Course
Working with artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning (ML) with a need for a text-to-speech engine? In that case, you're going to need an open-source solution. Let's explore how text-to-speech (TTS) engines work and some of the best open-source options.
In this simple guide, I'll share more about TTS engines and list down some of the best options available.
What Is a Text-to-Speech (TTS) Engine?
Before we get started with the list, let's quickly define what a text-to-speech engine actually is.
A text-to-speech engine is a software that converts written text into spoken words. It utilizes natural language processing (NLP) to analyze and interpret written text and then uses a speech synthesizer to generate human-like speech.
TTS engines are commonly used in applications such as virtual assistants, navigation systems, and accessibility tools.
Interested in working with NLP? DataCamp’s Natural Language Processing in Python skill track will help you get your technical know-how up to speed.
What Are Open-Source Text-to-Speech (TTS) Engines?
Open-source Text-to-Speech (TTS) engines are valuable tools for converting written text into spoken words, enabling applications in accessibility, automated voice responses, and virtual assistants, among other areas.
They are usually developed by a community of developers and released under an open-source license, allowing anyone to use, modify, and distribute the software freely.
The 7 Best Open Source Text-to-Speech (TTS) Engines
Here are some well-known open-source TTS engines:
1. MaryTTS (Multimodal Interaction Architecture)
A flexible, modular architecture for building TTS systems, including a voice-building tool for generating new voices from recorded audio data.
Here's an overview diagram of the architecture behind this engine:
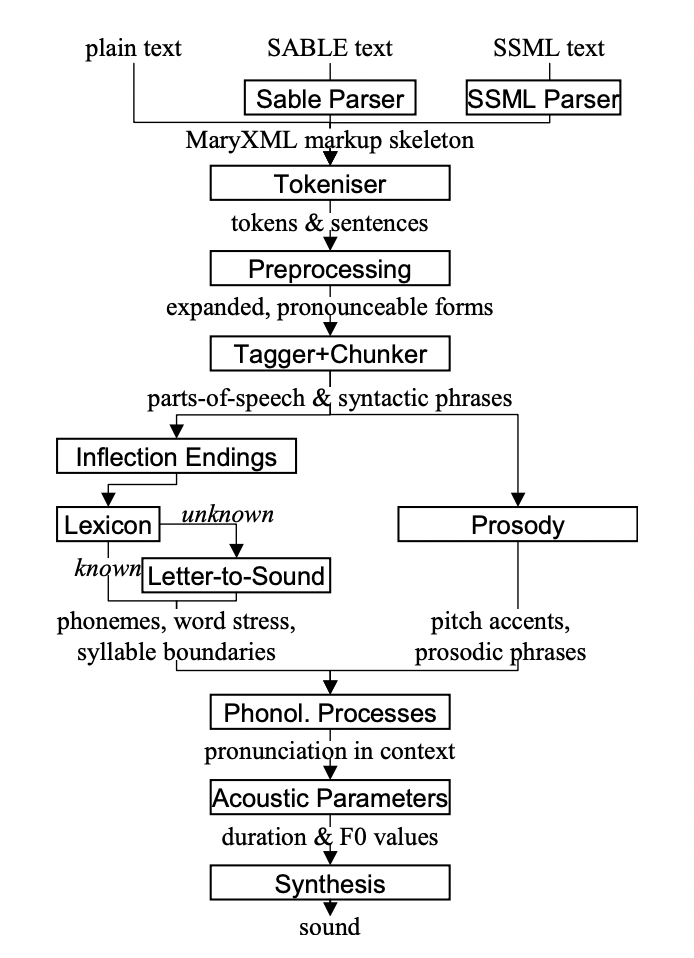
Source: MaryTTS GitHub
This architecture includes some basic components such as:
- A markup language parser: A component that reads and interprets the markup language used in the text field.
- A processor: A component that takes in the parsed text and performs any necessary actions, such as converting it to speech or generating visual output.
- A synthesizer: A component responsible for producing the final output, whether it be audio or visual. It helps to add speech characteristics, such as intonation and inflection, to make the output sound more natural.
Pros: The MaryTTS architecture is highly customizable, allowing developers to create their own parsers, processors, and synthesizers to fit their specific needs. This also allows for flexibility in integrating the software into different platforms and applications.
Cons: Due to its highly customizable nature, there may be a learning curve for developers who are unfamiliar with markup language and text-to-speech technology.
Link: GitHub
2. eSpeak
 A compact open-source software speech synthesizer for English and other languages, eSpeak produces clear and intelligible speech across a wide range of languages. It's known for its simplicity and small footprint.
A compact open-source software speech synthesizer for English and other languages, eSpeak produces clear and intelligible speech across a wide range of languages. It's known for its simplicity and small footprint.
eSpeak can be run on various platforms, including Windows, Linux, macOS, and Android.
Pros: Easy to use, supports many languages and voices.
Cons: Limited features and customization options, and written in C.
Link: GitHub
3. Festival Speech Synthesis System
Developed by the University of Edinburgh, Festival offers a general framework for building speech synthesis systems as well as including examples of various modules. It's widely used for research and educational purposes.
The figure below shows the general utterance structure of Festival. It involves a tree shape with links between nodes showing a relation.
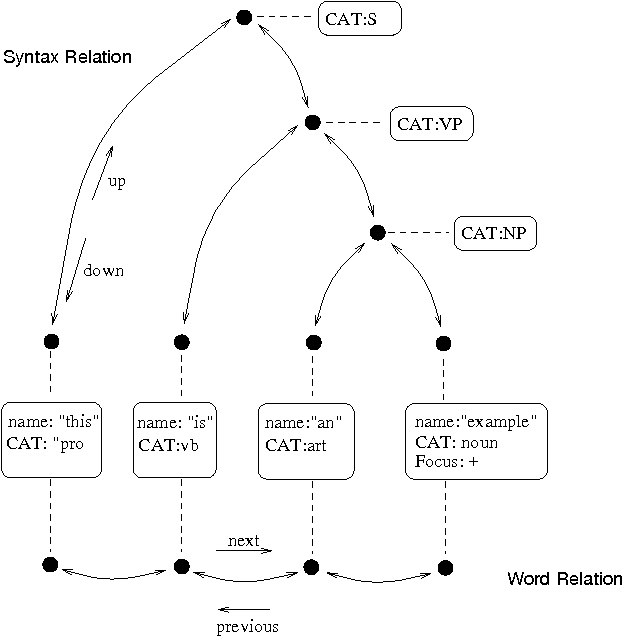
Source: Semanticscholar
Pros: Highly customizable, suitable for research purposes.
Cons: Difficult to use for beginners, requires some coding knowledge.
Link: GitHub
4. Mimic
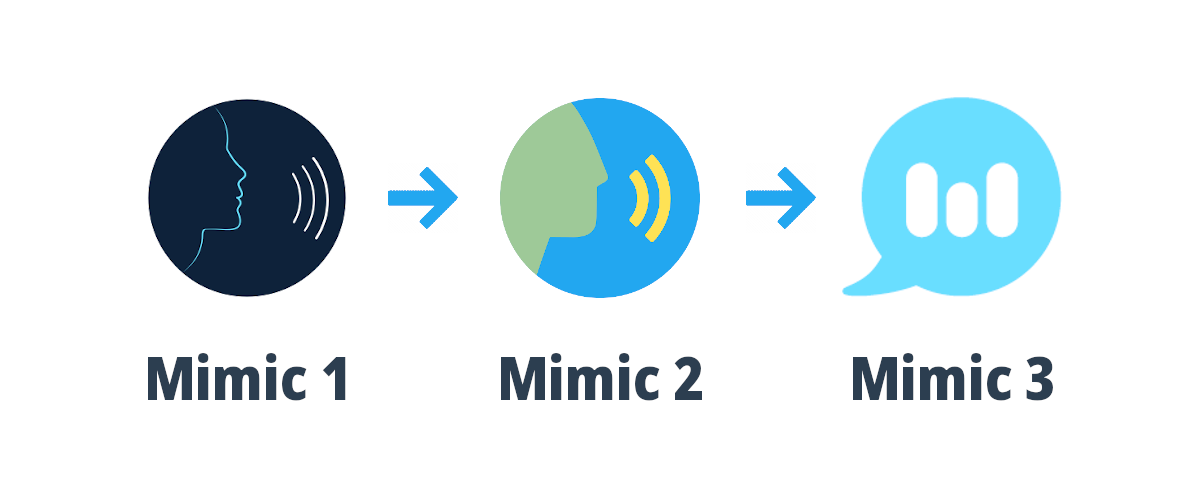
Source: Mimic
Developed by Mycroft AI, Mimic is capable of producing highly natural-sounding speech. It includes Mimic 1, based on the Festival Speech Synthesis System, and Mimic 2, which uses deep neural networks for voice synthesis.
Pros: Offers both traditional and modern voice synthesis methods and supports multiple languages.
Cons: Limited documentation.
Link: GitHub
5. Mozilla TTS
A deep learning-based TTS engine that aims to create more natural and human-like speech synthesis. It leverages modern neural network architectures, particularly sequence-to-sequence models.
Pros: Uses advanced technology for more natural speech and is free to use.
Cons: Limited language support.
Link: GitHub
6. Tacotron 2 (by NVIDIA)
Although not an engine per se, Tacotron 2 is a neural network model architecture for generating natural speech. Open-source implementations of Tacotron 2 are available, and it has inspired many developments in speech synthesis technology.
This system allows users to synthesize speech using raw transcripts without any additional prosody information.
Pros: Developed by NVIDIA, good to be used as a neural network model.
Cons: Requires some technical knowledge to implement.
Although this engine can be quite technically difficult to master, you can always familiarize yourself with related neural network models through online resources. One such place would be our neural networks guide or our tutorial on neural networks.
Link: GitHub
7. ESPnet-TTS
Part of the ESPnet project, this TTS engine is designed for end-to-end speech processing, including both speech recognition and synthesis. It uses modern deep-learning techniques to generate speech.
Pros: Modern and flexible, supports multiple languages.
Cons: Requires some technical knowledge to implement.
Link: GitHub
8. Coqui TTS
Coqui TTS is a modern open-source text-to-speech framework that provides an array of pre-trained models for various languages and accents. Built on top of TensorFlow, it supports neural network-based TTS models like Tacotron 2, FastSpeech, and more.
Pros:
- Offers pre-trained models for quick deployment.
- Highly modular, enabling users to experiment with different neural TTS architectures.
- Actively maintained with a strong community and detailed documentation.
Cons:
- Requires familiarity with deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch.
- Resource-intensive for training custom models.
Link: GitHub
9. Larynx
Larynx, developed by the Mycroft AI team, is an advanced TTS system that offers high-quality voice synthesis with support for multiple languages. It is based on Tacotron 2 and WaveGlow for natural-sounding speech generation.
Pros:
-
Produces realistic and human-like voice synthesis.
-
Supports a wide range of languages and voices out of the box.
-
Simple to set up and use compared to other neural TTS engines.
Cons:
-
Requires significant computational resources for training and inference.
-
Limited customization options compared to some other engines.
Link: GitHub
Open-Source TTS Engines Compared
| TTS system | Architecture | Pros | Cons | Use cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MaryTTS | Modular architecture | Highly customizable, flexible integration | Learning curve for developers | Ideal for developers and researchers creating customized TTS applications, especially in accessibility projects. |
| eSpeak | Compact open-source synthesizer | Simple, supports many languages | Limited features and customization | Suitable for applications requiring a wide range of language support and minimal system resources. |
| Festival | General framework with examples of modules | Highly customizable, suitable for research | Difficult for beginners, requires coding | Best for academic research and development projects needing deep customization and experimentation. |
| Mimic | Traditional and neural network synthesis | Natural-sounding speech, supports multiple languages | Limited documentation | Well-suited for high-quality voice synthesis projects, like virtual assistants or multimedia apps. |
| Mozilla TTS | Deep learning-based, seq-to-seq models | Advanced technology for natural speech, free to use | Limited language support | Ideal for developers using cutting-edge deep learning techniques for natural-sounding TTS. |
| Tacotron 2 | Neural network model for speech generation | Good as a neural network model | Technical knowledge required | Perfect for research and development in neural network-based speech synthesis. |
| ESPnet-TTS | End-to-end speech processing | Modern and flexible, supports multiple languages | Technical knowledge required | Aimed at developers and researchers working on advanced speech synthesis and recognition projects. |
| Coqui TTS | Neural TTS with pre-trained models | Pre-trained models, modular, strong community support | Requires familiarity with deep learning | Great for advanced customization, supporting accents and languages, suitable for ML practitioners. |
| Larynx | Tacotron 2 and WaveGlow | High-quality, human-like voice synthesis | Resource-intensive, limited customization | Ideal for natural-sounding voice assistants, voiceovers, or accessibility applications. |
Applications of TTS Engines
Here are some ways the above TTS engines can be used:
1. Virtual assistants
Through the use of text-to-speech engines like the ones mentioned above, virtual assistants can be made. These virtual assistants can be similar to enterprise voice assistants such as Siri and Alexa.
Some of them can even be used for accessibility assistance for users with visual impairments, allowing them to hear written text instead of reading it.
2. Automatic voice responses with AI voice
TTS engines are also used in automated response systems, such as phone or chatbot assistants. These engines can read out responses based on specific prompts and interactions, providing a more human-like experience for users.
3. Video and image voiceover
Text-to-speech technology can also generate voiceovers for videos or images, allowing for more dynamic and engaging content.
For example, the eSpeak engine can be used to add voiceovers to videos in different languages, making them more accessible and appealing to a wider audience.
This is especially useful for applications in marketing, e-learning, and entertainment industries.
Challenges of Using Open-Source TTS Engines
Using an open-source option can be cost-effective and offers more flexibility for customization. However, there are some challenges that come with using these engines:
1. Limited language support
Many open-source TTS engines have limited language support compared to commercial solutions.
This limitation may be a barrier for users who need TTS in less commonly used languages.
2. Customization and implementation
Most open-source TTS engines require some coding knowledge to customize and implement. This makes it hard for regular business stakeholders to use them without technical support.
This may be a challenge for individuals or organizations without technical expertise.
3. Cost considerations
While open-source engines are free to use, they may require additional resources and time for customization and implementation.
Additionally, an engineer or analyst with the relevant know-how of TTS engines has to be hired or trained.
Therefore, in some cases, commercial solutions may be more cost-effective in the long run.
4. Support and documentation
Having limited resources and being community-driven, open-source projects may not always have extensive support and documentation available.
Source: ESPnet Documentation
This can make it challenging for users to troubleshoot issues or learn how to use the engine effectively.
However, as these engines continue to gain popularity and more developers contribute to them, this challenge may diminish over time.
5. Security and performance
Since open-source engines are developed and maintained by a community, there may be concerns about security and performance.
However, these risks can be mitigated through proper vetting and monitoring of the engine's code and updates.
Additionally, choosing reliable and reputable open-source projects can help alleviate these concerns.
Choosing The Best Engine for TTS Integration
Let's now discuss how to go about selecting the right engine for your text-to-speech model.
Here are some factors to consider:
1. Purpose and use case
Start by identifying your specific use case and the purpose of using TTS. Understand what features and customization options are necessary for your project, and then choose an engine accordingly.
2. Language support
If you require support for a particular language or multiple languages, make sure to select an engine that offers such capabilities.

In that case, going for the eSpeak engine may be a better option for you.
3. Cost and budget
Consider your budget and resources before selecting an engine. While open-source options may be cost-effective in the long run, they may require additional resources for customization and implementation.
4. Technical expertise
Evaluate the skill level of your team or yourself when working with TTS engines. If you do not have technical expertise, consider opting for a commercial solution that offers user-friendly interfaces and support.
5. Performance and quality
Ensure that the engine you choose provides high-quality, natural-sounding speech output. You may also want to test different engines to see which one best matches your desired level of performance.
Final Thoughts
Text-to-speech technology has come a long way in providing more natural and human-like speech output. With numerous open-source options available, it’s now more accessible and cost-effective to integrate TTS into various applications.
However, you'll also have to expect some limitations and challenges that come with using open-source engines before making a decision. I hope this guide has provided a greater understanding of TTS engines and helped you in selecting the best one for your needs.
Looking for ways to do this process in reverse? Check out our Spoken Language Processing in Python course.
Master NLP in Python Today
FAQs
What factors should be considered when deciding between open-source and commercial TTS engines?
Open-source TTS engines are generally free and offer flexibility for customization, but they may require technical expertise, have limited language support, and offer less documentation and support. Commercial solutions might be more user-friendly, provide more extensive language options, and come with dedicated support, but they can be costly. The decision should be based on budget, technical skill level, specific project requirements, and desired customization.
How do the voices generated by TTS engines compare to human speech in terms of naturalness and clarity?
The naturalness and clarity of voices generated by TTS engines can vary significantly. Engines leveraging modern neural network technologies like Tacotron 2 and Mozilla TTS tend to produce more human-like, natural-sounding speech. Simpler engines like eSpeak may produce clear but more robotic-sounding speech. Testing different engines and adjusting parameters can help in achieving a desired level of naturalness.
Are there any ethical considerations when using TTS technology in applications?
Yes, ethical considerations include ensuring the technology is used responsibly and not for deceptive purposes, such as mimicking real people's voices without consent. Accessibility improvements should respect privacy and data security. Developers should also be mindful of potential biases in TTS models that could affect the representation of different accents or dialects.
What are some common challenges developers face when integrating TTS engines into applications?
Developers may face challenges such as dealing with limited language support, requiring coding skills for customization, the need for additional resources for implementation, potential security vulnerabilities, and the complexity of achieving high-quality, natural-sounding speech. Additionally, varying documentation levels and community support can impact the ease of integration.
Can TTS engines be used for real-time applications, and what are the potential limitations?
TTS engines can be used for real-time applications like live virtual assistants or automated customer service systems. Limitations may include processing delays, the need for efficient hardware to reduce latency, and the challenge of maintaining high-quality speech output in real-time. Ensuring low latency and high performance is crucial for a seamless user experience.
How can developers contribute to improving open-source TTS engines?
Developers can contribute by participating in the community, reporting issues, submitting bug fixes, and developing new features or languages. They can also help improve documentation and create tutorials or guides for new users. Engaging with the community through forums and GitHub repositories can foster collaboration and innovation.
How do TTS engines handle text with complex intonations or emotions?
TTS engines, especially those utilizing modern neural networks, are increasingly capable of handling complex intonations and emotions by analyzing contextual cues in text. Some advanced engines can modulate pitch, pace, and tone to simulate human emotions. However, achieving nuanced emotional expression remains a challenge and an area of ongoing research.

I'm Austin, a blogger and tech writer with years of experience both as a data scientist and a data analyst in healthcare. Starting my tech journey with a background in biology, I now help others make the same transition through my tech blog. My passion for technology has led me to my writing contributions to dozens of SaaS companies, inspiring others and sharing my experiences.



