and even lighting information. This rich textual information helps the model learn a more nuanced understanding of visual storytelling.
Training process
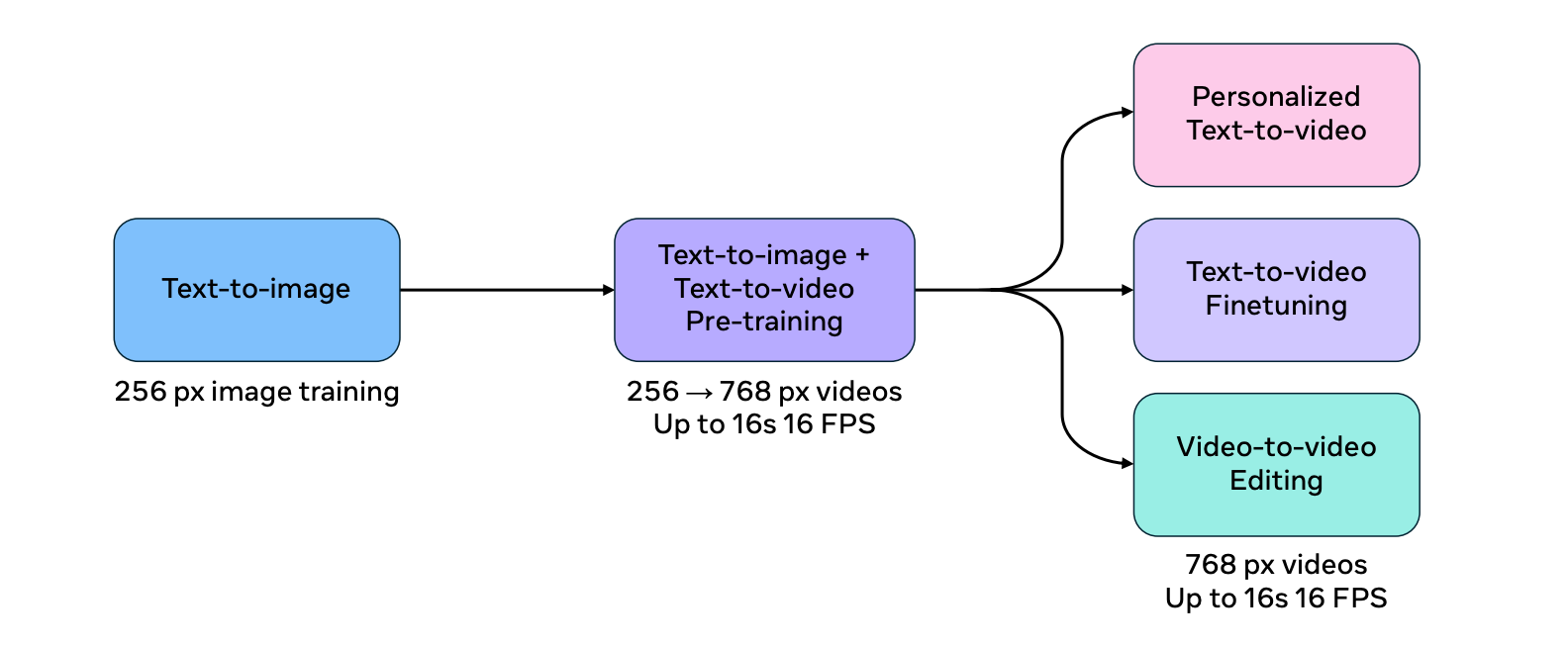
The training process for Movie Gen Video is divided into several stages to improve efficiency and model scalability.
The model is first trained on the text-to-image task using lower-resolution images. This "warm-up" phase allows the model to learn fundamental visual concepts before tackling the more complex task of video generation.
The model is then trained jointly on both the text-to-image and text-to-video tasks, progressively increasing the resolution of the input data. This joint training approach helps the model use the abundance and diversity of image-text datasets while also learning the complexities of video generation.
Source: Movie Gen research paper
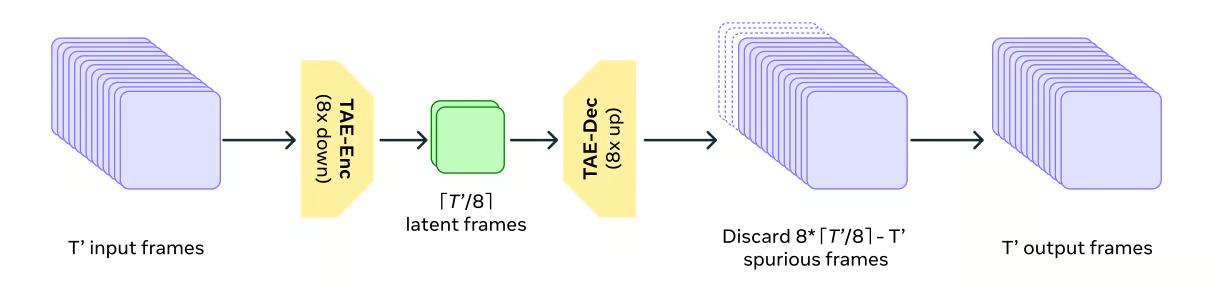
To handle the computational demands of video data, Movie Gen Video uses a Temporal Autoencoder model (TAE) to compress and decompress the videos in time. This is analogous to zipping and unzipping files on a computer, allowing the model to work with a more manageable representation of the video data.
Source: Movie Gen research paper
Movie Gen Video uses a training objective called Flow Matching. Instead of directly generating the final video, flow matching guides the model to gradually transform a sample of random noise into the desired video output, step by step.
Flow Matching involves predicting the velocity of samples in the latent space rather than directly predicting the samples themselves. This method is more efficient and performant than traditional diffusion-based methods.
Fine-tuning
To improve the quality and aesthetics of the generated videos, the model undergoes supervised fine-tuning using a smaller set of manually curated videos with high-quality captions. This is like an artist refining their technique through expert guidance, leading to more visually appealing and realistic video outputs.
The final Movie Gen Video model is created by averaging multiple models trained with different datasets, hyperparameters, and pretraining checkpoints. This technique helps combine the strengths of different models, leading to more robust and reliable performance.
Upsampling
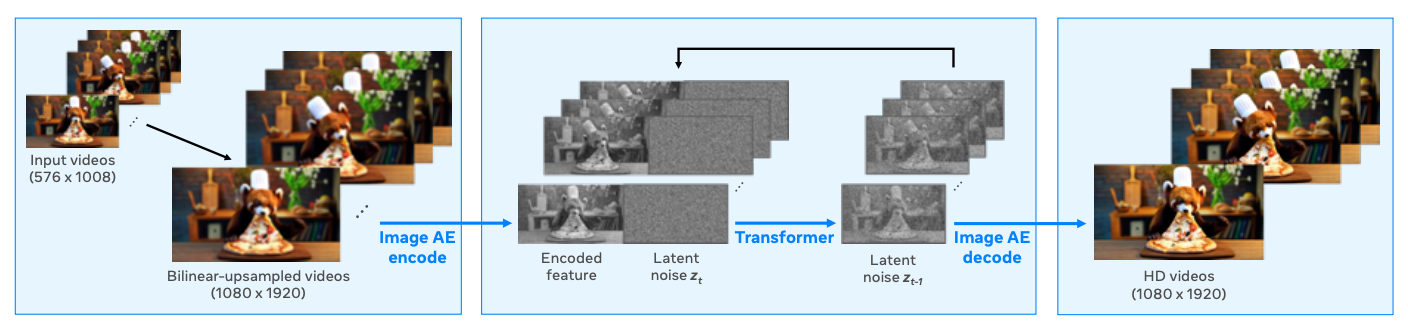
The model produces videos at a resolution of 768 pixels and uses upsampling to exchange the resolution to full HD 1080p, resulting in sharper and more visually appealing videos. This approach is commonly used because it provides a computationally efficient solution since the base model can process fewer tokens while still producing high-resolution outputs.
The Spatial Upsampler functions as a video-to-video generation model. It takes the lower-resolution video as input, upsamples it to the target resolution using bilinear interpolation, and then encodes it into a latent space using a frame-wise Variational Autoencoder (VAE).
A latent space model then generates the latents of the HD video, conditioned on the encoded latents of the lower-resolution video. Finally, the VAE decoder transforms the resulting HD video latents back into the pixel space, producing the final high-resolution output.
Source: Movie Gen research paper
Evaluation the Movie Gen Model
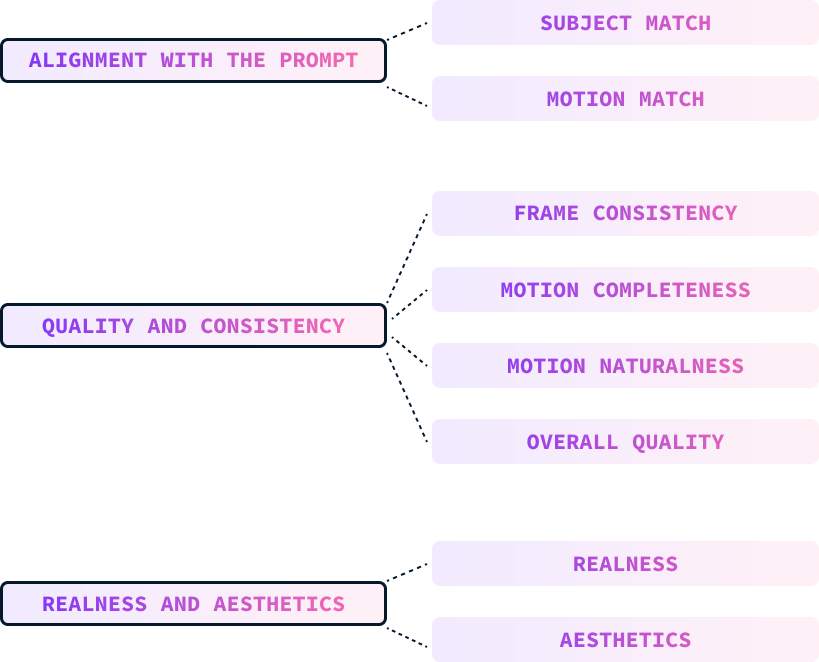
Evaluating a text-to-video model is more challenging than a text-to-image model because of the added temporal dimension. The Meta team used three main measures to evaluate the model:
- Alignment with the prompt
- Quality and consistency
- Realness and aesthetics
These parameters are evaluated manually by humans who grade the videos according to these parameters.
Alignment with the prompt
Prompt alignment measures how well the generated video matches the input text prompt, including descriptions of the subject, motion, background, and other details. This is further broken down into:
- Subject match: Focuses on the alignment of subject appearance, background, lighting, and style.
- Motion match: Assesses the alignment of motion-related descriptions.
Quality and consistency
The quality and consistency of the generated video are evaluated independently of the text prompt. This measure is broken down into:
- Frame consistency: Checks for inconsistencies or artifacts in object appearance, lighting, and background across frames.
- Motion completeness: Assesses whether the video contains a sufficient amount of motion, particularly for unusual subjects or activities.
- Motion naturalness: Judges the realism and naturalness of the motion, considering aspects like limb movement, facial expressions, and adherence to physics.
- Overall quality: A holistic judgment that considers the balance of the previous three sub-axes to determine the overall goodness of the video.
Realness and aesthetics
Evaluators were asked to rate the model's ability to produce photorealistic and aesthetically pleasing videos. This criteria is divided into:
- Realness: Assesses how closely the video resembles a real video, or for fantastical prompts, how well it mimics a realistic art style.
- Aesthetics: Judges the visual appeal of the video based on factors like content, lighting, color, and camera effects.
Evaluation benchmark
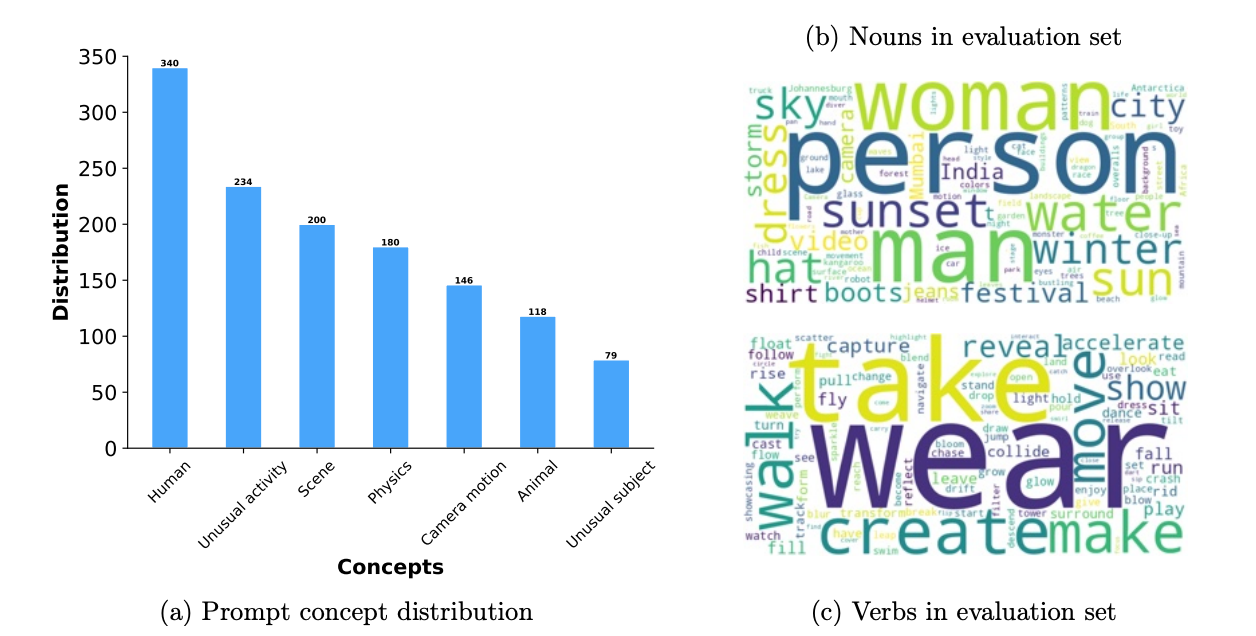
The benchmark data was designed to evaluate video generations comprehensively. It includes 1,000 prompts that cover various testing aspects, such as human activity, animals, nature, physics, and unusual subjects or activities.
Their benchmark is over three times larger than those used in previous studies. Each prompt is tagged with a motion level (high, medium, low) to assess generation quality across different motion intensities.
The evaluation uses the entire prompt set and examines specific testing metrics, particularly focusing on how well models handle unusual subjects and motions to test their generalization capabilities.
The following diagram shows a breakdown of the prompts used in the evaluation. On the left, we are given the distribution of the concepts of the prompts. On the right side, we see common nouns and verbs used inside the prompts (the bigger the word, the more frequent it is):
Source: Movie Gen research paper
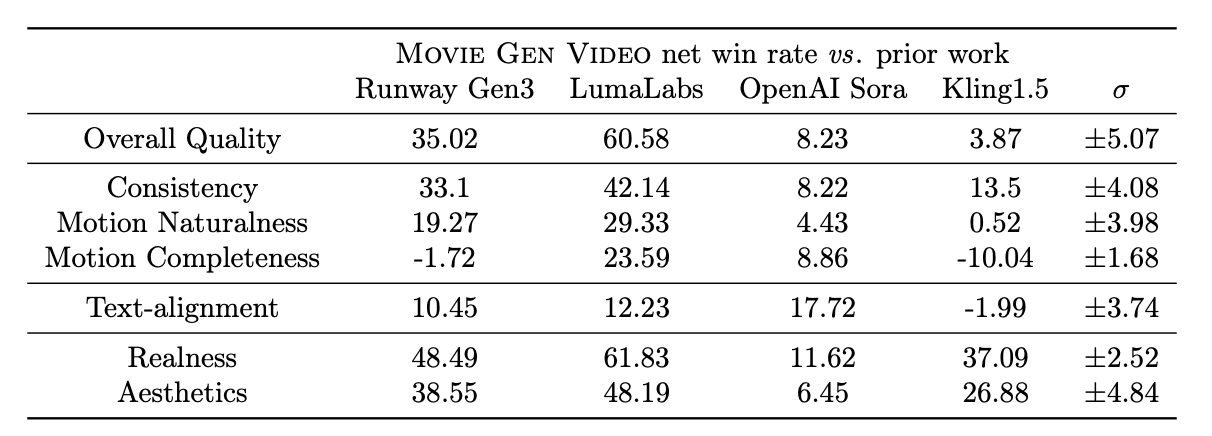
The table below shows the results of the human evaluation of the videos produced by different models over several evaluation criteria. The numbers represent net win rates which are calculated as (Win % - Loss %). It ranges from -100 (complete loss) to 100 (complete win), with 0 indicating a tie.
Source: Movie Gen research paper
Meta Movie Gen vs. Sora vs. Runway Gen 3
According to their experiments, Movie Gen Video has strong performance in text-to-video generation, outperforming several existing models, including commercial systems like Runway Gen3 and LumaLabs, based on human evaluations using the MovieGen Video Bench. Specifically, Movie Gen Video shows significant advantages in:
- Overall quality: Evaluators consistently rated Movie Gen's outputs as having higher overall quality, particularly in terms of visual fidelity, motion naturalness, and alignment with the text prompts.
- Motion naturalness and consistency: Movie Gen exhibits a significant edge in generating videos with natural and consistent motion, outperforming Runway Gen3 and OpenAI's Sora in these aspects. This strength is likely attributed to the model's ability to learn and simulate real-world physics through its Flow Matching training objective and the extensive use of video data during training.
- Realness and aesthetics: Movie Gen also excels in generating videos with higher realness and aesthetic appeal compared to Runway Gen3, LumaLabs, and Kling1.5.
While MovieGen generally outperforms other models, Kling1.5 sometimes generates videos with larger motion magnitudes, although at the cost of distortions and inconsistencies. This highlights the trade-off between motion completeness and visual quality, where Movie Gen Video prioritizes generating realistic and consistent motion over simply maximizing movement magnitude.
Below are some screenshots from the Meta Connect 2024 presentation showcasing a few comparison examples of video generation prompts:

Source: Movie Gen research paper
Here are some comparison examples of video personalization where a photo is used to generate a personalized video:

Source: Movie Gen research paper
Finally, the screenshots below showcase comparison examples of video editing:

Source: Movie Gen research paper
Overall, it seems that Meta Movie Gen pushed the bar and set a new standard in text-to-video models. The evaluation procedure highlighted in the paper appears fair but, of course, it’s hard to know for sure unless these models become publicly available and neutral third parties can compare them.
Model Limitations
While Meta Movie Gen looks great in media generation, there are still areas for improvement.
The model sometimes struggles with complex scenes involving intricate geometry, object manipulation, and realistic physics simulations. For example, generating convincing interactions between objects, accurately depicting state transformations (like melting or shattering), and realistically simulating the effects of gravity or collisions can still pose challenges for the models.
Audio synchronization can be problematic in certain scenarios. Specifically, when dealing with motions that are visually small, occluded, or require a high level of visual understanding to generate the corresponding sound, the models may struggle to achieve perfect synchronization. Examples of such challenges include accurately synchronizing footsteps with a walking person, generating appropriate sounds for objects that are partially hidden from view, and recognizing subtle hand movements on a guitar to produce the correct musical notes.
Additionally, the Movie Gen Audio model, as currently designed, does not support voice generation.
Safety Considerations and Model Release
Realistic AI-generated videos bring significant risks and ethical challenges that must be considered. These risks include the manipulation of trust and the spread of misinformation through deepfakes, which could damage reputations, misinform the public, and harm businesses.
On one hand, it can be an Instagram feature that lets me create a cool video with myself in it to share with my friends but on the other hand, the same feature makes it possible for me to create a fake video of someone else. As these technologies improve, it may become impossible to distinguish them from the real thing.
AI-generated content poses privacy threats, potentially leading to extortion, blackmail, or cyberbullying.
Moreover, these AI tools could undermine art and copyright by mimicking unique art styles without credit. Solutions involve spreading awareness and education about media literacy, investing in detection technology, establishing legal and ethical frameworks, and employing watermarking for authentication.
While AI video generation holds great potential, it requires careful handling to maintain trust and authenticity.
Meta has been open with its AI developments by open-sourcing the Llama models. However, for safety reasons, the Meta Movie Gen models aren’t going to be released yet. According to their article, multiple improvements and safety considerations are required before deploying them.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we introduced Meta's Movie Gen models, a suite of AI models for generating and editing videos using text prompts.
We explored the four distinct models, their capabilities, and how they work. Through a comparative analysis, we showcased how Meta Movie Gen stacks up against other AI video generation tools.
While Meta Movie Gen has set a new benchmark in the field, the technology's potential misuse raises significant concerns. Meta has acknowledged these risks and is taking a cautious approach to releasing these models.
To learn more about Meta AI’s ecosystem, I recommend these blogs:
FAQs
When will Meta Movie Gen be released?
Meta hasn't announced a specific release date for Movie Gen. It's currently focused on research and development, aiming to improve the model's capabilities and address potential issues before a wider release. While there's no official timeline, I think it's possible that Meta might initially integrate Movie Gen features into their existing platforms like Instagram or Facebook, rather than releasing the full model directly.
How long can the Meta Movie Gen be?
Currently, Meta Movie Gen can generate videos up to 16 seconds long. This limitation might be due to the computational demands of generating longer, high-quality videos. Future developments could potentially extend the maximum video length.
Will Meta Movie Gen be open-sourced?
Meta hasn't confirmed whether Movie Gen will be open-sourced. However, they have a history of open-sourcing some of their AI models, like Llama. It's possible that they might choose to open-source parts of Movie Gen or release it under a specific license to encourage research and development by the broader AI community.
What's the video quality of Meta Movie Gen?
Meta Movie Gen generates videos in 1080p HD resolution, providing high-quality output suitable for various applications.