Course
In an age where 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are produced each day, data literacy has become a critical skill. The rapid rise of data has not only transformed how we do business, but it also demands a new set of competencies from every organization's workforce.
Organizations that invest in organization-wide data literacy are more than twice as likely to report transformational outcomes across dimensions such as quality of decision-making, innovation, customer experience, and more. This emphasizes the importance of understanding data and leveraging it effectively. Now, more than ever, it's vital for leaders to drive data literacy within their organizations.
In this article, we’ll explore what data literacy is, what the most important data literacy concepts are, how you can drive data literacy within your organization, and more. And if you're looking to build your own data literacy program, be sure to check out The Secret to Successful Data Literacy Programs Webinar.
Empower Your Team with Data Literacy
Enhance your team's data literacy and decision-making capabilities with DataCamp for Business. Access diverse courses, hands-on projects, and centralized insights for teams of 2 or more.

What is Data Literacy?
Data literacy is the ability to read, write, analyze, communicate, and reason with data. It’s a skill that allows individuals and organizations to make better, data-driven decisions.
As with other key competencies, it’s not a one-size-fits-all concept; multiple facets make up data literacy. It is more than just data analysis; instead, it involves understanding what data means and how to present those findings, including the ability to:
- Read data. The ability to interpret data in various forms, such as graphs, charts, or reports. For example, being able to read a company's annual financial report and understand its performance.
- Work with data. The collection and production of data, which can mean setting up an experiment to collect data or creating a survey to gather insights.
- Communicate with data. The ability to use data to tell a story or make a case. A good example would be using customer data to create a business case for a new product.
- Reason with data. Navigating ambiguity with data and leveraging data to drive business decisions.
As an individual skillset, the term data literacy suggests a binary. However, this is far from the case. It’s a spectrum that ranges from the ability to make data-driven decisions and tell data stories to more advanced data science, data engineering, and machine learning skills.
From an organizational perspective, leaders should think of data literacy in terms of a scale of fluency. An organization with high degrees of data literacy encompasses a wide range of data skills within its workforce.
Why is Data Literacy Important?
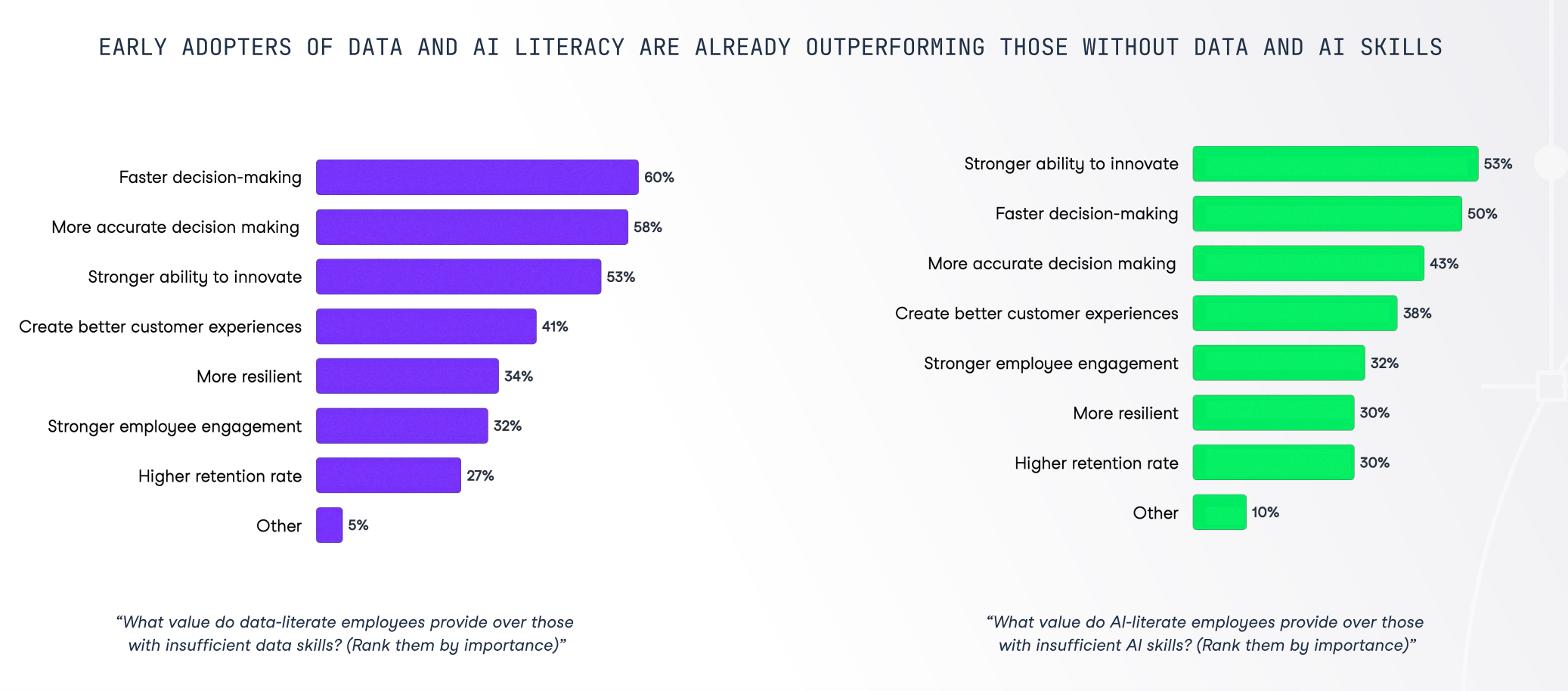
Data literacy, the ability to navigate and interpret the vast digital information landscape, is fast becoming an essential life skill and a valuable asset in the job market. In our State of Data & AI Literacy Report, we asked leaders in the UK and the USA how they view the value of data literacy within their organization and how important it is a skillset for individuals to develop.
The need for data and AI literacy - The State of Data Literacy Report
Why is data literacy important for individuals?
Data literacy skills are attractive to employers
Our report confirms the importance business and data leaders attach to a data-literate workforce. The report indicates that 40% of leaders in the US and UK view decreased productivity as the primary risk of insufficient data skills, with inaccurate decision-making (39%), slower decision-making (37%), and hindered innovation (31%) also posing substantial risks.
Leaders are proactive in mitigating these risks, with 79% prepared to offer higher salaries to candidates with strong data literacy skills. Among them, 21% are ready to propose a salary increase of 10-15%, and over a quarter would consider a 30% salary premium. These figures reaffirm the premium value attached to data literacy in the contemporary business landscape.
Data literacy skills foster responsible digital citizenship
More broadly, data literacy can help build a more engaged population. Over the past two years, we’ve seen the rise of awe-inspiring AI tools like ChatGPT and Sora AI that generate human-like text and images.
Unfortunately, while the beneficial use cases for these tools are endless, they can also be used to accelerate and power misinformation. This sentiment is echoed by Anjali Samani, Director of Data Science & Data Intelligence at Salesforce.
She believes that, in a time of fake news, deepfakes, and post-truth politics, data literacy is more important than ever.
Everyone should become data literate. Everyone should teach kids how to be data literate and ask important questions about the data and the world around them. In the past, you could say seeing is believing. But with deepfakes and AI-powered misinformation, we can no longer say that. If you're not asking the right questions about the data and the technologies we see, you could be doing yourself and future generations a disservice.
Anjali Samani, Director of Data Science & Decision Intelligence at Salesforce
Why is data literacy important for organizations?
Data literacy skills help organizations improve performance
Investing in comprehensive data literacy programs yields substantial benefits for organizations, setting them apart from their competitors.
According to respondents to our State of Data & AI Literacy Report, data upskilling programs significantly enhance the quality (75%) of decision-making, with 88% saying this is the case when combined with AI training.
This prompts a ripple effect, accelerating improvements in innovation (75% improved, 52% substantial), customer experience (81% improved, 60% substantial), and employee retention (82% improved, 69% substantial).
Critically, these enhancements are not isolated to process improvements. They also lead to tangible business outcomes, including revenue maximization (81% improved, 69% substantial) and cost reduction (85% improved, 65% substantial). It is no surprise that organizations have seen these enhancements.
As Jordan Morrow, author of Be Data Literate put it on the DataFramed podcast, data literacy creates comfort within the organization to use data, which drives results.
Data literacy is about creating comfort and confidence in utilizing data within the organization, and it doesn’t mean everyone has to become super technical or be something they are not, but it means everyone is able to drive results with data
Jordan Morrow, Author of Be Data Literate
Data literacy is a key component of driving a data culture
A data culture refers to an environment where decisions are consistently backed by data and everyone within the organization, regardless of their role, is encouraged and empowered to use data in their work. It is a culture of inquiry, curiosity, and data-informed decision-making.
This culture, however, is threatened by low data literacy levels, a challenge most keenly felt by Chief Data Officers (CDOs). CDOs frequently cite inadequate data culture and skills as significant obstacles to their success.
Sudaman Thoppan Mohanchandralal, Founder of NautilusPrinciple, a Data & Analytics strategy advisory firm, and Former Chief Data Officer at Allianz Benelux, emphasizes this point.
Sudaman argues that a data culture is not just an optional luxury but critical to a company's success. He states, "Data culture is not just an option; it is mission critical." This sentiment underlines the vital role of data literacy in driving a successful data culture.
Data culture is not just an option; it is mission critical.
Sudaman Thoppan Mohanchandralal, Founder of Nautilus Principle, and Former Chief Data Officer at Allianz Benelux
AI literacy is also becoming increasingly important for individual and organisation - we have a separate guide on AI literacy here.
Key Data Literacy Skills Organizations Should Develop
While every organization should look at data literacy in the context of its organizational culture and mission, we can start off with a framework of data literacy skills every organization should look to develop in its people.
Specifically, these skills can be divided according to the definition of data literacy, of reading, writing, analyzing, communicating, and reasoning with data.
You can check out the framework by reading our State of Data Literacy 2024 report. Alternatively, you can also download an editable version of the framework.
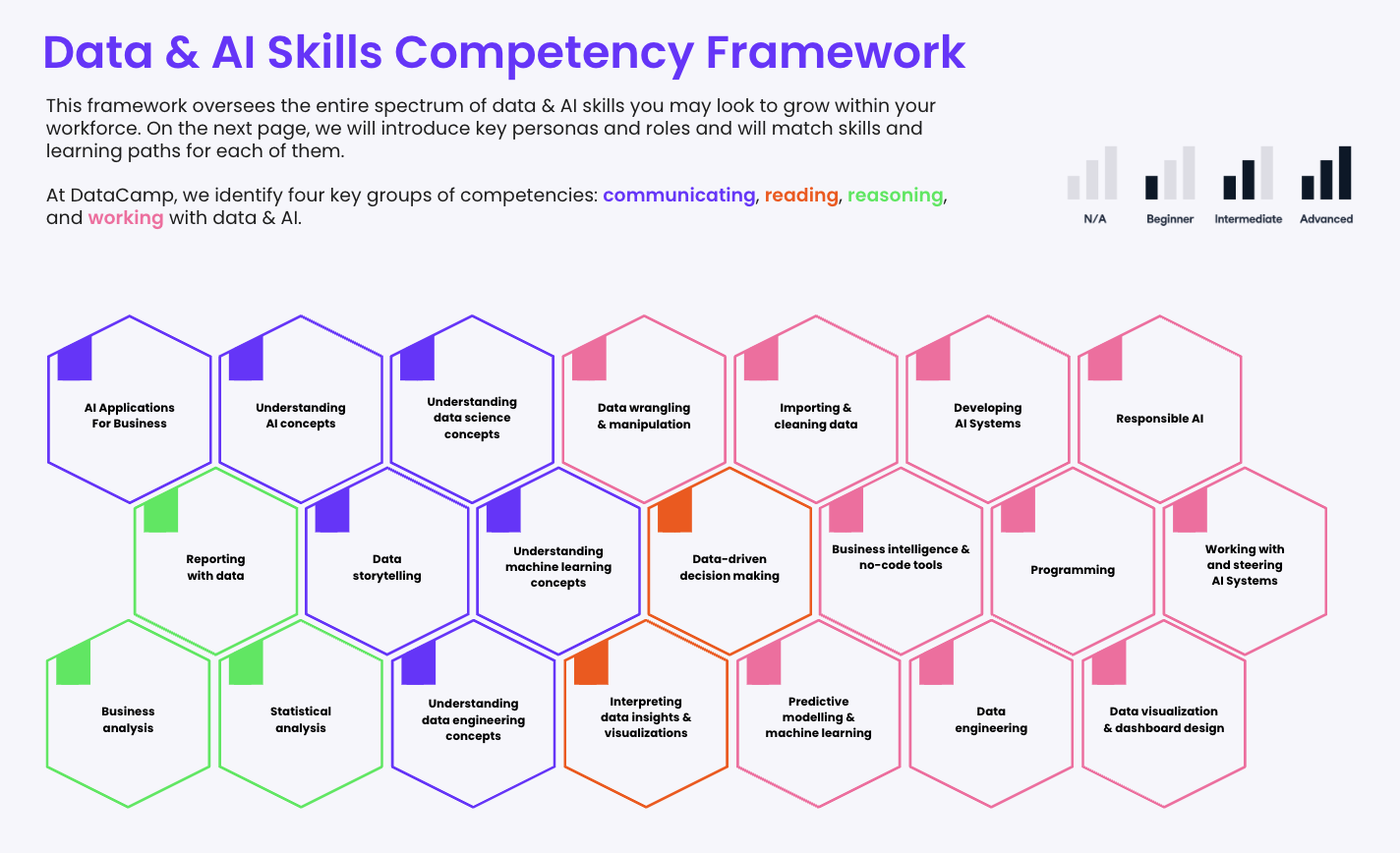
The data and AI competency framework
Read data
This skill focuses on understanding the data and using that understanding to make informed decisions. It could be data from a report or dashboard about a particular aspect of the business.
- Interpreting data insights and visualizations. Being able to understand and make sense of data-based findings and their representations.
- Data-driven decision-making. Using data and analysis to inform business decisions.
Writing and analyzing data
The next level of complexity comes in the form of working with data in a less processed way. This could mean capturing and processing information or using raw data to create visualizations that explain it.
- Data wrangling and manipulation. Transforming and organizing data for analysis.
- Predictive modeling and machine learning. Training and using predictive models to make predictions about future events.
- Data engineering. Designing and building the infrastructure and processes for collecting, storing, and analyzing data.
- Programming. Mastery of programming languages to perform data-related tasks.
- Importing and cleaning data. Reading data from various sources and ensuring they are of free of data quality issues.
- Data visualization and dashboard design. Creating graphical representations of data and designing interactive dashboards for data exploration and analysis.
Communicating with data
This factor is an extension of the two mentioned above. As well as taking data and making it presentable, this skill is about explaining that data to non-experts in a way that is understandable. Often, this means understanding more advanced data topics.
- Data storytelling. The art of effectively communicating insights and findings from data analysis.
- Understanding data science concepts. Being knowledgeable and conversational about the methods, theories, and tools used in the field of data science.
- Understanding data engineering concepts. Being familiar with the processes and technologies involved in the design, construction, and maintenance of data pipelines and infrastructure.
- Understanding machine learning concepts. Being knowledgeable about the possibilities and limitations of machine learning, and the techniques used to train and operate predictive models.
Reasoning with data
The final data literacy skill organizations need is for individuals to be able to reason with data. This means extrapolating data insights to make strategies and gain insights into micro and macro trends, and pulling this information together to present findings.
- Business analysis. Using data and analysis to understand and improve business processes and operations.
- Statistical analysis. Using statistical methods to analyze and make inferences from data.
- Reporting with data. Presenting data-based findings and insights in a clear and concise manner.
Who is Responsible for Data Literacy
As businesses increasingly embrace data-driven approaches, the question of who should drive data literacy within the organization becomes paramount. Many stakeholders are invested, from Chief Information Officers to Chief Marketing Officers and beyond, but the responsibility may best fit with the Chief Data Officer (CDO).
The advent of the Chief Data Officer role is a testament to the growing importance of data for organizations. In the past ten years alone, the number of Chief Data Officers within organizations has increased sevenfold, going from 12% in 2012 to 82.6% in 2023. Chief Data Officers are mandated with ensuring data is treated as an asset within the organization, and that includes enabling everyone with the mindset and skills to take advantage of data within their day-to-day tasks.
Organizations without a dedicated CDO can assign the task to other data leaders, but it's essential that the role not be solitary. The Learning and Development function or Chief Learning Officer should co-own this endeavor, helping to assess current skills and contextualize data literacy within the organization's future skill set. You can learn more about who owns the data literacy agenda in this podcast.
3 Critical Data Literacy Challenges Organizations Face
In the State of Data & AI Literacy 2024 report, we sought to understand from data & learning leaders at the forefront of data and AI literacy upskilling what their most pressing challenges were.
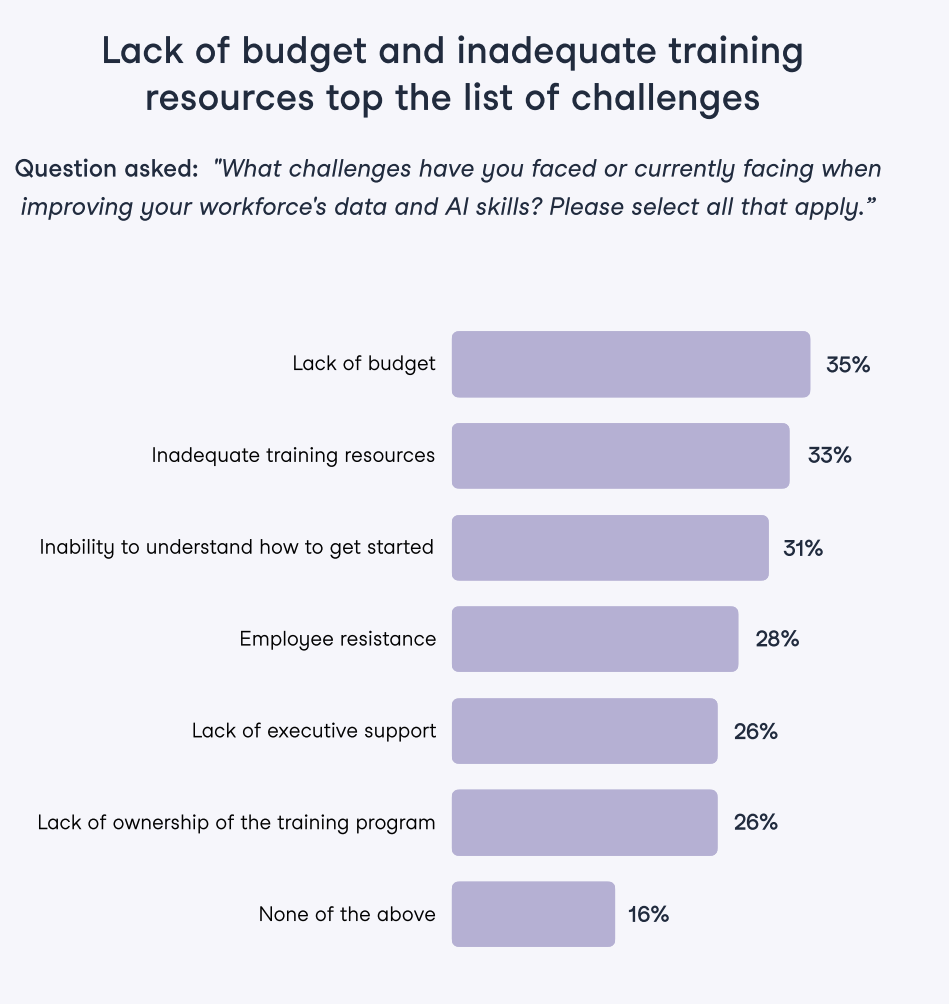
The challenges of building a data literacy program - The State of Data & AI Literacy Report 2024
Looking at these challenges more broadly, we can easily group them into three distinct categories:
- Executive sponsorship, comprising lack of ownership, lack of executive support, and lack of budget.
- Learning experience and outcomes, which covers inadequate training resources.
- Cultural, focusing purely on employee and cultural resistance and adoption of data upskilling.
Let’s break down how to combat these three challenges.
1. Executive sponsorship
When surveyed about the biggest challenges leaders face when improving their workforce’s data skills, the biggest culprits were related to executive sponsorship. Namely, these four factors stood out as their challenges:
- Lack of budget (35%)
- Inability to understand how to get started (31%)
- Lack of executive support (26%)
- Lack of ownership of the training program (26%)
Executive sponsorship challenges suggest that many organizations have yet to devise comprehensive data strategies that put people at the center of data transformation.
According to Vijay Yadav, Director of Quantitative Sciences & Head of Data Science at the Center for Mathematical Sciences at Merck, successful data strategies also mean prioritizing culture and skills transformation initiatives.
Data culture and skills are a big part of a successful data strategy. Because ultimately, what leaders need to understand is whether everybody in the company sees data as an asset and, if so, how do they see it?
Vijay Yadav, Director of Quantitative Sciences & Head of Data Science at the Center for Mathematical Sciences at Merck
So how can leaders gain executive sponsorship when approaching data literacy programs?
According to Valerie Logan, CEO of the Data Lodge, it’s all about communicating the two sides of ROI for data literacy: the return on investment and the risk of ignoring. You can listen to Valerie’s insights on DataFramed here.
2. Learning experience and outcomes
The second biggest set of challenges leaders discussed when approaching data literacy programs are learning experience related.
33% of leaders pointed to inadequate training resources as the biggest challenge when upskilling for data literacy. We dug deeper here and asked leaders who use third-party learning providers what their biggest challenges were with their learning providers.
29% of respondents stated that video-based only learning makes it difficult to apply learned skills in the real world.
Additionally, 29% of respondents stated that employees struggle to understand where to start learning, with 24% stating that even if they do understand where to get started, the skills people learn are not relevant to their roles.
These results showcase how traditional learning providers center their learning content around a large breadth of video-based content and resources, which, counterintuitively, makes it difficult for employees to know where to begin and apply their skills.
The easiest way to avoid such challenges is by partnering with the correct learning provider.
At DataCamp, interactive, curated learning is at the heart of our learning philosophy. To see that in action, you can learn more about DataCamp for Business customer stories in the case study section below.
Training 2 or more people? Check out our Business solutions
Get your team access to the full DataCamp library, with centralized reporting, assignments, projects and more

3. Organizational culture
The third set of challenges leaders face when driving data literacy programs is related to employee engagement.
According to the State of Data & AI Literacy Report, 28% of leaders point to employee resistance as one of their biggest data literacy challenges.
In many ways, this resistance is linked heavily to the first two sets of challenges, as organizations that do not have executive buy-in and do not invest in adequate training resources will not be able to gain adoption from the wider organization.
However, the biggest win leaders can have here is humanizing data.
On a webinar, Cindi Howson, Chief Data Strategy Officer at ThoughtSpot, explained that while data should be used to hold teams and individuals accountable, it shouldn’t be used to punish individuals or disincentivize the use of data.
No one wants to feel belittled, and when you make data hard and inaccessible, that’s the first feeling folks get. Moreover, leaders shouldn’t use data to punish individuals. We need to use data to improve business processes, to keep teams accountable, but we need to ensure people feel confident surfacing data to discuss business outcomes.
Cindy Howson, Chief Data Strategy Officer at ThoughtSpot
How to Become a Data-Literate Organization
Becoming a data-literate organization involves more than just adopting tools or technologies. It requires cultivating a culture that values data, fostering a workforce that can understand and use data, and implementing practices that continually leverage data for decision-making.
Here, we outline a framework to help guide your organization's journey toward data literacy.
A step-by-step data literacy framework for building data skills
Before delving into the specifics of our framework, it's important to remember that each organization is unique in its journey toward data literacy.
The journey depends on your organization's specific context, including the industry, current data maturity, and specific goals.
Therefore, these steps should serve as a guide, not a rigid roadmap, adaptable to your organization's unique situation.
For a more in-depth understanding of the nuances in this journey and how other organizations have successfully navigated it, we recommend checking out our State of Data Literacy Report.
Download the State of Data & AI Literacy Report 2024
Uncover what 550+ leaders in the US & UK believe about the state of their teams’ data & AI skills.
1. Assess your data literacy skill gap
The first step towards building a data-literate organization is understanding where your team currently stands.
- Conduct a comprehensive assessment of your team's data skills.
- Determine what skills they already possess and where gaps exist.
- Use surveys or skill tests to assess competency in statistics, data visualization, data cleaning, and other essential data literacy skills.
Remember, the goal is not to transform everyone into a data scientist but to ensure everyone can understand and use data in their roles. You can learn more about DataCamp’s assessments and how they help pinpoint your organization’s strengths and skill gaps on a separate page. You can also take the data maturity assessment to understand your team's approach to data.
2. Build a data literacy pilot project
With a clear understanding of your team's skills and gaps, you can then develop a pilot project aimed at improving data literacy. This could be a training program or a hands-on project where team members can apply data skills.
Ensure the pilot project aligns with your organization's overall objectives and includes a diverse group of participants from different departments or roles. You can learn how to kickstart a data literacy pilot project by watching the following webinar.
3. Measure the ROI of your data literacy pilot project
As with any investment, it's important to evaluate the return. Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect the objectives of your pilot project. This might include the number of employees trained, improvements in data-related tasks, or better decision-making resulting from data insights.
Assessing the ROI can help justify further investments in data literacy and guide the refinement of future programs. Measuring ROI for data literacy programs can be challenging, a good example comes from Bloomberg, who used the Kirkpatrick model of evaluation for learning ROI in their data upskilling program.
4. Scale your pilot project to multiple personas and competencies
If your pilot project proves successful, the next step is to scale it across your organization. This step involves tailoring the project to cater to different roles and competencies. The training provided to a marketing professional, for example, may be different from that for a product manager.
However, the end goal remains the same: to enhance everyone's ability to use and understand data.
5. Build a learning ecosystem
Building a data-literate organization is not a one-time event but a continuous learning process.
You’ll want to create a learning ecosystem with regular training sessions, knowledge-sharing platforms, and resources such as guides or online courses. This process fosters a culture of continuous learning and ensures your team's data literacy skills stay up-to-date.
6. Rinse & Repeat
Finally, remember that building data literacy is a cyclic process. As your organization grows and evolves, new data literacy needs will arise. Hence, it is important to regularly reassess your team's skills, refine your learning programs, and continue fostering a data-driven culture.
Key principles for a successful data literacy program
Implementing a data literacy program is not just about training or skill development but also about shaping a data-informed culture.
Here are some key principles that can guide your journey to ensure your data literacy program is effective and successful.
Make sure to align learning objectives with business objectives
When designing your data literacy program, it's vital to align your learning objectives with your organization's business goals.
What are the key business challenges your organization faces, and how can data literacy help address them?
For instance, if one of your business objectives is to improve customer satisfaction, one learning objective could be training your customer service team to use data to understand customer behavior and preferences better. Elizabeth Reinhart, Data & AI Analytics Capability Building Senior Manager at Allianz, describes the importance of aligning learning objectives to business objectives in this case study.
We have set different learning objectives for data analytics skills, depending on the different target groups, and shaping tailored learning journeys for each of these groups is crucial.
Elizabeth Reinhart, Data & AI Analytics Capability Building Senior Manager at Allianz
Focus on communications & engagement
A data literacy program is about developing skills and driving a cultural shift toward a data-informed mindset. This process requires continuous communication and engagement.
Keep your team informed about why data literacy is important, how it will help them in their roles, and the program's progress.
Additionally, promote engagement through interactive learning experiences, forums for knowledge sharing, and recognitions or rewards for progress.
Keep it personalized
Every individual in your organization will have different data needs based on their role and current skill level. A one-size-fits-all approach to data literacy may not yield the desired results.
Instead, personalize the learning experience based on the needs of the individual. This could mean providing different training modules for different departments or roles or offering various levels of training from beginner to advanced.
Why personas are foundational in succeeding in data literacy programs
An easy way to succeed in all these principles is by developing data personas for your upskilling program. Not only do data personas help create tailored learning paths and align learning objectives within business outcomes, but they also help in building successful communication programs.
Emily Hayward, Data & Digital Change Manager at CBRE, explains this perfectly on the DataFramed podcast. She argues that data persona work helps anyone managing an upskilling program can evangelize their learning program:
Our data personas were really important for helping us create demand amongst colleagues. It helped us really understand what learning they needed, and we could justify why we've given them some learning content over others based on their persona and their role. It also helped us in our communications because it helped us personalize our messaging and our approach. Our persona work helped us answer “What's in it for me,” because I guarantee you that's all people really care about. How is it going to help them be smarter, quicker, better, and more productive at their job? Part of the persona work really helped bring that to life for people.
Emily Hayward, Data & Digital Change Manager at CBRE
Data Literacy Examples and Case Studies
Allianz upskilled 6,000 people on data skills
Established in 1890, Allianz has long utilized data in its global insurance and asset management services. Its Group Data Analytics team at Allianz SE took the initiative to empower every employee with data literacy, extending the program beyond typical insurance roles to include HR and Communications.
Allianz partnered with DataCamp to create personalized learning solutions, featuring 22 tailored learning paths and three capstone projects with real Allianz use cases.
They launched the program with a trial involving 100 people and quickly scaled it to engage over 6,000 learners.
Feedback was overwhelmingly positive, with a 4.2/5 average rating from Allianz learners and employees, saving an average of 1.9 hours per week thanks to their new skills.
Overall, the program offered 19,000 hands-on learning hours across diverse topics, reinforcing Allianz's commitment to data literacy.
CBRE upskilled 2,000+ people on data skills
CBRE, a global leader in commercial real estate, recognized the need to build data literacy to drive efficiencies, enhance client outcomes, and prepare for the industry's rapidly changing landscape. They sought a comprehensive and scalable data upskilling solution for their 2,000+ employees in the UK and Ireland to achieve these goals.
CBRE partnered with DataCamp for Business to develop a tailored, holistic data literacy program that focused on engagement, personalization, and inclusion, meeting the specific needs of various employee personas across the organization.
By partnering with DataCamp for Business, CBRE employees saved 1-2 hours per learner per week, 81% of the workforce reported increased confidence in working with data, and the program achieved an 88% positive engagement rate.
Essential Data Literacy Resources
We’ve collated an assortment of resources that can help you and your organization get started with your data literacy journey.
Top data literacy courses
- Introduction to Data Literacy
- Data Literacy Professional Skill Track
- Understanding Data Topics Skill Track
Top data literacy books
- Data Analytics for Absolute Beginners: A Deconstructed Guide to Data Literacy by Oliver Theobald
- Be Data Literate: The Data Literacy Skills Everyone Needs To Succeed by Jordan Morrow
- Data Smart: Using Data Science to Transform Information into Insight by John W. Foreman
Top data literacy podcasts & webinars
- Building the Case for Data Literacy
- Scaling the Data Culture at Salesforce
- How Organizations Can Bridge the Data Literacy Gap
- The State of Data Literacy in 2024 Webinar
- Building Sustainable Learning Cultures Webinar
- Drive Data & AI Literacy Webinar
- The Secret to Successful Data Literacy Programs Webinar
- Unlocking Data Cultures: Empowering People Through Data Literacy Programs Webinar
Top data literacy cheat sheets
- The Data-Information-Knowledge-Wisdom Pyramid
- Data Governance Fundamentals Cheat Sheet
- Data Science Cheat Sheet for Business Leaders
- Data Storytelling & Communication Cheat Sheet
- Data Visualization Cheat Sheet
- Descriptive Statistics Cheat Sheet

A collection of data literacy cheat sheets
Conclusion
In a data-driven world, data literacy is no longer just a desirable skill; it's a necessity. As we've discussed throughout this article, data literacy is vital at both an individual and organizational level. It empowers individuals to navigate today's digital landscape, enhances their employability, and enables businesses to make informed decisions, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge. However, becoming a data-literate organization isn't a one-size-fits-all journey.
It requires understanding your organization's unique needs, aligning learning objectives with business goals, and fostering a continuous learning culture. The key is to start small with a pilot project, measure its impact, and then scale according to the needs of your organization. DataCamp for Business can help all throughout this journey. We’ve worked with more than 3,500+ organizations on their data literacy ambitions. To learn more about how we can help transform your organization’s data literacy, you can speak to a learning expert.
Training 2 or more people? Check out our Business solutions
Get your team access to the full DataCamp library, with centralized reporting, assignments, projects and more


Adel is a Data Science educator, speaker, and VP of Media at DataCamp. Adel has released various courses and live training on data analysis, machine learning, and data engineering. He is passionate about spreading data skills and data literacy throughout organizations and the intersection of technology and society. He has an MSc in Data Science and Business Analytics. In his free time, you can find him hanging out with his cat Louis.

A senior editor in the AI and edtech space. Committed to exploring data and AI trends.
FAQs
What is data literacy?
Data literacy is the ability to read, write, analyze, communicate, and reason with data. It involves understanding what data means, how to interpret it, and how to effectively present findings.
Why is data literacy important for individuals?
Data literacy skills are attractive to employers and can lead to higher salaries. It helps individuals make better, data-driven decisions and fosters responsible digital citizenship in a world of misinformation.
Why is data literacy important for organizations?
Data literacy helps organizations improve performance by enhancing decision-making, innovation, customer experience, and employee retention. It is a key component of driving a data culture, where data is consistently used to inform decisions throughout the organization.
How can organizations drive data literacy?
Organizations can drive data literacy by investing in comprehensive data literacy programs, offering training and resources to employees, and promoting a culture of inquiry and data-informed decision-making.
How do you measure data literacy?
Data literacy can be measured through a combination of assessments and practical application. Assessments can include quizzes or tests on data-related concepts, while practical application can involve tasks that require data analysis or interpretation. An individual's ability to accurately and effectively work with and understand data in these contexts can provide a measure of their data literacy. You can also assess your organization, department or team's data maturity level, with our data maturity assessment.
What are the risks of insufficient data skills?
Insufficient data skills can lead to inaccurate decision-making, slow decision-making, reduced productivity, and hindered innovation. These risks can have a negative impact on an organization's performance.
What are the critical challenges organizations face in data literacy?
The critical challenges organizations face in data literacy include lack of executive sponsorship, inadequate training resources, and employee resistance and adoption of data upskilling.
What are some key principles for a successful data literacy program?
Some key principles include aligning learning objectives with business objectives, focusing on communications and engagement, and personalizing the learning experience based on individual needs and roles.